Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Problem 3: A woman is moving to a new house and will spend much of her morning lifting boxes into a truck. She's always
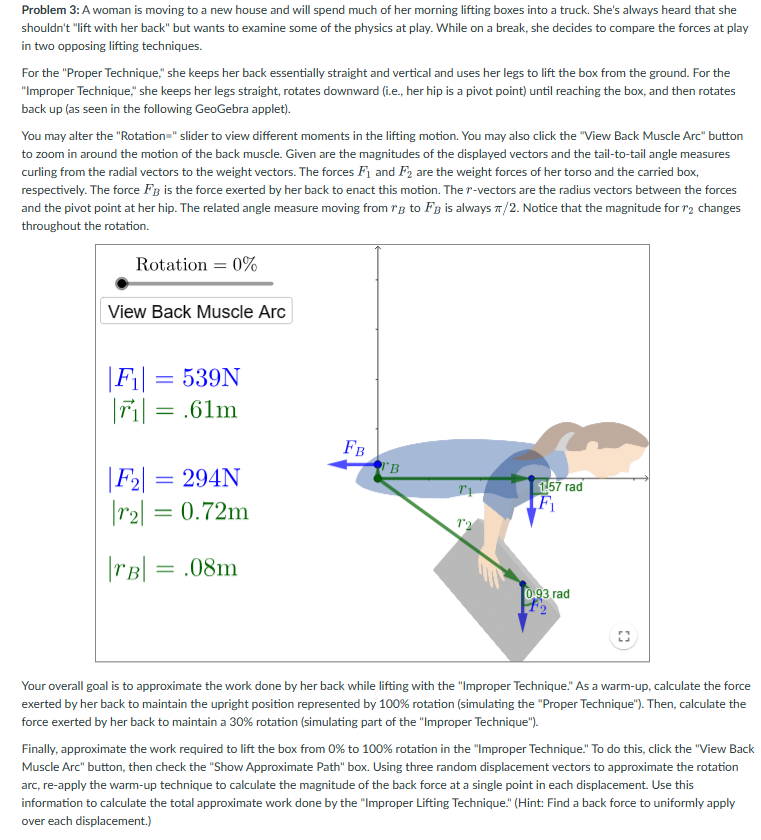
Problem 3: A woman is moving to a new house and will spend much of her morning lifting boxes into a truck. She's always heard that she shouldn't "lift with her back" but wants to examine some of the physics at play. While on a break, she decides to compare the forces at play in two opposing lifting techniques. For the "Proper Technique," she keeps her back essentially straight and vertical and uses her legs to lift the box from the ground. For the "Improper Technique," she keeps her legs straight, rotates downward (i.e., her hip is a pivot point) until reaching the box, and then rotates back up (as seen in the following GeoGebra applet). You may alter the "Rotation=" slider to view different moments in the lifting motion. You may also click the "View Back Muscle Arc" button to zoom in around the motion of the back muscle. Given are the magnitudes of the displayed vectors and the tail-to-tail angle measures curling from the radial vectors to the weight vectors. The forces F and F2 are the weight forces of her torso and the carried box, respectively. The force FB is the force exerted by her back to enact this motion. The r-vectors are the radius vectors between the forces and the pivot point at her hip. The related angle measure moving from B to FB is always /2. Notice that the magnitude for 12 changes throughout the rotation. Rotation = 0% View Back Muscle Arc |F = 539N |r| = .61m |F2| = 294N |r2| = 0.72m |TB| = .08m FB Ti 12 1.57 rad F 0,93 rad Your overall goal is to approximate the work done by her back while lifting with the "Improper Technique." As a warm-up, calculate the force exerted by her back to maintain the upright position represented by 100% rotation (simulating the "Proper Technique"). Then, calculate the force exerted by her back to maintain a 30% rotation (simulating part of the "Improper Technique"). Finally, approximate the work required to lift the box from 0% to 100% rotation in the "Improper Technique." To do this, click the "View Back Muscle Arc" button, then check the "Show Approximate Path" box. Using three random displacement vectors to approximate the rotation arc, re-apply the warm-up technique to calculate the magnitude of the back force at a single point in each displacement. Use this information to calculate the total approximate work done by the "Improper Lifting Technique." (Hint: Find a back force to uniformly apply over each displacement.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


