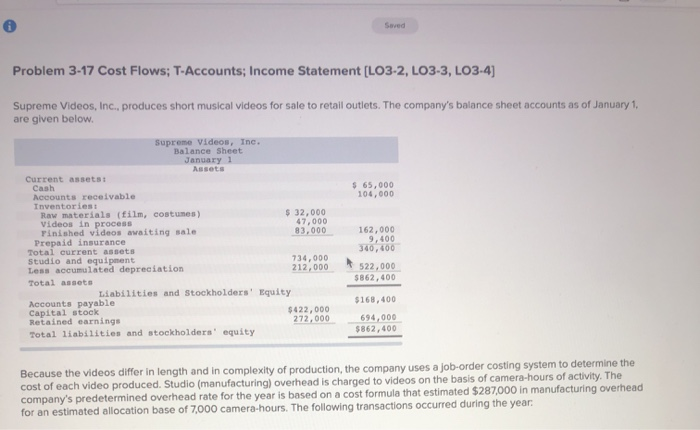
Problem 3-17 Cost Flows; T-Accounts; Income Statement [LO3-2, LO3-3, LO3-4) Supreme Videos, Inc., produces short musical videos for sale to retail outlets. The company's balance sheet accounts as of January 1, are given below. Supreme Videos, Inc. Balance Sheet January 1 Assets Current assets: Cash $ 65,000 Accounts receivable 104,000 Inventories: Raw materials (film, costumes) $ 32,000 Videos in process 47,000 Finished videos awaiting sale 83.000 162,000 Prepaid insurance 9,400 Total current assets 340,400 Studio and equipment 734,000 Less accumulated depreciation 212,000 522,000 Total assets $862,400 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable $168.400 Capital stock $ 422,000 Retained earnings 272,000 694,000 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $862,400 Because the videos differ in length and in complexity of production, the company uses a job-order costing system to determine the cost of each video produced. Studio (manufacturing) overhead is charged to videos on the basis of camera-hours of activity. The company's predetermined overhead rate for the year is based on a cost formula that estimated $287,000 in manufacturing overhead for an estimated allocation base of 7,000 camera-hours. The following transactions occurred during the year. a. Film, costumes, and similar raw materials purchased on account, $187,000. b. Film, costumes, and other raw materials used in production, $202,000 (85% of this material was considered direct to the videos in production, and the other 15% was considered indirect). c. Utility costs incurred on account in the production studio, $74,000. d. Depreciation recorded on the studio, cameras, and other equipment, $86,000. Three-fourths of this depreciation related to production of the videos, and the remainder related to equipment used in marketing and administration. e. Advertising expense incurred on account, $132,000. f. Costs for salaries and wages were incurred on account as follows: Direct labor (actors and directors) Indirect labor (carpenters to build sets, costume designers, and so forth) Administrative salaries $ 84,000 $ 112,000 $ 97,000 9. Prepaid insurance expired during the year, 57,200 (80% related to production of videos, and 20% related to marketing and administrative activities) h. Miscellaneous marketing and administrative expenses incurred on account, $8,800. 1. Studio (manufacturing) overhead was applied to videos in production. The company used 7,250 camera-hours during the year. J. Videos that cost $552,000 to produce according to their job cost sheets were transferred to the finished videos warehouse to awalt sale and shipment k. Sales for the year totaled $929,000 and were all on account. The total cost to produce these videos according to their job cost sheets was $602,000. 1. Collections from customers during the year totaled $852,000, m. Payments to suppliers on account during the year, 5502,000; payments to employees for salaries and wages, $287.000. Required: 1. Prepare a T-account for each account on the company's balance sheet and enter the beginning balances. 2. Record the transactions directly into the T-accounts. Key your entries to the letters (a) through (m) above. 3. Is the Studio (manufacturing) Overhead account underapplied or overapplied for the year? By how much? 4. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured. 5. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold. 6. Prepare an income statement for the year