
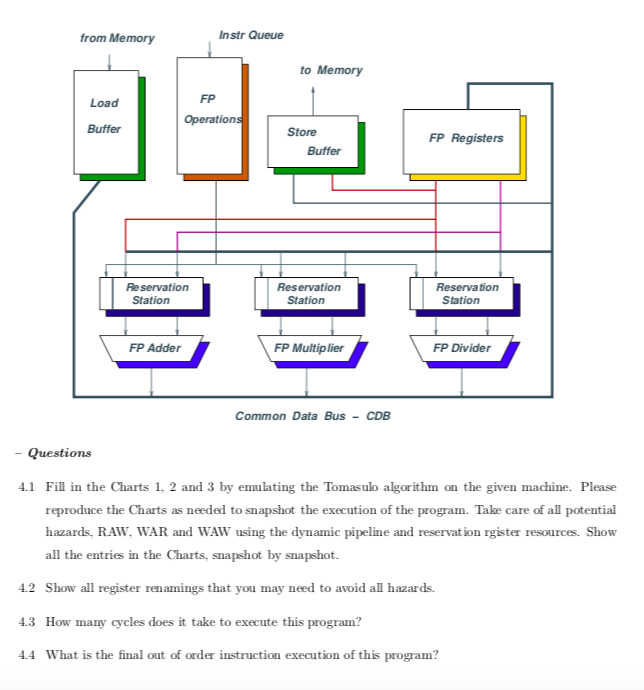
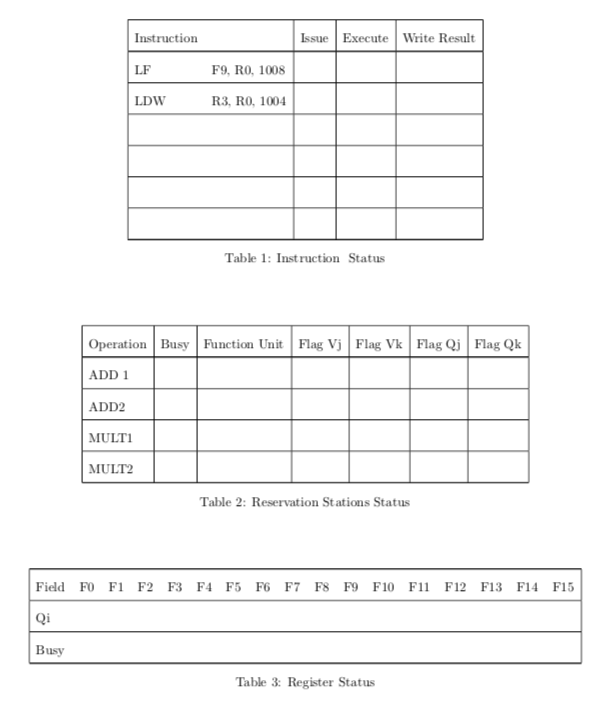
Problem 5: We would like to evaluate a cubic polynomial Dr- Ar2 + Br- C using a LOAD/STORE instruction set architecture. D, A and B are both 32-bit intergers whereas C. and a are float ing point numbers. Assume that is already in register F7 and that the constants A, B. C are in memory locations 1000, 1004, 1008, respectively, whereas D is in location 2000. The code block below implements the polynomial in LOAD/STORE assembly like language, with comments. 1. LF F9, RO, 1008 2. LDW R3, RO, 1004 3. MULF F2, R3, F7 4 SUBF F9, F2, F9 5. MULF F2, F7, F7 6. LDW R2, RO, 1000 F2BX R2A MULF F4, R2, F2 8. SUBF F9, F4, F9 R4-D F4 DX F7Dx xx 9. LDW R4, RO, 2000 10. MULF F4, R4, F7 11. MULF F7, F2, F4 12. SUBF F9, F7, F9 We would like to evaluate the polynomial on the LOAD/STORE pipeline machine, augmented to implement the Tomasulo dynamic pipeline architecture; an example machine is shown in the next Figure. This machine has 1 Load Buffer (6 registers) 1 Instruction Queue (6 registers). 2 Add/Subtract Units, 2 Multiply/Divide Units 1 Sore Buffer, 16 FP registers, and 16 Integer Registers. We assume that the latencies of the floating-point addition and multiplication operations are 2 and 6 cycles, respectively Assume that 2 instructions can be issued at a time. Also, the Reservation Station status and the Register status are shown in the following Charts. Initially, the buffer contains the following instructions 1. LF F9, RO, 1008 2. LD R3, RO, 1004 Problem 5: We would like to evaluate a cubic polynomial Dr- Ar2 + Br- C using a LOAD/STORE instruction set architecture. D, A and B are both 32-bit intergers whereas C. and a are float ing point numbers. Assume that is already in register F7 and that the constants A, B. C are in memory locations 1000, 1004, 1008, respectively, whereas D is in location 2000. The code block below implements the polynomial in LOAD/STORE assembly like language, with comments. 1. LF F9, RO, 1008 2. LDW R3, RO, 1004 3. MULF F2, R3, F7 4 SUBF F9, F2, F9 5. MULF F2, F7, F7 6. LDW R2, RO, 1000 F2BX R2A MULF F4, R2, F2 8. SUBF F9, F4, F9 R4-D F4 DX F7Dx xx 9. LDW R4, RO, 2000 10. MULF F4, R4, F7 11. MULF F7, F2, F4 12. SUBF F9, F7, F9 We would like to evaluate the polynomial on the LOAD/STORE pipeline machine, augmented to implement the Tomasulo dynamic pipeline architecture; an example machine is shown in the next Figure. This machine has 1 Load Buffer (6 registers) 1 Instruction Queue (6 registers). 2 Add/Subtract Units, 2 Multiply/Divide Units 1 Sore Buffer, 16 FP registers, and 16 Integer Registers. We assume that the latencies of the floating-point addition and multiplication operations are 2 and 6 cycles, respectively Assume that 2 instructions can be issued at a time. Also, the Reservation Station status and the Register status are shown in the following Charts. Initially, the buffer contains the following instructions 1. LF F9, RO, 1008 2. LD R3, RO, 1004









