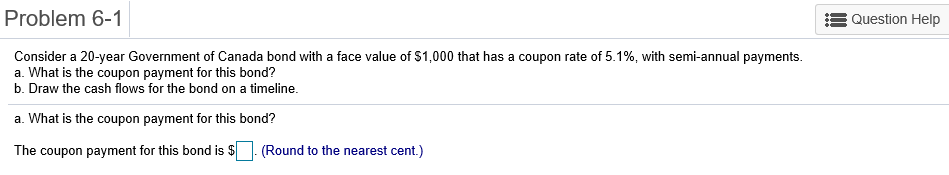
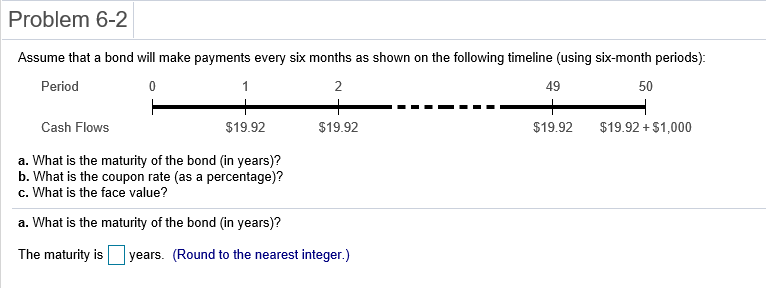

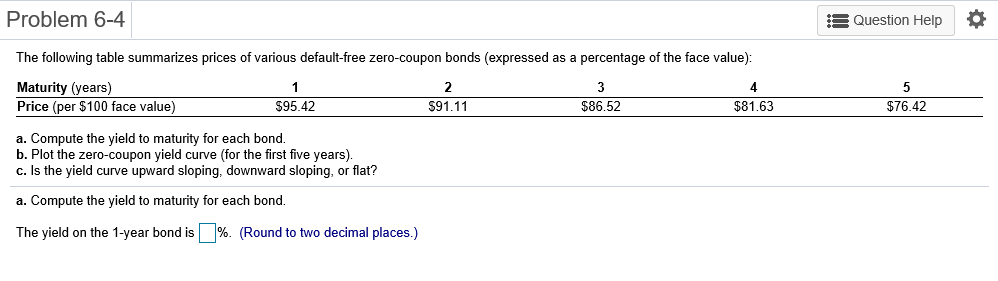
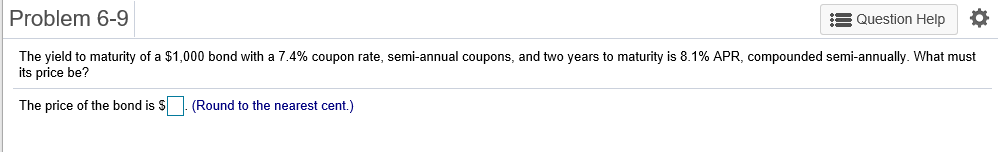
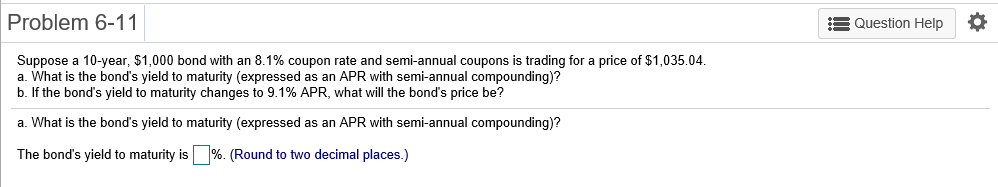
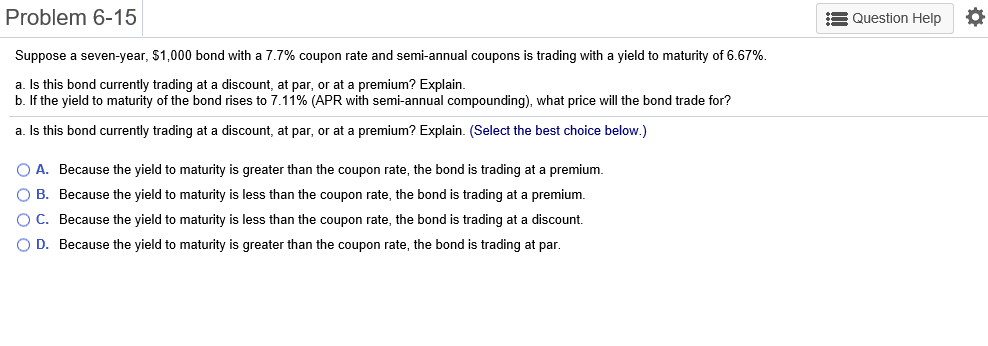
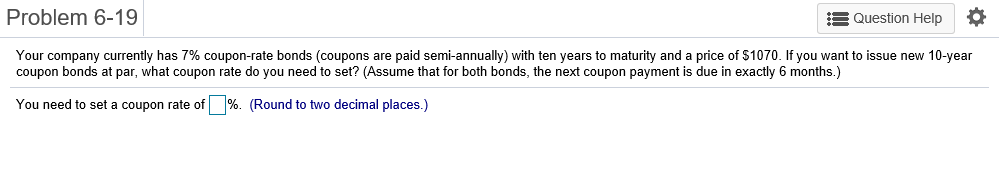
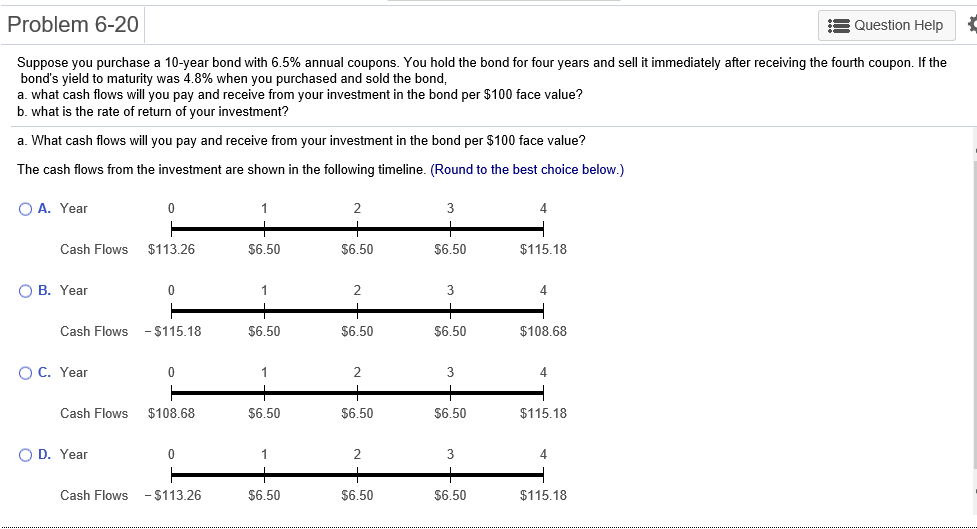
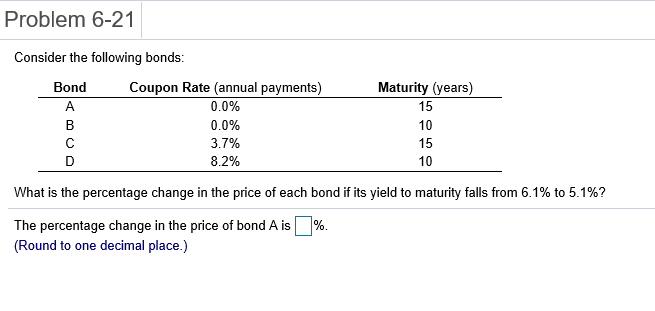


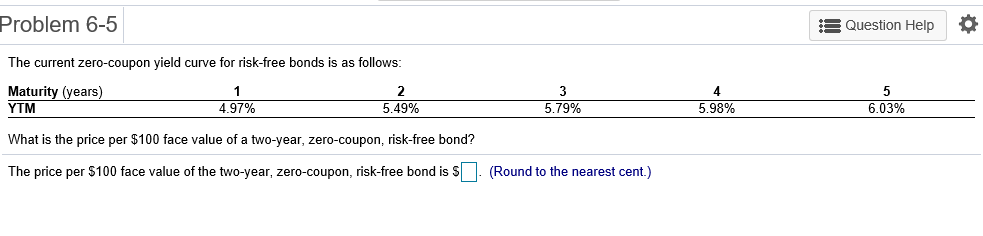
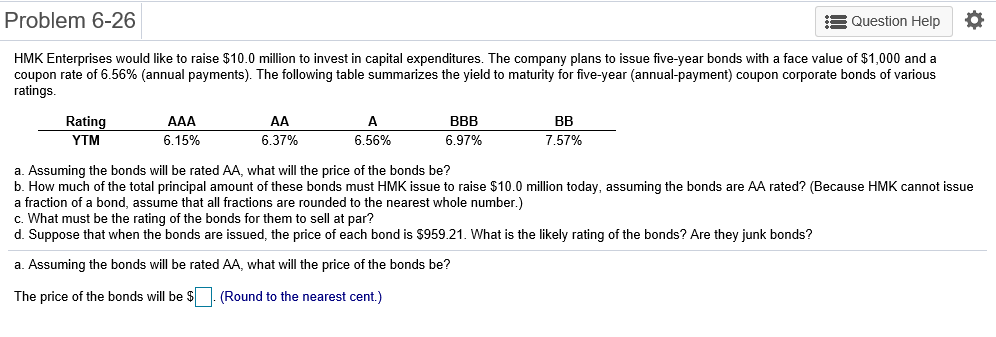
Problem 6-1 Question Help Consider a 20-year Government of Canada bond with a face value of $1,000 that has a coupon rate of 5.1%, with semi-annual payments. a. What is the coupon payment for this bond? b. Draw the cash flows for the bond on a timeline. a. What is the coupon payment for this bond? The coupon payment for this bond is $(Round to the nearest cent.) Problem 6-2 Assume that a bond will make payments every six months as shown on the following timeline (using six-month periods): Period 2 49 50 1 N Cash Flows $19.92 $19.92 $19.92 $19.92 + $1,000 a. What is the maturity of the bond (in years)? b. What is the coupon rate (as a percentage)? c. What is the face value? a. What is the maturity of the bond (in years)? The maturity is years. (Round to the nearest integer.) Problem 6-3 Question Help Your company wants to raise $7.0 million by issuing 25-year zero-coupon bonds. If the yield to maturity on the bonds will be 7% (EAR), what total face value amount of bonds must you issue? The total face value amount of bonds that you must issue is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) Problem 6-4 Question Help The following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of the face value): Maturity (years) 1 2 4 Price (per $100 face value) $95.42 S91.11 $86.52 $81.63 3 5 $76.42 a. Compute the yield to maturity for each bond. b. Plot the zero-coupon yield curve (for the first five years). c. Is the yield curve upward sloping, downward sloping, or flat? a. Compute the yield to maturity for each bond. The yield on the 1-year bond is %. (Round to two decimal places.) Problem 6-9 s Question Help 0 The yield to maturity of a $1,000 bond with a 7.4% coupon rate, semi-annual coupons, and two years to maturity is 8.1% APR, compounded semi-annually. What must its price be? The price of the bond is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) Problem 6-11 A Question Help Suppose a 10-year, $1,000 bond with an 8.1% coupon rate and semi-annual coupons is trading for a price of $1,035.04. a. What is the bond's yield to maturity (expressed as an APR with semi-annual compounding)? b. If the bond's yield to maturity changes to 9.1% APR, what will the bond's price be? a. What is the bond's yield to maturity (expressed as an APR with semi-annual compounding)? The bond's yield to maturity is %. (Round to two decimal places.) Problem 6-15 A Question Help Suppose a seven-year, $1,000 bond with a 7.7% coupon rate and semi-annual coupons is trading with a yield to maturity of 6.67%. a. Is this bond currently trading at a discount, at par, or at a premium? Explain. b. If the yield to maturity of the bond rises to 7.11% (APR with semi-annual compounding), what price will the bond trade for? a. Is this bond currently trading at a discount, at par, or at a premium? Explain. (Select the best choice below.) O A. Because the yield to maturity is greater than the coupon rate, the bond is trading at a premium. O B. Because the yield to maturity is less than the coupon rate, the bond is trading at a premium. OC. Because the yield to maturity is less than the coupon rate, the bond is trading at a discount. OD. Because the yield to maturity is greater than the coupon rate, the bond is trading at par. Problem 6-19 A Question Help Your company currently has 7% coupon-rate bonds (coupons are paid semi-annually) with ten years to maturity and a price of $1070. If you want to issue new 10-year coupon bonds at par, what coupon rate do you need to set? (Assume that for both bonds, the next coupon payment is due in exactly 6 months.) You need to set a coupon rate of %. (Round to two decimal places.) Problem 6-20 Question Help Suppose you purchase a 10-year bond with 6.5% annual coupons. You hold the bond for four years and sell it immediately after receiving the fourth coupon. If the bond's yield to maturity was 4.8% when you purchased and sold the bond, a what cash flows will you pay and receive from your investment in the bond per $100 face value? b. what is the rate of return of your investment? a. What cash flows will you pay and receive from your investment in the bond per $100 face value? The cash flows from the investment are shown in the following timeline. (Round to the best choice below.) O A. Year 0 4 2 1 1 $6.50 Cash Flows $113.26 $6.50 $6.50 $115.18 OB. Year 0 3 4 1 Cash Flows -$115.18 $6.50 $6.50 $6.50 $108.68 O C. Year 0 1 2 3 4 Cash Flows $108.68 $6.50 $6.50 $6.50 $115.18 OD. Year 0 1 2 3 4 Cash Flows -$113.26 $6.50 $6.50 $6.50 $115.18 Problem 6-21 Consider the following bonds: Bond Coupon Rate (annual payments) A 0.0% 0.0% 3.7% D 8.2% B Maturity (years) 15 10 15 10 What is the percentage change in the price of each bond if its yield to maturity falls from 6.1% to 5.1%? % The percentage change in the price of bond A is (Round to one decimal place.) Problem 6-23 Suppose you purchase a 30-year zero-coupon bond with a yield to maturity of 6.2%. You hold the bond for five years before selling it. a. If the bond's yield to maturity is 6.2% when you sell it, what is the rate of return of your investment? b. If the bond's yield to maturity is 7.2% when you sell it, what is the rate of return of your investment? c. If the bond's yield to maturity is 5.2% when you sell it, what is the rate of return of your investment? d. Even if a bond has no chance of default is your investment risk free if you plan to sell it before it matures? Explain. a. If the bond's yield to maturity is 6.2% when you sell it, what is the rate of return of your investment? The rate of return of your investment is %. (Round to two decimal places.) Problem 6-24 The following table summarizes the yields to maturity on several one-year, zero-coupon securities. Security Yield (%) Government of Canada 3.14 AAA corporate 3.23 BBB corporate 4.27 B corporate 4.91 a. What is the price (expressed as a percentage of the face value) of a one-year, zero-coupon corporate bond with an AAA rating? b. What is the credit spread on AAA-rated corporate bonds? c. What is the credit spread on B-rated corporate bonds? d. How does the credit spread change with the bond rating? Why? a. What is the price (expressed as a percentage of the face value) of a one-year, zero-coupon corporate bond with an AAA rating? The price of this bond is %. (Round to three decimal places.) Problem 6-25 A Question Help Andrew Industries is contemplating issuing a 30-year bond with a coupon rate of 7.07% (annual coupon payments) and a face value of $1,000. Andrew believes it can get a rating of A from Standard & Poor's. However, due to recent financial difficulties at the company, Standard & Poor's is warning that it may downgrade Andrew Industries' bonds to BBB. Yields on A-rated, long-term bonds are currently 6.44%, and yields on BBB-rated bonds are 6.86%. a. What is the price of the bond if Andrew Industries maintains the A rating for the bond issue? b. What will be the price of the bond if it is downgraded? a. What is the price of the bond if Andrew Industries maintains the A rating for the bond issue? If Andrew maintains the A rating for the bond issue, the price of the bond is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) Problem 6-5 3 Question Help The current zero-coupon yield curve for risk-free bonds is as follows: Maturity (years) 2 YTM 4.97% 5.49% 1 4 5 3 5.79% 5.98% 6.03% What is the price per $100 face value of a two-year, zero-coupon, risk-free bond? The price per $100 face value of the two-year, zero-coupon, risk-free bond is $. (Round to the nearest cent.) Problem 6-26 Question Help HMK Enterprises would like to raise $10.0 million to invest in capital expenditures. The company plans to issue five-year bonds with a face value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 6.56% (annual payments). The following table summarizes the yield to maturity for five-year (annual-payment) coupon corporate bonds of various ratings Rating YTM AAA 6.15% 6.37% A 6.56% BBB 6.97% BB 7.57% a. Assuming the bonds will be rated AA, what will the price of the bonds be? b. How much of the total principal amount of these bonds must HMK issue to raise $10.0 million today, assuming the bonds are AA rated? (Because HMK cannot issue a fraction of a bond, assume that all fractions are rounded to the nearest whole number.) c. What must be the rating of the bonds for them to sell at par? d. Suppose that when the bonds are issued the price of each bond is $959.21. What is the likely rating of the bonds? Are they junk bonds? a. Assuming the bonds will be rated AA, what will the price of the bonds be? The price of the bonds will be (Round to the nearest cent.)