Problem 7-23 Greta, an elderly investor, has a degree of risk aversion of A = 5 when applied to return on wealth over a
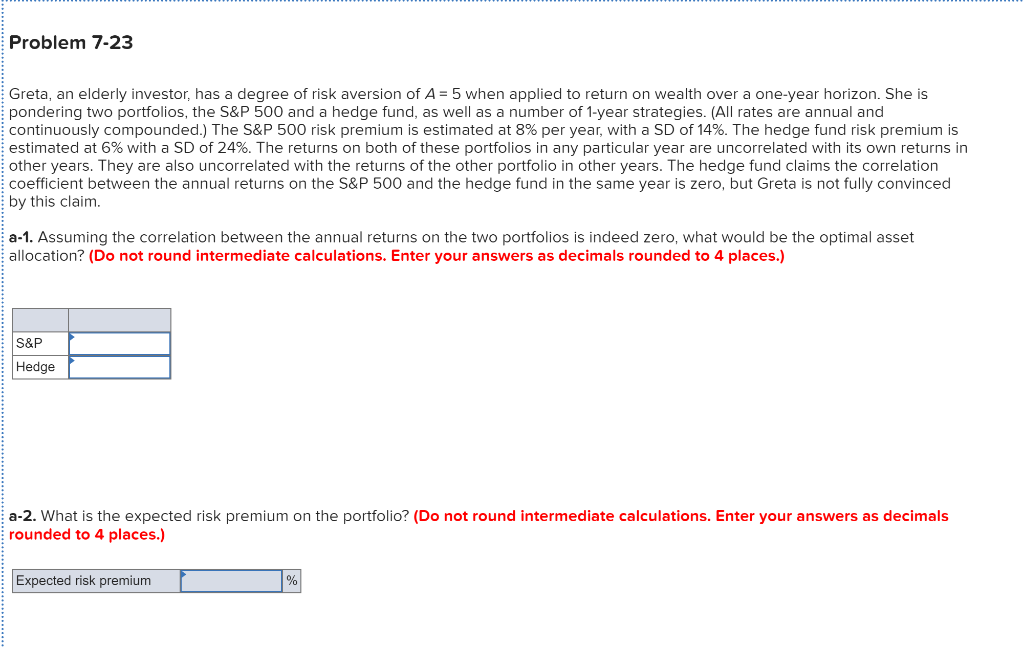
Problem 7-23 Greta, an elderly investor, has a degree of risk aversion of A = 5 when applied to return on wealth over a one-year horizon. She is pondering two portfolios, the S&P 500 and a hedge fund, as well as a number of 1-year strategies. (All rates are annual and continuously compounded.) The S&P 500 risk premium is estimated at 8% per year, with a SD of 14%. The hedge fund risk premium is estimated at 6% with a SD of 24%. The returns on both of these portfolios in any particular year are uncorrelated with its own returns in other years. They are also uncorrelated with the returns of the other portfolio in other years. The hedge fund claims the correlation coefficient between the annual returns on the S&P 500 and the hedge fund in the same year is zero, but Greta is not fully convinced by this claim. a-1. Assuming the correlation between the annual returns on the two portfolios is indeed zero, what would be the optimal asset allocation? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers as decimals rounded to 4 places.) S&P Hedge a-2. What is the expected risk premium on the portfolio? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers as decimals rounded to 4 places.) Expected risk premium %
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To solve the problem we need to determine the optimal asset allocation between the SP 500 and the hedge fund using utility maximization The utility fu...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


