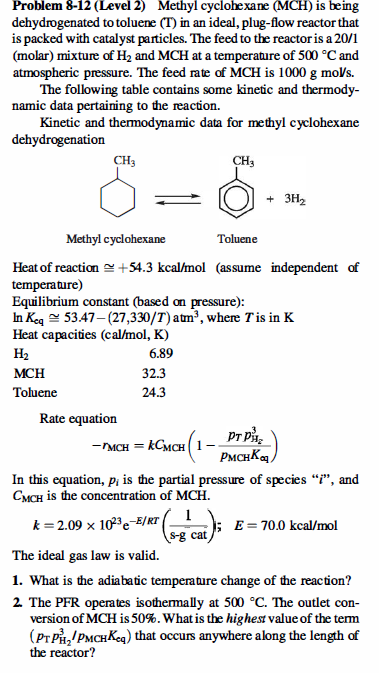

Problem 8-12 (Level 2) Methyl cyclohexane (MCH) is being dehydrogenated to toluene (T) in an ideal, plug-flow reactor that is packed with catalyst particles. The feed to the reactor is a 20/1 (molar) mixture of H2 and MCH at a temperature of 500C and atmospheric pressure. The feed rate of MCH is 1000gmoV/s. The following table contains some kinetic and thermodynamic data pertaining to the reaction. Kinetic and thermodynamic data for methyl cyclohexane dehydrogenation Heat of reaction +54.3kcal/mol (assume independent of temperature) Equilibrium constant (based on pressure): lnKeq53.47(27,330/T)atm3, where T is in K Lant anmaitian (nnl1manV Rate equation rMCH=kCMCH(1pMCHKqpTpHz3) In this equation, pi is the partial pressure of species " i ", and CMCH is the concentration of MCH. k=2.091023eE/RT(sgcat1);E=70.0kcal/mol The ideal gas law is valid. 1. What is the adiabatic temperature change of the reaction? 2. The PFR operates isothermally at 500C. The outlet conversion of MCH is 50%. What is the highest value of the term (pTpH23/pMCHKeq) that occurs anywhere along the length of the reactor? 3. Based on your answer to Question 2 , simplify the rate equation. Then calculate the weight of catalyst that is required to obtain an outlet MCH conversion of 50% if the reactor is operated isothermally at 500C ? You may assume that transport effects are not important, and you may neglect pressure drop through the reactor. 4. What weight of catalyst is required to obtain an outlet MCH conversion of 50% if the reactor is operated adiabatically with an inlet temperature of 500C ? You may assume that transport effects are not important, and you may neglect pressure drop through the reactor. Problem 8-12 (Level 2) Methyl cyclohexane (MCH) is being dehydrogenated to toluene (T) in an ideal, plug-flow reactor that is packed with catalyst particles. The feed to the reactor is a 20/1 (molar) mixture of H2 and MCH at a temperature of 500C and atmospheric pressure. The feed rate of MCH is 1000gmoV/s. The following table contains some kinetic and thermodynamic data pertaining to the reaction. Kinetic and thermodynamic data for methyl cyclohexane dehydrogenation Heat of reaction +54.3kcal/mol (assume independent of temperature) Equilibrium constant (based on pressure): lnKeq53.47(27,330/T)atm3, where T is in K Lant anmaitian (nnl1manV Rate equation rMCH=kCMCH(1pMCHKqpTpHz3) In this equation, pi is the partial pressure of species " i ", and CMCH is the concentration of MCH. k=2.091023eE/RT(sgcat1);E=70.0kcal/mol The ideal gas law is valid. 1. What is the adiabatic temperature change of the reaction? 2. The PFR operates isothermally at 500C. The outlet conversion of MCH is 50%. What is the highest value of the term (pTpH23/pMCHKeq) that occurs anywhere along the length of the reactor? 3. Based on your answer to Question 2 , simplify the rate equation. Then calculate the weight of catalyst that is required to obtain an outlet MCH conversion of 50% if the reactor is operated isothermally at 500C ? You may assume that transport effects are not important, and you may neglect pressure drop through the reactor. 4. What weight of catalyst is required to obtain an outlet MCH conversion of 50% if the reactor is operated adiabatically with an inlet temperature of 500C ? You may assume that transport effects are not important, and you may neglect pressure drop through the reactor








