Question
Problem A. The pseudocode as below illustrates the basic push() and pop() operations of an array-based stack, where top is initialized as 0 when the
Problem A. The pseudocode as below illustrates the basic push() and pop() operations of an array-based stack, where top is initialized as 0 when the stack is empty. Assuming that at a given moment, SIZE is equal to 20, top is equal to 8, this code is used in a concurrent environment (top and stack[] are in shared memory section), process P0 is about to call push() and process P1 is about to call pop() concurrently.
push(item) {
if (top
stack[top] = item; // LINE A
top++; // LINE B }
else ERROR }
pop() {
if (top > 0) {
top--; // LINE X
return stack[top]; // LINE Y }
else ERROR }
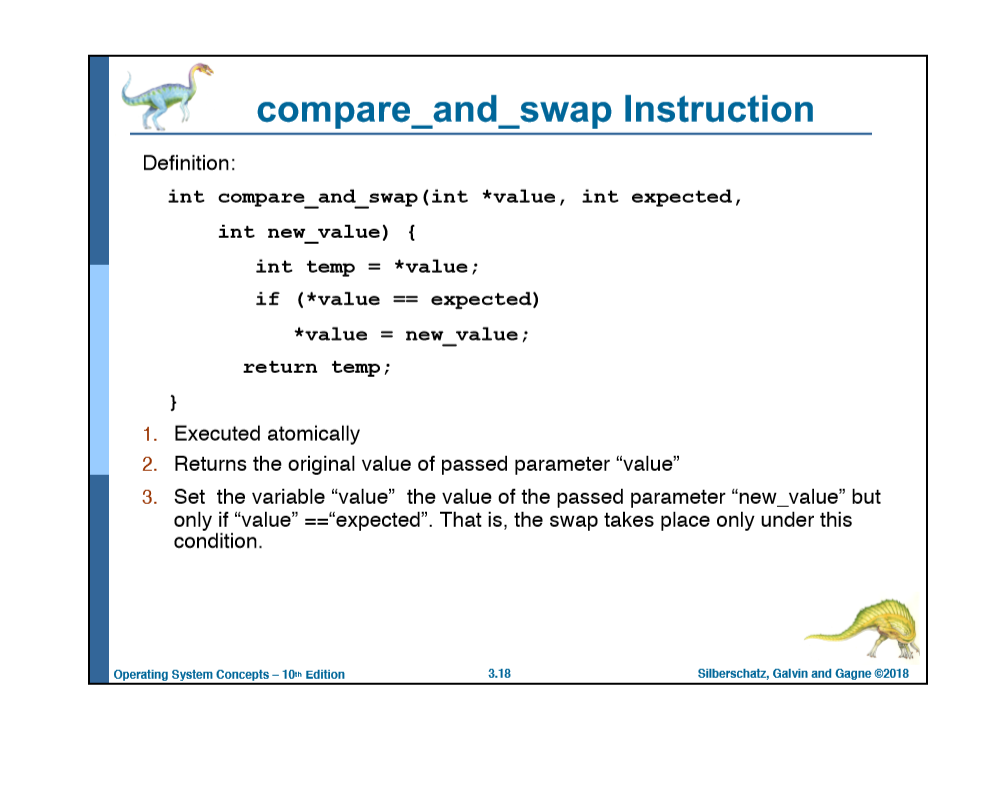
Problem C. Use the atomic compare_and_swap instruction to fix the race condition in Problem A.
a. Write a C statement to declare and initialize a shared variable lockTop, whose value is -1 when unlocked and 0 when locked
b. Re-write the push() function to call the compare_and_swap() function defined in the PPT Slide 3.18 for Section III
c. Re-write the pop() function to call the compare_and_swap() function defined in the PPT Slide 3.18 for Section III
d. Does this solution satisfy the mutual-exclusion requirement? Does it satisfy the bounded-waiting requirement?
Just problem C
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


