Problem set questions Microeconomics
Questions 1-6
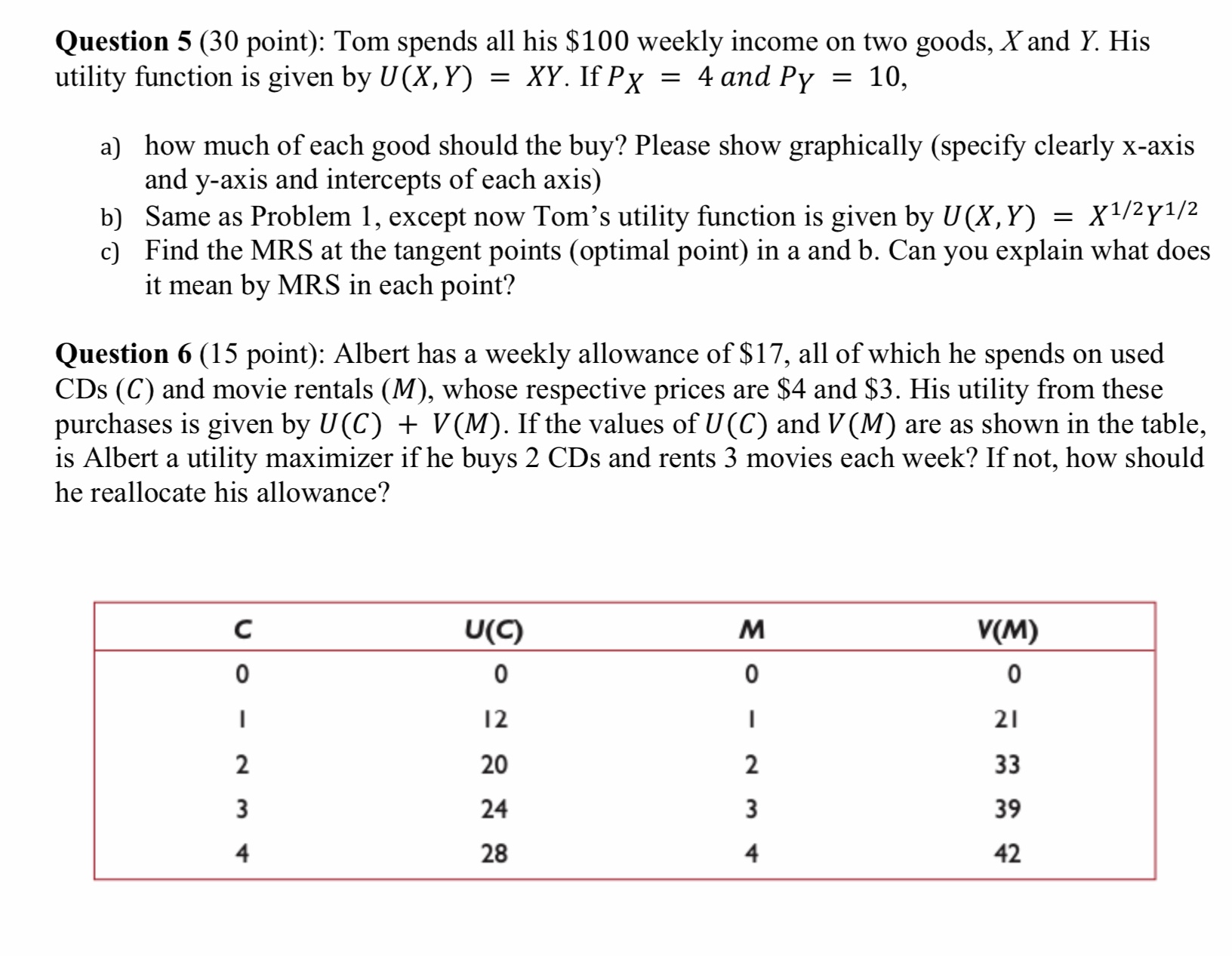
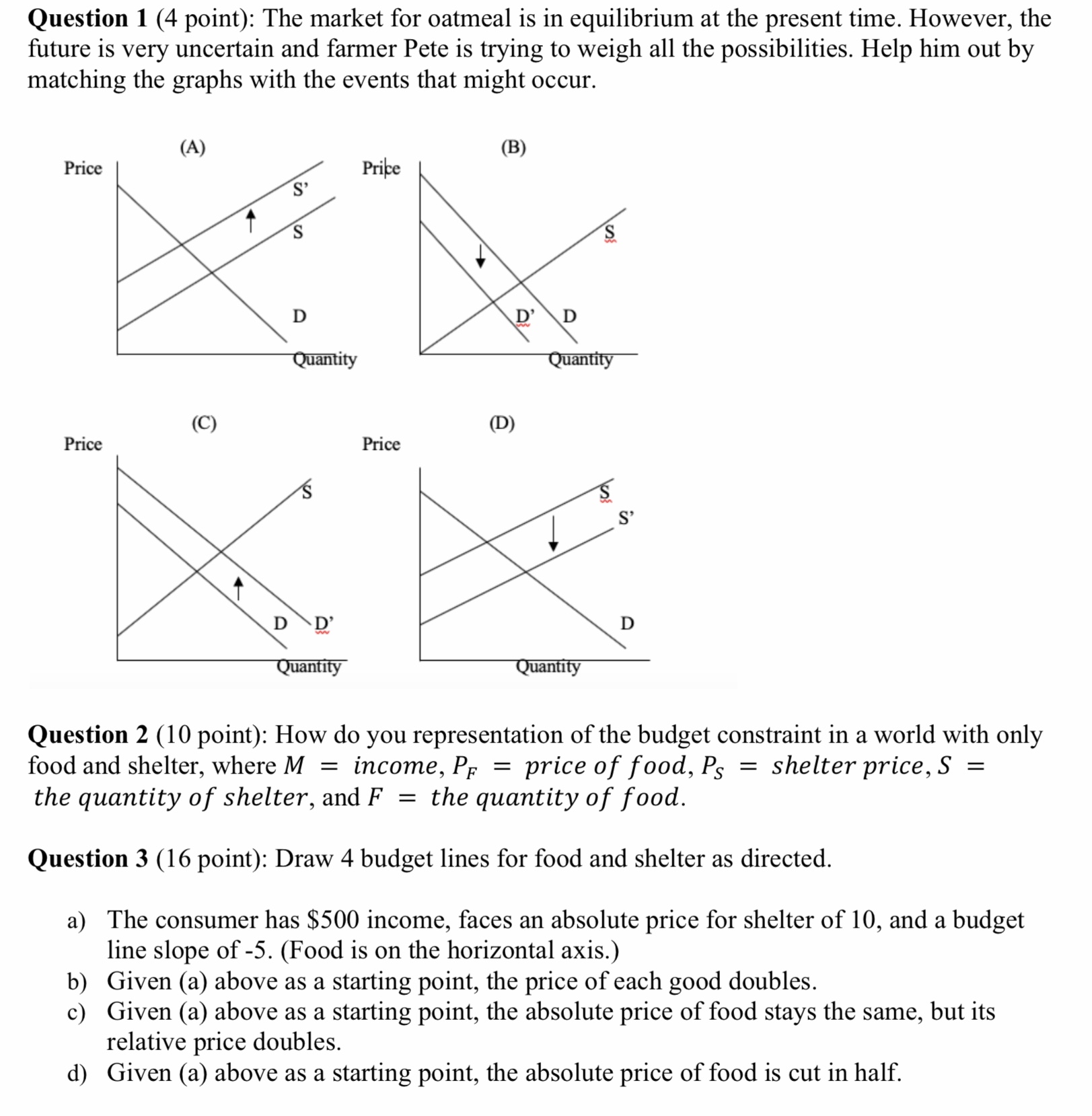
Question 5 (30 point): Tom spends all his $100 weekly income on two goods, X and Y. His utility function is given by U (X, Y) = X Y. If P X = 4 and Py = 10, a) how much of each good should the buy? Please show graphically (specify clearly x-axis and y-axis and intercepts of each axis) b) Same as Problem 1, except now Tom's utility function is given by U (X, Y) = X1/2 Y\"2 c] Find the MRS at the tangent points (optimal point) in a and b. Can you explain what does it mean by MRS in each point? Question 6 (15 point): Albert has a weekly allowance of $17, all of which he spends on used CDs (C) and movie rentals (M), whose respective prices are $4 and $3. His utility from these purchases is given by U (C) + V(M). If the values of U (C) and V(M) are as shown in the table, is Albert a utility maximizer if he buys 2 CD5 and rents 3 movies each week? If not, how should he reallocate his allowance? Question 1 (4 point): The market for oatmeal is in equilibrium at the present time. However, the future is very uncertain and farmer Pete is trying to weigh all the possibilities. Help him out by matching the graphs with the events that might occur. (A) . (B) (C) Question 2 (10 point): How do you representation of the budget constraint in a world with only food and shelter, where M = income, PF = price of food, P5 = shelter price, 5 = the quantity of shelter, and F = the quantity of food. Question 3 (16 point): Draw 4 budget lines for food and shelter as directed. a) The consumer has $500 income, faces an absolute price for shelter of 10, and a budget line slope of -5. (Food is on the horizontal axis.) b) Given (a) above as a starting point, the price of each good doubles. 0) Given (a) above as a starting point, the absolute price of food stays the same, but its relative price doubles. (1) Given (a) above as a starting point, the absolute price of food is cut in half. Question 4 (25 point): You have two goods food and Shelter. When you have vertical axis for the number of food and horizonal axis for the number of shelters. Assume you have MRS = 3 in this case. a) What does it mean by MRS of food (on the vertical axis) for shelter (on the horizontal axis) =3? b) if the price of food is 5, and if the shelter price is 10, then the consumer is not maximizing his utility. Sketch a budget line, assuming the consumer has $100 to spend, and draw in a possible indifference curve that illustrates the situation described here. Then, on the same graph, show with a simple sketch what could be done to correct the