Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Problem Solving: Free-Body Diagrams and Newton's Laws 1. Draw a sketch of the situation. 2. Consider only one object (at a time), and draw
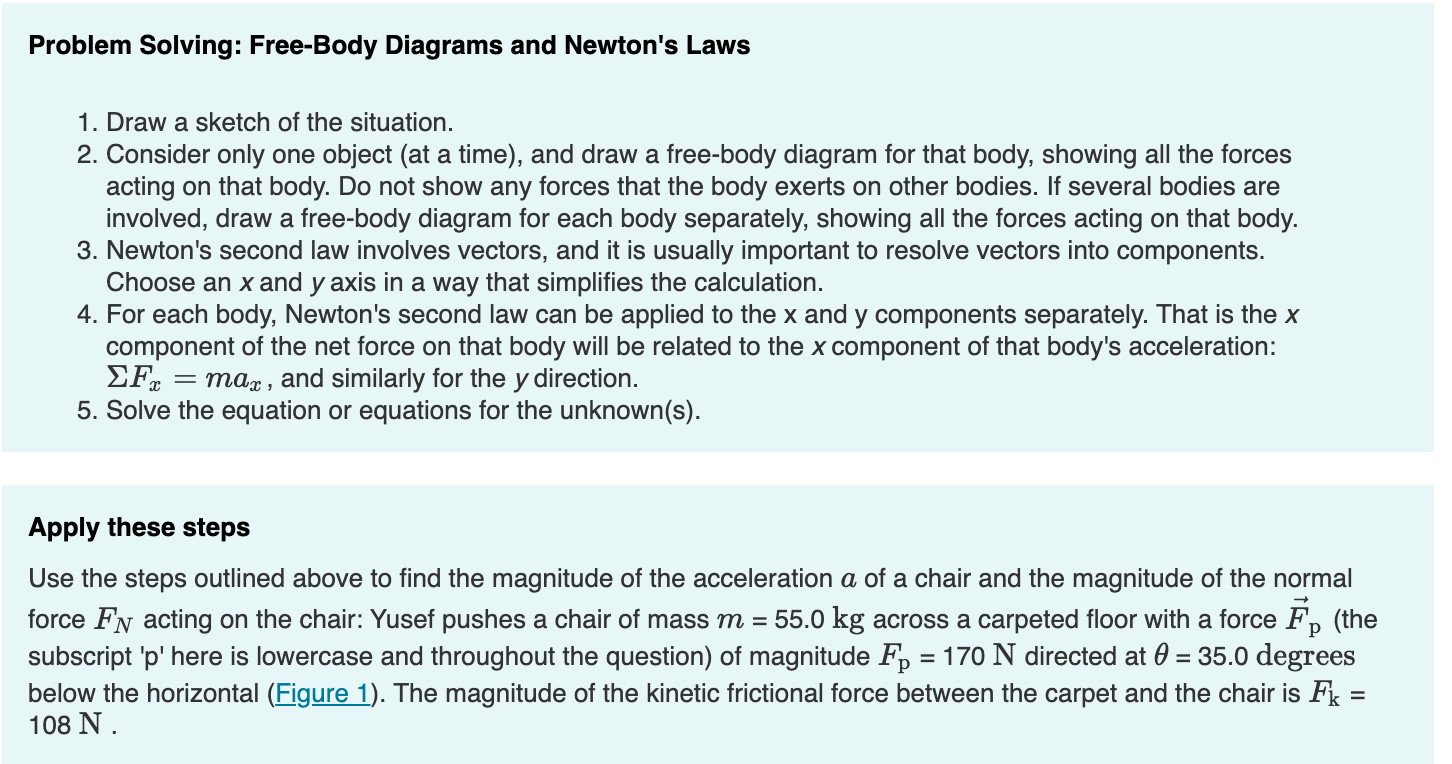
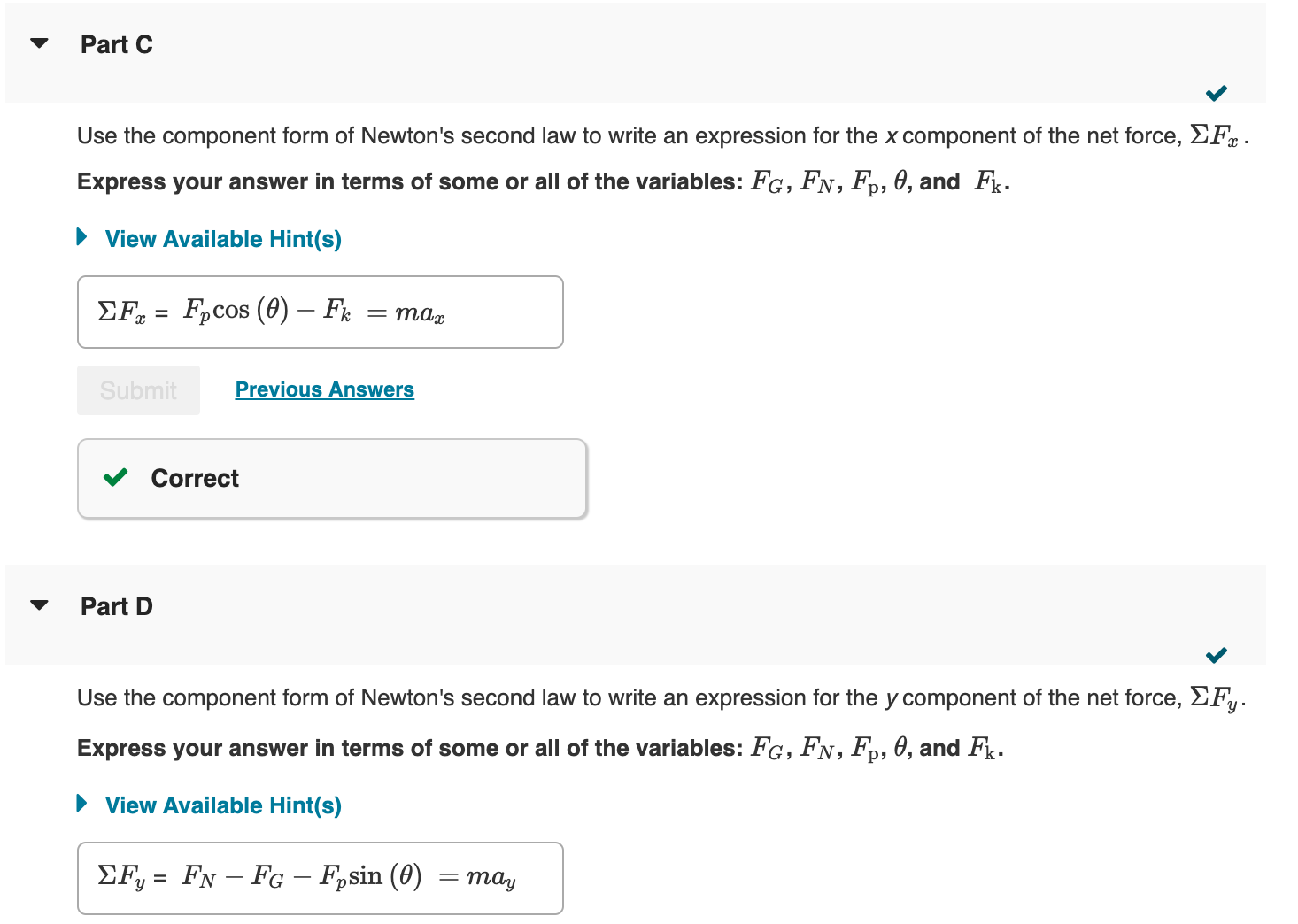
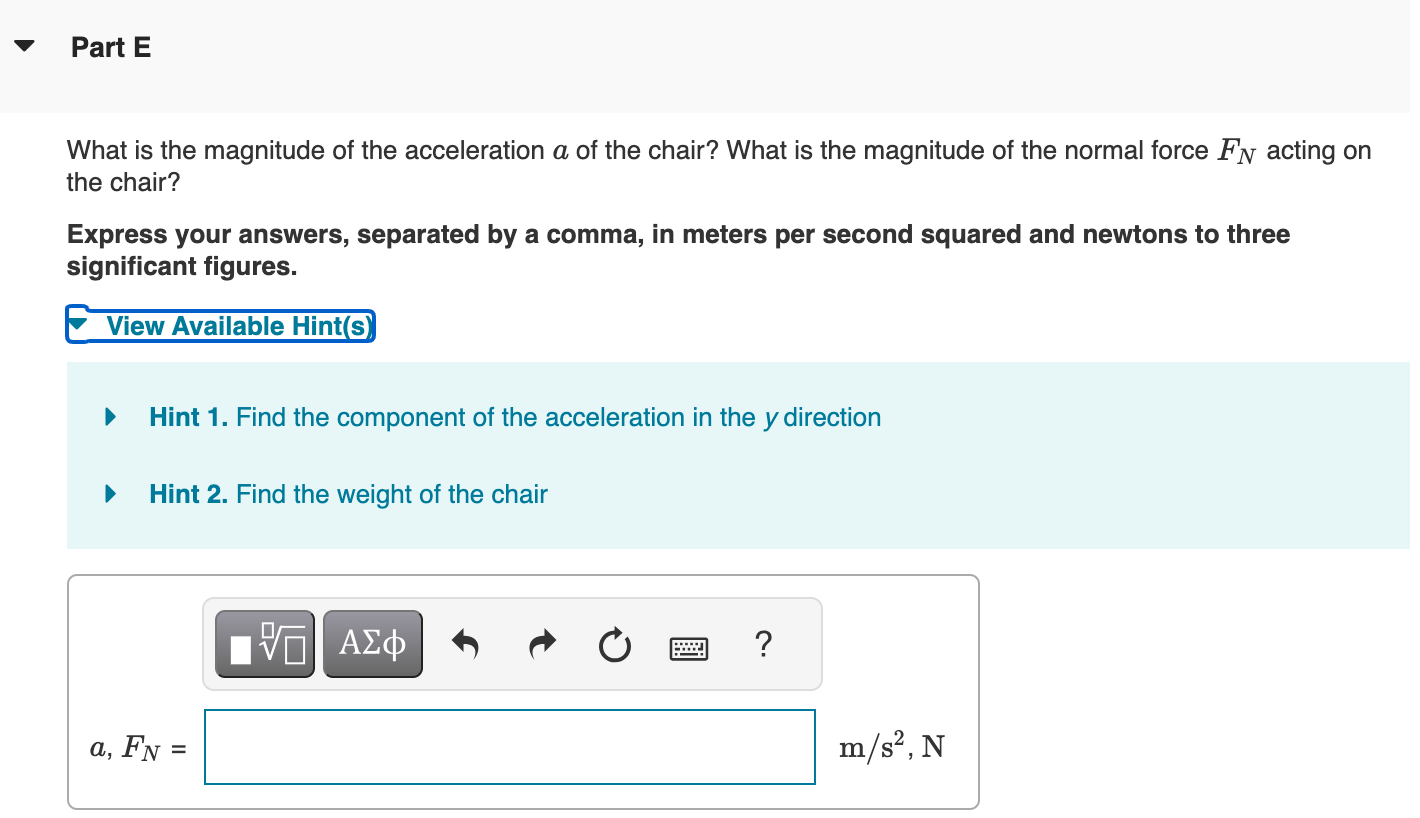


Problem Solving: Free-Body Diagrams and Newton's Laws 1. Draw a sketch of the situation. 2. Consider only one object (at a time), and draw a free-body diagram for that body, showing all the forces acting on that body. Do not show any forces that the body exerts on other bodies. If several bodies are involved, draw a free-body diagram for each body separately, showing all the forces acting on that body. 3. Newton's second law involves vectors, and it is usually important to resolve vectors into components. Choose an x and y axis in a way that simplifies the calculation. 4. For each body, Newton's second law can be applied to the x and y components separately. That is the x component of the net force on that body will be related to the x component of that body's acceleration: Fx = max, and similarly for the y direction. 5. Solve the equation or equations for the unknown(s). Apply these steps Use the steps outlined above to find the magnitude of the acceleration a of a chair and the magnitude of the normal force FN acting on the chair: Yusef pushes a chair of mass m = 55.0 kg across a carpeted floor with a force Fp (the subscript 'p' here is lowercase and throughout the question) of magnitude Fp = 170 N directed at 0 = 35.0 degrees below the horizontal (Figure 1). The magnitude of the kinetic frictional force between the carpet and the chair is F = 108 N. Part C Use the component form of Newton's second law to write an expression for the x component of the net force, Fx. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables: FG, FN, Fp, 0, and Fk. View Available Hint(s) Fx = Fpcos (0) - Fk = max Submit Previous Answers Part D Correct Use the component form of Newton's second law to write an expression for the y component of the net force, Fy. Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables: FG, FN, Fp, 0, and Fk. View Available Hint(s) = Fy FN-FG - Fpsin (0) = may Part E What is the magnitude of the acceleration a of the chair? What is the magnitude of the normal force FN acting on the chair? Express your answers, separated by a comma, in meters per second squared and newtons to three significant figures. View Available Hint(s) Hint 1. Find the component of the acceleration in the y direction Hint 2. Find the weight of the chair a, FN = = ? m/s, N hand. Part E Figure What is the magnitude of the acceleration a of the chair? What is the magnitude of the normal force FN acting on the chair? Express your answers, separated by a comma, in meters per second squared and newtons to three significant figures. View Available Hint(s) Hint 1. Find the component of the acceleration in the y direction The chair only moves in the postive x direction. What is ay? Express your answer in meters per second squared. ay = 0 m/s Submit Previous Answers = a + a Because 1 of 1 Correct The magnitude of the acceleration, a is found from ax and ay:a = ay = 0, a = ax Hint 2. Find the weight of the chair What is the weight of the chair? Express the weight in newtons to three significant figures. View Available Hint(s) FG = 540 N Submit Previous Answers Correct Correct Important: If you use this answer in later parts, use the full unrounded value in your calculations. Now you can use the equation you obtained by summing the forces in the y direction to find FN. ? c. a, FN 0.378,629 = Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining m/s, N
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


