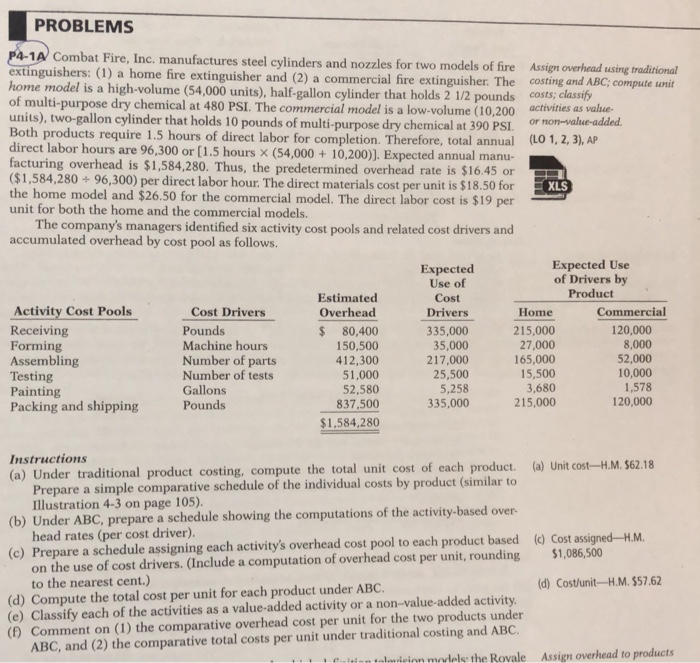
PROBLEMS 1A Combat Fire, Inc. manufactures steel cylinders and nozzles for two models of fire Assign overhead using tradi extinguishers: (1) a home fire extinguisher and (2) a commercial fire extinguisher. The costing and ABC; compute un p4 ional me model is a high-volume (54,000 units), half-gallon cylinder that holds 2 1/2 pounds costsclassify of multi-purpose dry chemical at 480 PSI. The commercial model is a low-volume (10,200 activities as value- units), two-gallon cylinder that holds 10 pounds of multi-purpose dry chemical at 390 PSI or non-value-added Both products require 1.5 hours of direct labor for completion. Therefore, total annual (LO 1, 2, 3), AP direct labor hours are 96,300 or [1.5 hours x (54,00010,200)). Expected annual manu- facturing overhead is $1,584,280. Thus, the predetermined overhead rate is $16.45 or ($1,584,280 +96,300) per direct labor hour. The direct materials cost per unit is $18.50 for the home model and $26.50 for the commercial model. The direct labor cost is $19 per unit for both the home and the commercial models. XLS The company's managers identified six activity cost pools and related cost drivers and accumulated overhead by cost pool as follows Expected Use of Cost Drivers Expected Use of Drivers b Product Activity Cost Pools Receiving Forming Assembling Testing Painting Packing and shipping Cost Drivers Pounds Machine hours Number of parts Number of tests Gallons Pounds Estimated Overhead $ 80,400 150,500 412,300 51,000 52,580 837,500 Home 215,000 27,000 165,000 15,500 3,680 215,000 Commercial 120,000 8,000 52,000 10,000 1,578 120,000 335,000 35,000 217,000 25,500 Instructions (a) Under traditiona I product costing, compute the total unit cost of each product. product (similar t (b) Under ABC, prepare a schedule showing the computations of the activity-based over (c) Prepare a schedule assigning each activity's overhead cost pool to each product based () Cost assigned-H.M Illustration 4-3 on page 105) head rates (per cost driver) on the use of cost drivers. (Include a computation of overhead cost per unit, rounding to the nearest cent.) (d) Cost/unit-H.M.$57.62 (d) Compute the total cost per unit for each product under ABC. (e) Classify each of the activities as a value-added activity or a non-value-added activity () Comment on (1) the comparative overhead cost per unit for the two products under ABC, and (2) the comparative total costs per unit under traditional costing and ABC tinn tulmdriom models the Rovale Assign overhead to products