Question: Problems (total 75 pts) S 1. (10 pts) Use figure 5 in the attached illustrations as a model to show the operations of the algorithm

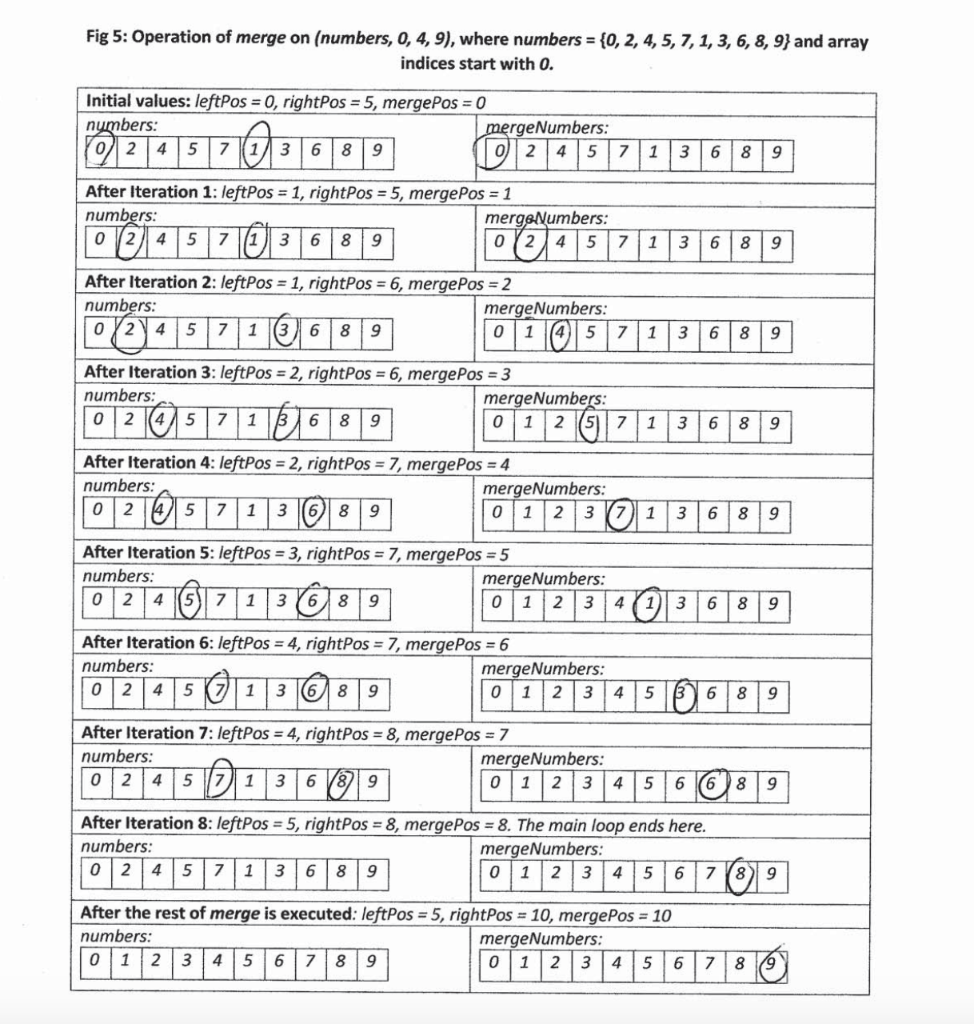
Problems (total 75 pts) S 1. (10 pts) Use figure 5 in the attached illustrations as a model to show the operations of the algorithm merge, used by merge sort on (A, 0, 4, 9), where A = {0, 1, 5, 7, 8, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9). 2. (20 pts) Draw the decision trees for selection sort and merge sort on arrays of 3 elements and determine the worst-case numbers of comparisons performed by both sorts. 3. (20 pts) Based on the decision tree model what is the minimal worst-case number of comparisons performed on an array of 4 elements by any comparison sort? Among the sorting algorithms you've learned in class, which one of them performs exactly that many comparisons on an array of 4 elements. Support your answer with the decision tree for that sort on 4 elements. 4. (10 pts) Recall the O(n log n)-time algorithm given in class that on an input array A of integers and a given integer intVal, finds two indices i and j, where A[i] + A[j] = intVal. Show how the algorithm can be modified in order to find indices i and j, where A[i] A[j] = intVal instead. Analyze the running time of the modified algorithm. 5. (15 pts) Suppose that you are given a set of locks and keys, each of which is labelled with a tag number. Suppose also that each lock can be opened only with the key labelled with the same tag number and no two locks have the same tag number. Design an algorithm that finds the number of locks that can be opened with the given keys. More precisely, you may assume that the input of your algorithm is two integer arrays L and K of equal length that store the tag numbers of the given locks and keys, respectively. Your algorithm will output an integer m that represents the number of tag numbers in array L that also appear in array K. To receive full credit the running time of your algorithm must be O(n log n), where n is the length of both array L and array K. Fig 5: Operation of merge on (numbers, 0, 4, 9), where numbers = {0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 1, 3, 6, 8, 9} and array indices start with 0. Initial values: leftPos = 0, rightPos = 5, mergePos = 0 numbers: mergeNumbers: 2 5 7 024 1 3 6 8 9 After Iteration 1: leftPos = 1, rightPos = 5, mergePos = 1 numbers: merge Numbers: 0 4 5 7 10 3 6 8 9 0 4 5 71 3 6 8 9 After Iteration 2: leftPos = 1, rightPos = 6, mergePos = 2 numbers: mergeNumbers: 0 4 8 9 0 1 7136 89 [@ 1 05 After Iteration 3: leftPos = 2, rightPos = 6, merge Pos = 3 numbers: mergeNumbers: 02057 1 18 6 8 9 0 1 2 5 7 1 3 6 89 After Iteration 4: leftPos = 2, rightPos = 7, mergePos = 4 numbers: mergeNumbers: 012105 7 1 3 6 8 9 0 1 2 3 7) 1 3 6 8 9 After Iteration 5: leftPos = 3, rightPos = 7, mergePos = 5 numbers: mergeNumbers: 0 24 57 13 1689 0 1 2 3 4 1 3 6 8 9 After Iteration 6: leftPos = 4, rightPos = 7, merge Pos = 6 numbers: mergeNumbers: 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 6 8 9 After Iteration 7: leftPos = 4, rightPos = 8, mergePos = 7 numbers: mergeNumbers: 0245 1 36V8219 0 1 2 3 4 5 6689 After Iteration 8: leftPos = 5, rightPos = 8, mergePos = 8. The main loop ends here. numbers: mergeNumbers: 0 2 4 5 7 1 3 6 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 After the rest of merge is executed: leftPos = 5, rightPos = 10, mergePos = 10 numbers: mergeNumbers: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 8 9
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


