Question
Programming Activity 7-2 Guidance ================================= This activity builds upon the work done in activity 7-1. It requires you to create and work with a static
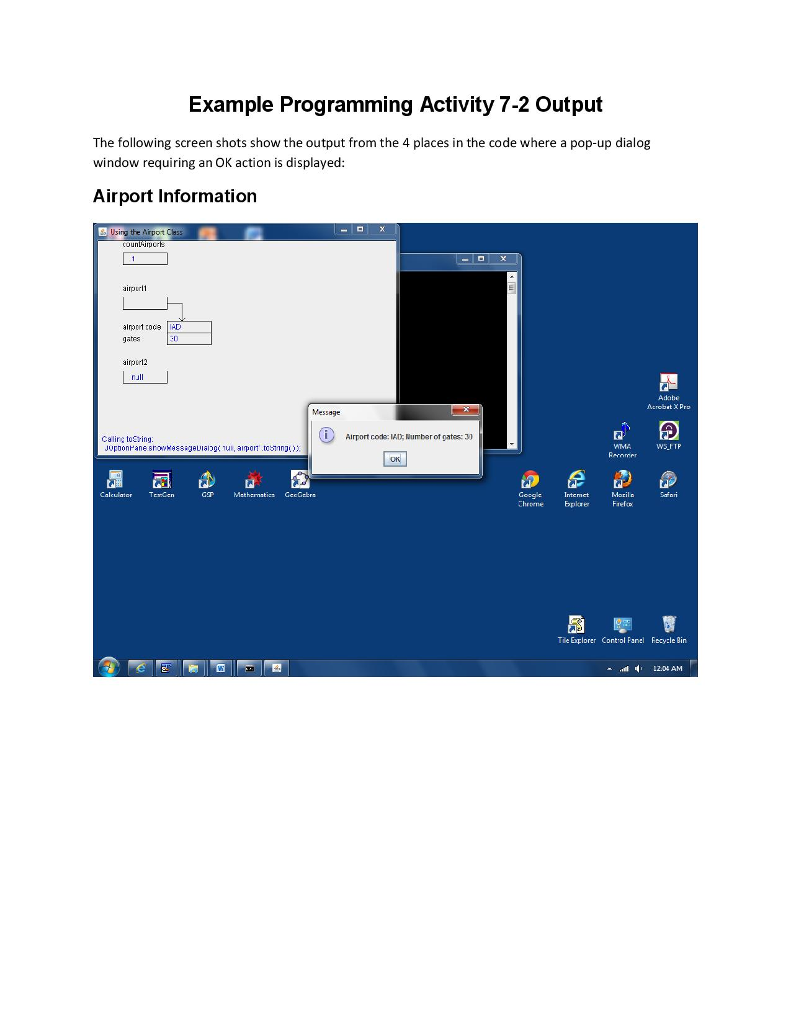
Programming Activity 7-2 Guidance ================================= This activity builds upon the work done in activity 7-1. It requires you to create and work with a static class variable. It also requires you to create toString() and equals() functions. The framework comments provide detailed instructions. Make sure you read and follow them. Main class ---------- You will make changes to and compile Airport.java. However, to run the program you run it from AirportClient.java. This means that AirportClient.java must be the current opened source file in TextPad when you choose to run the application. Part 1 ------ The static field countAirports is not a constant and should be private. Part 2 ------ Static fields are referenced by using the class name, rather than an object name. To reference the static field countAirports, use Airport.countAirports. Part 4 ------ Since the getCountAirports() function references a static field, this function must be declared as a static function (using the static keyword). Part 5 ------ The following example shows the format for the String returned by toString(): Airport code: IAD; Number of gates: 30
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Main Java Class:
public class Airport { // Instance variables private String airportCode; private int gates;
// 1. ***** Add a static class variable ***** // countAirports is an int // assign an initial value of 0 // Part 1 student code starts here:
// Part 1 student code ends here.
// 2. ***** Modify this method ***** // Default constructor: // method name: Airport // return value: none // parameters: none // function: sets the airportCode to an empty String // ***** adds 1 to countAirports class variable public Airport() { airportCode = ""; // Part 2 student code starts here:
// Part 2 student code ends here. }
// 3. ***** Modify this method ***** // Overloaded constructor: // method name: Airport // return value: none // parameters: a String startAirportCode and an int startGates // function: calls the setAirportCode method, passing the // startAirportCode parameter; // calls the setGates method, passing the startGates parameter // ***** adds 1 to countAirports class variable public Airport(String startAirportCode, int startGates) { airportCode = startAirportCode; setGates(startGates); // Part 3 student code starts here:
// Part 3 student code ends here. }
// Accessor method for the airportCode instance variable // method name: getAirportCode // return value: String // parameters: none // function: returns airportCode public String getAirportCode() { return airportCode; }
// Accessor method for the gates instance variable // method name: getGates // return value: int // parameters: none // function: returns gates public int getGates() { return gates; }
// 4. ***** Write this static method ***** // Accessor method for the countAirports class variable // method name: getCountAirports // return value: int // parameters: none // function: returns countAirports // Part 4 student code starts here:
// Part 4 student code ends here.
// Mutator method for the airportCode instance variable // method name: setAirportCode // return value: void // parameters: String newAirportCode // function: assigns airportCode the value of the // newAirportCode parameter public void setAirportCode(String newAirportCode) { airportCode = newAirportCode; }
// Mutator method for the gates instance variable // method name: setGates // return value: void // parameters: int newGates // function: validates the newGates parameter. // if newGates is greater than or equal to 0, // sets gates to newGates; // otherwise, prints an error message to System.err // and does not change value of gates public void setGates(int newGates) { if (newGates
gates = newGates; }
// 5. ***** Write this method ***** // method name: toString // return value: String // parameters: none // function: returns a String that contains the airportCode // and gates // Part 5 student code starts here:
// Part 5 student code ends here.
// 6. ***** Write this method ***** // method name: equals // return value: boolean // parameter: Airport object // function: returns true if airportCode // and gates in this object // are equal to those in the parameter object; // returns false otherwise // Part 6 student code starts here:
// Part 6 student code ends here.
} // end of Airport class definition
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Second Java App:
public class Pause { /** wait method * @param seconds number of seconds to pause */ public static void wait( double seconds ) { try { Thread.sleep( (int)( seconds * 1000 ) ); } catch ( InterruptedException e ) { e.printStackTrace( ); } } }
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Final Java App:
import java.awt.Graphics; import java.awt.Color; import javax.swing.JOptionPane; import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class AirportClient extends JFrame { String action1, action2; boolean firstTime = true;
double animationPause = 6.0; // 6 seconds between animations Airport airport1, airport2; // declare Airport object references
public void workWithAirports( ) { animate( "Two airport object references declared:", "Airport airport1, airport2;" );
/* Instantiate airport1 using the overloaded constructor */ airport1 = new Airport( "IAD", 30 ); animate( "Instantiated airport1 using overloaded constructor:", "airport1 = new Airport( \"IAD\", 30 );" );
/* Call toString() */ animate( "Calling toString:", "JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, airport1.toString( ) );" ); JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, airport1.toString( ) );
/* Instantiate a second airport object using overloaded constructor*/ airport2 = new Airport( "IAD", 30 ); animate( "Instantiated airport2 using overloaded constructor:", "airport2 = new Airport( \"IAD\", 30 );" );
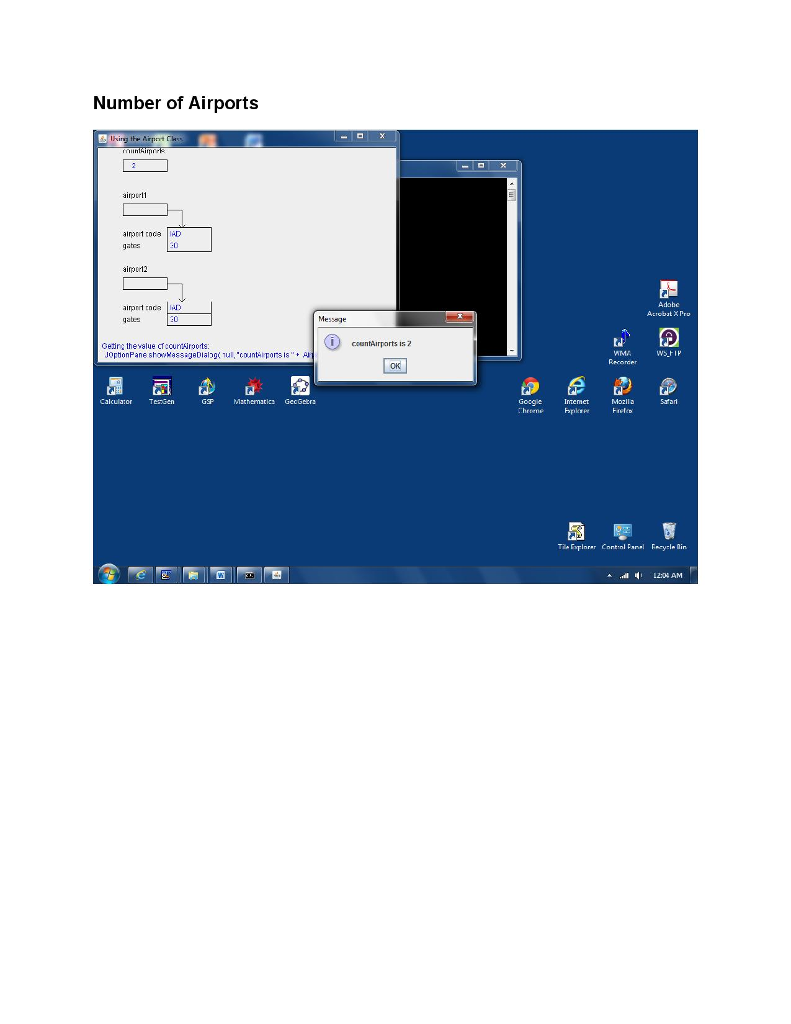
/* Get the value of countAirports */ animate( "Getting the value of countAirports:", "JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, \"countAirports is \" +" + " Airport.getCountAirports( ) );" ); JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, "countAirports is " + Airport.getCountAirports( ) );
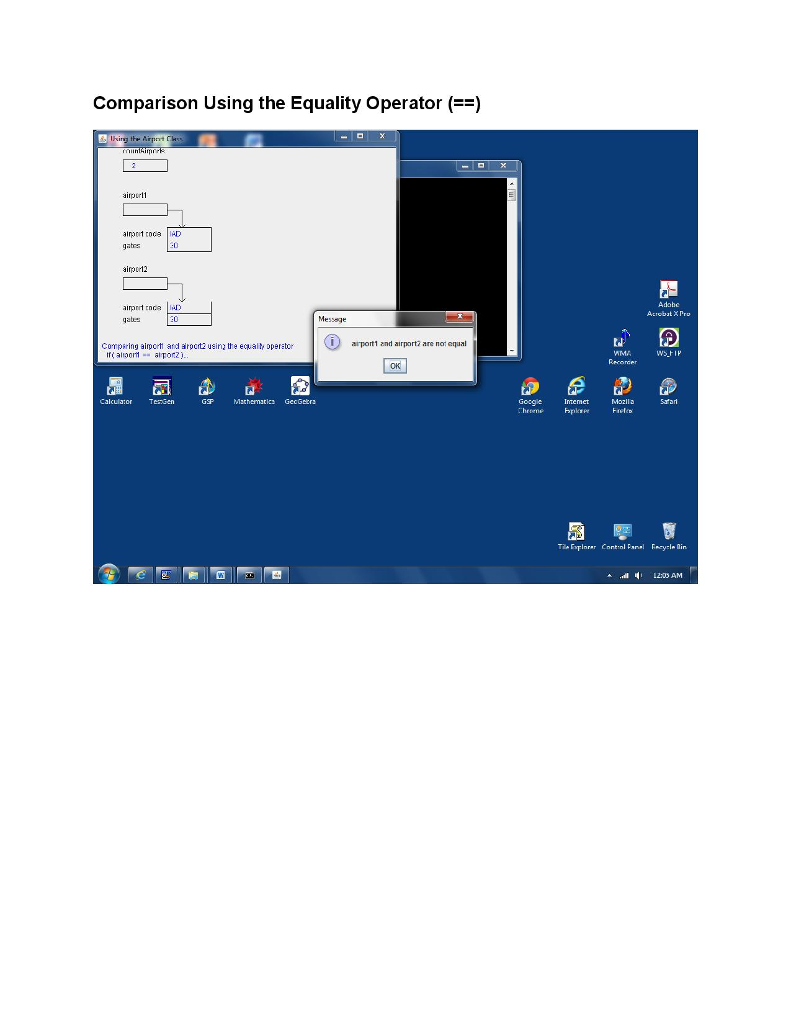
/* Compare the two airport objects */ animate( "Comparing airport1 and airport2 using the equality operator ", " if ( airport1 == airport2 )..." ); if ( airport1 == airport2 ) JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, "airport1 and airport2 are equal" ); else JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, "airport1 and airport2 are not equal" );
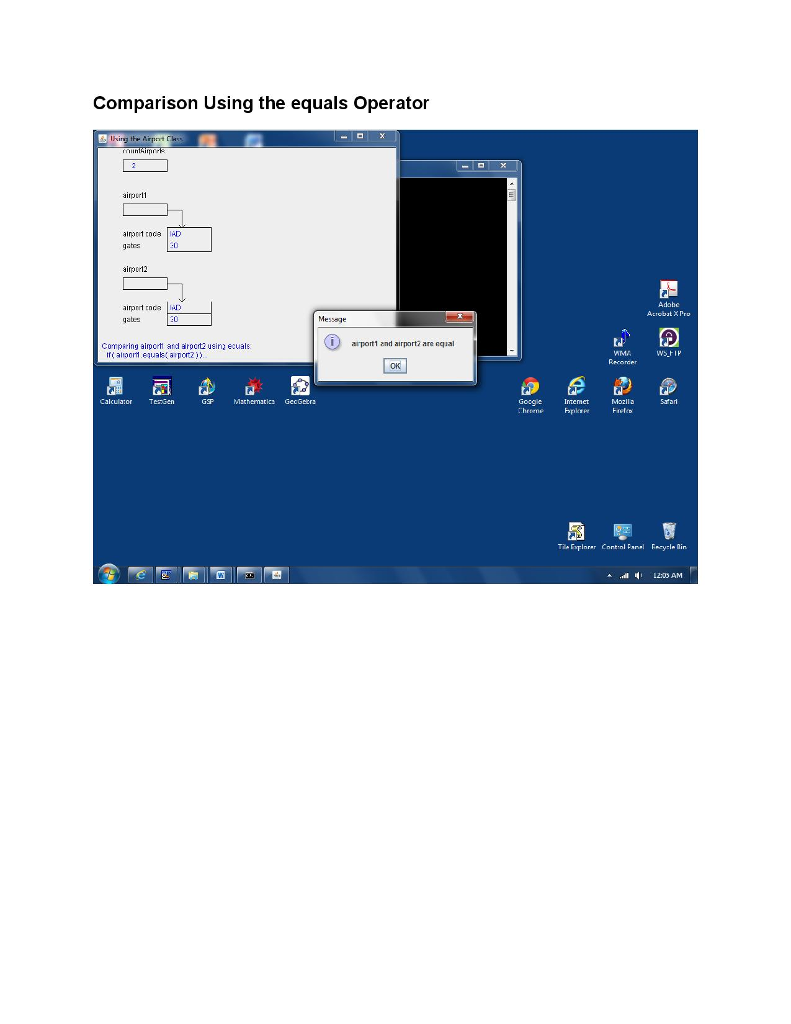
/* Compare the two Airport objects */ animate( "Comparing airport1 and airport2 using equals:", " if ( airport1.equals( airport2 ) )..." ); if ( airport1.equals( airport2 ) ) JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, "airport1 and airport2 are equal" ); else JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, "airport1 and airport2 are not equal" );
/* Finished */ animate( "Actions are complete, exiting", "" ); System.exit( 1 ); }
public AirportClient( ) { super( "Using the Airport Class" ); setSize( 520, 400 ); setVisible( true ); }
public void paint( Graphics g ) { super.paint( g ); if ( firstTime ) firstTime = false; else { int boxL = 75, boxH = 20; int sX = 50, sY = 50;
// countAirports g.setColor( Color.BLACK ); g.drawRect( sX, sY, boxL, boxH ); g.drawString( "countAirports", sX, sY - 10 ); g.setColor( Color.BLUE ); g.drawString( Integer.toString( Airport.getCountAirports( ) ), sX + 15, sY + 15 );
// airport1 sY = 125; if ( airport1 != null ) { // object reference box g.setColor( Color.BLACK ); g.drawRect( sX, sY, boxL, boxH ); g.drawString( "airport1", sX, sY - 10 ); draw( g, sX, sY, airport1 ); // draw airport object } else { // indicate null reference g.setColor( Color.BLACK ); g.drawRect( sX, sY, boxL, boxH ); g.drawString( "airport1", sX, sY - 10 ); g.setColor( Color.BLUE ); g.drawString( "null", sX + 15, sY + 15 ); }
sY = 250; if ( airport2 != null ) { // object reference box g.setColor( Color.BLACK ); g.drawRect( sX, sY, boxL, boxH ); g.drawString( "airport2", sX, sY - 10 ); draw( g, sX, sY, airport2 ); // draw airport object } else { // indicate null reference g.setColor( Color.BLACK ); g.drawRect( sX, sY, boxL, boxH ); g.drawString( "airport2", sX, sY - 10 ); g.setColor( Color.BLUE ); g.drawString( "null", sX + 15, sY + 15 ); }
// display action at bottom of screen g.setColor( Color.BLUE ); g.drawString( action1, 15, 370 ); g.drawString( action2, 20, 385 ); } }
private void draw( Graphics g, int sX, int sY, Airport a ) { int boxL = 75, boxH = 20;
// arrow g.setColor( Color.BLACK ); g.drawLine( sX + boxL, sY + boxH / 2, sX + boxL + 25, sY + boxH / 2 ); g.drawLine( sX + boxL + 25, sY + boxH / 2, sX + boxL + 25, sY + boxH * 2 ); g.drawLine( sX + boxL + 25 - 5, sY + boxH * 2 - 5, sX + boxL + 25, sY + boxH * 2 ); g.drawLine( sX + boxL + 25 + 5, sY + boxH * 2 - 5, sX + boxL + 25, sY + boxH * 2 );
// airportCode g.setColor( Color.BLACK ); g.drawString( "airport code", sX + boxL - 75, sY + 2 * boxH + 15 ); g.drawRect( sX + boxL, sY + 2 * boxH, boxL, boxH ); g.setColor( Color.BLUE ); g.drawString( a.getAirportCode( ), sX + boxL + 5, sY + 2 * boxH + 15 );
// gates g.setColor( Color.BLACK ); g.drawString( "gates", sX + boxL - 75, sY + 3 * boxH + 15 ); g.drawRect( sX + boxL, sY + 3 * boxH, boxL, boxH ); g.setColor( Color.BLUE ); g.drawString( Integer.toString( a.getGates( ) ), sX + boxL + 5, sY + 3 * boxH + 15 ); }
private void animate( String a1, String a2 ) { action1 = a1; action2 = a2; repaint( ); Pause.wait( animationPause ); }
public static void main( String[] args ) { AirportClient app = new AirportClient( ); app.workWithAirports( ); app.setDefaultCloseOperation( JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE ); } }
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Output Animation:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


