Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
project note needed Revised book on St Cent Management Pastormance Evaluation - A pine 1. Present and Revised Cost and Profit Structure Present Particular Given
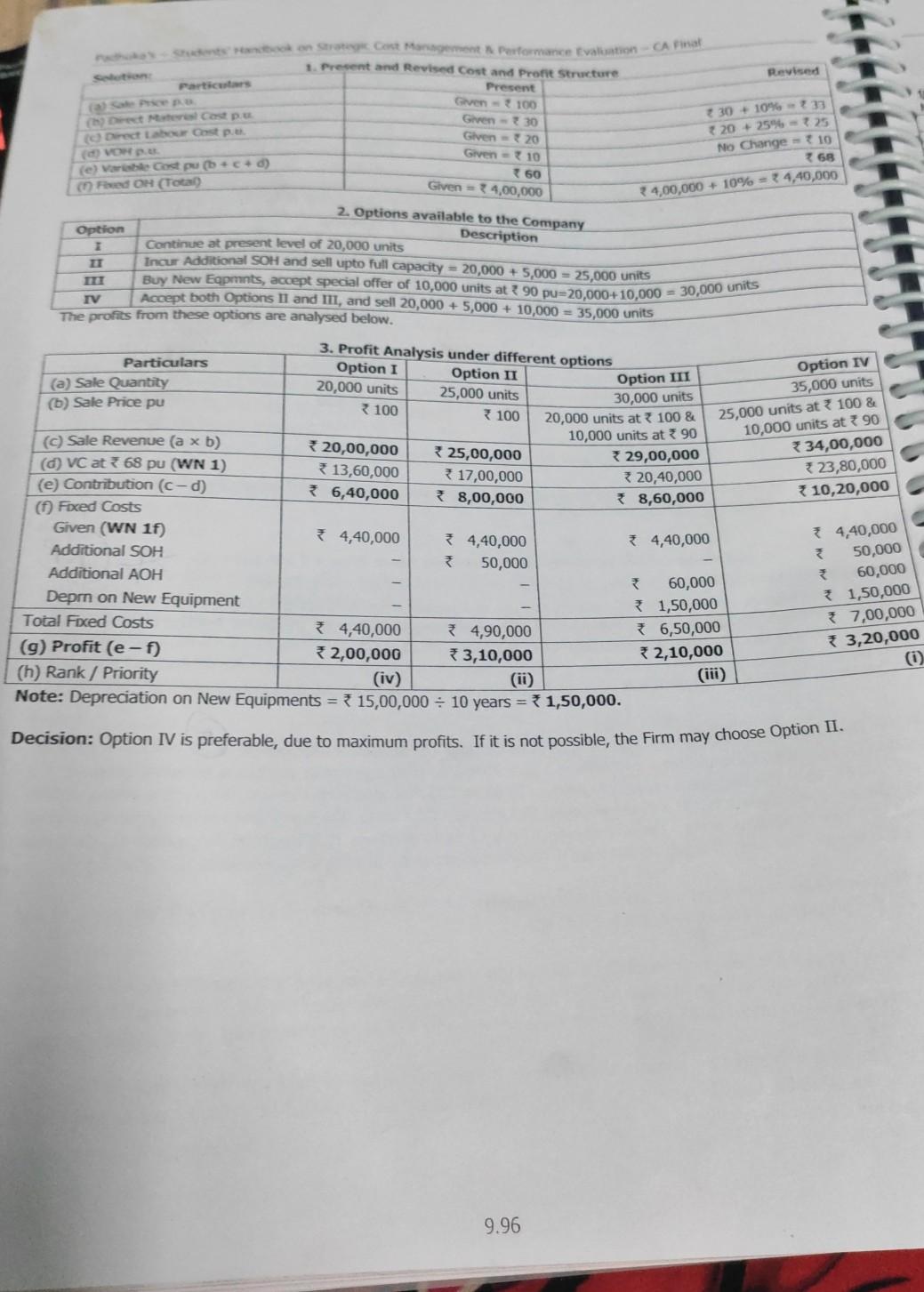
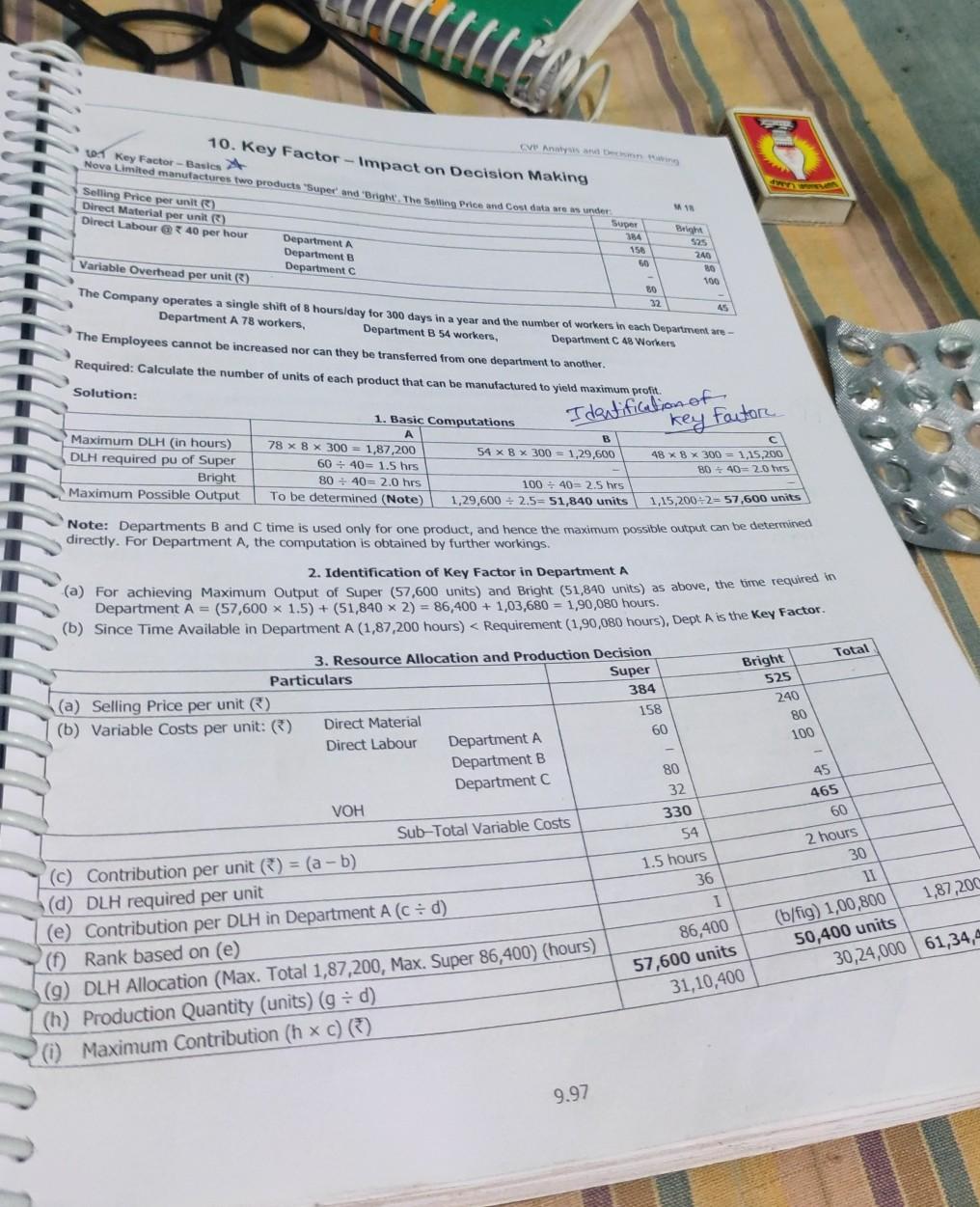
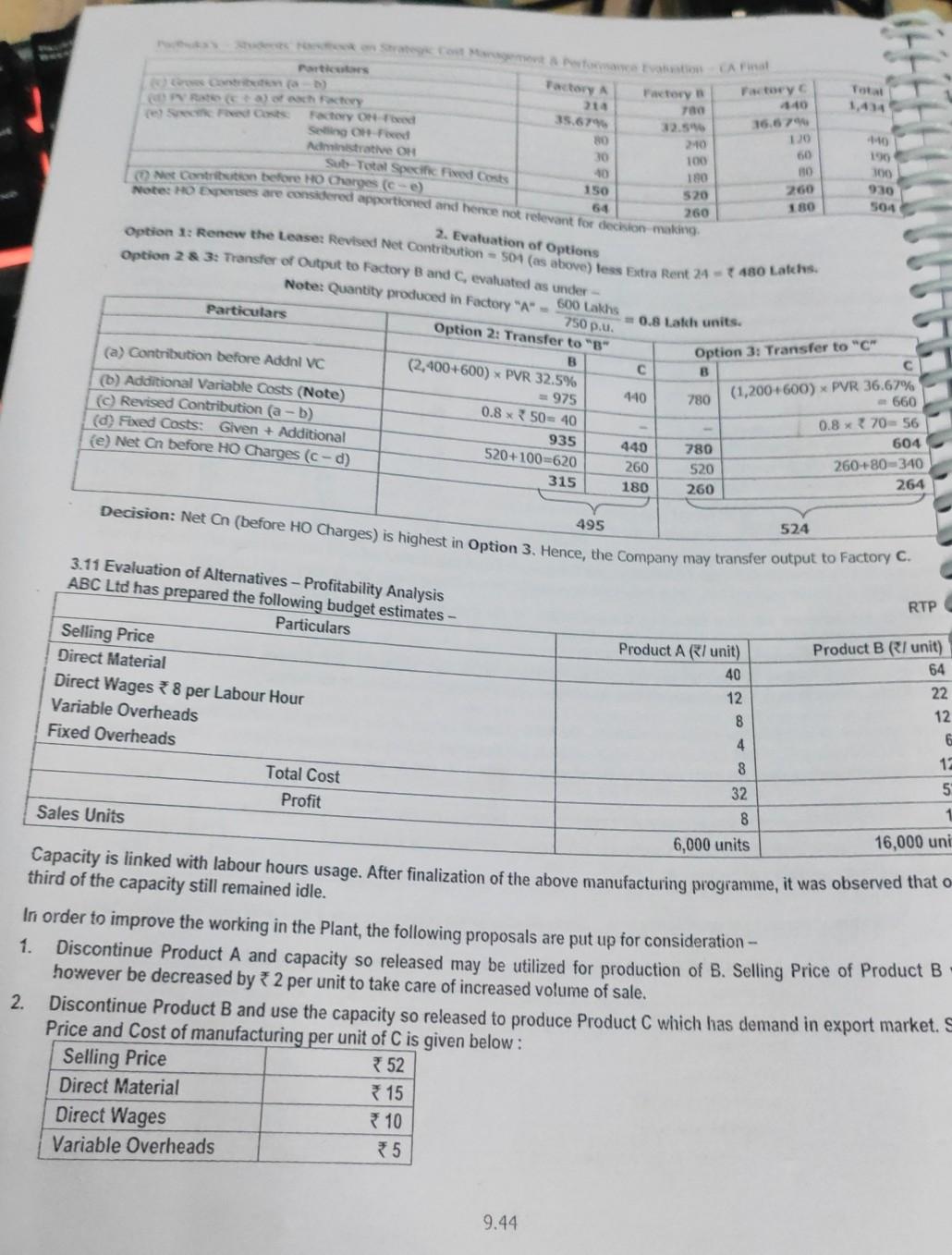
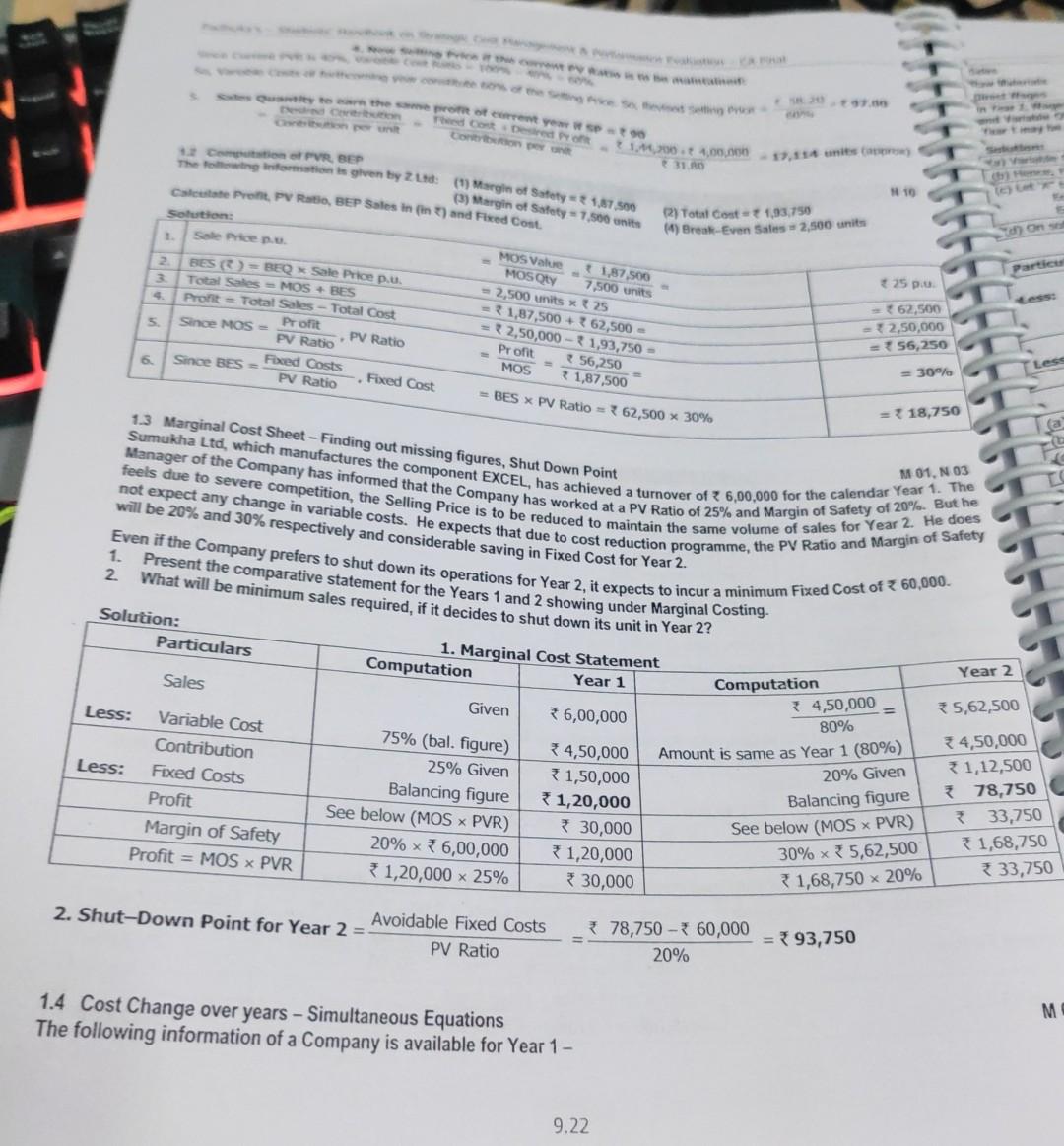

project note needed
Revised book on St Cent Management Pastormance Evaluation - A pine 1. Present and Revised Cost and Profit Structure Present Particular Given - 100 Giren - 30 Given 20 Given 10 160 Given = 4,00,000 et Me Cost pe Direct Labour Cost pe (VOH (e) Varbe Gost pub+c+d) Fed OH (Total 30 + 10% 20 - 25% = 725 No Change = 10 7 68 24,00,000 + 10% = 34,40,000 Option III 30,000 units 2. Options available to the Company Option Description I Continue at present level of 20,000 units Incur Additional SOH and sell upto full capacity = 20,000 + 5,000 = 25,000 units Buy New Eqpmnts, accept special offer of 10,000 units at 90 pu=20,000+ 10,000 = 30,000 units IV Accept both Options II and II, and sell 20,000 + 5,000 + 10,000 = 35,000 units The profits from these options are analysed below. 3. Profit Analysis under different options Particulars Option I Option II (a) Sale Quantity 20,000 units 25,000 units (6) Sale Price pu 100 100 20,000 units at 100 & 10,000 units at 90 (c) Sale Revenue (a xb) 20,00,000 25,00,000 *29,00,000 (0) VC at 68 pu (WN 1) 13,60,000 17,00,000 320,40,000 (e) Contribution (C-d) * 6,40,000 8,00,000 * 8,60,000 (1) Fixed Costs Given (WN 1f) 4,40,000 4,40,000 4,40,000 Additional SOH 50,000 Additional AOH 60,000 Deprn on New Equipment 1,50,000 Total Fixed Costs *4,40,000 34,90,000 * 6,50,000 (g) Profit (e-f) *2,00,000 3,10,000 (h) Rank / Priority (iv) Note: Depreciation on New Equipments = 15,00,000 = 10 years = 1,50,000. Option IV 35,000 units 25,000 units at * 100 & 10,000 units at 3 90 *34,00,000 23,80,000 10,20,000 4,40,000 50,000 60,000 * 1,50,000 7,00,000 3,20,000 0 2,10,000 (iii) Decision: Option IV is preferable, due to maximum profits. If it is not possible, the Firm may choose Option II. 9.96 ve Anwys 10. Key Factor - Impact on Decision Making w Key Factor-Basies Nova Limited manufactures two products "Super' and 'Bright. The Selling Price and cost dina we an under Selling Price per unit() Direct Material per unit) Direct Labour @ 40 per hour Department Department Department Variable Overhead per unit() Super 384 156 50 Bright 525 240 ( 100 80 32 AS The Company operates a single shift of 8 hours/day for 300 days in a year and the number of workers in each Department are - Department A 78 workers, Department B 54 workers, Department C 48 Workers The Employees cannot be increased nor can they be transferred from one department to another. Required: Calculate the number of units of each product that can be manufactured to yield maximum profit. Solution: 1. Basic Computations Maximum DLH (in hours) 78 X 8 X 300 = 1,87,200 54 X 8 X 300 = 1.29,600 48 X 8 X 300 = 1,15,200 DLH required pu of Super 60.40= 1.5 hrs BD 40= 2.0 hs Bright 80 40= 2.0 hrs 100 40 2.5 hrs Maximum Possible Output To be determined (Note) 1,29,600 2.5=51,840 units Identification of key factor B Total Bright Note: Departments B and time is used only for one product, and hence the maximum possible output can be determined 1,15,200-257,600 units directly. For Department A, the computation is obtained by further workings. 2. Identification of Key Factor in Department A (a) For achieving Maximum Output of Super (57,600 units) and Bright (51,840 units) as above, the time required in Department A = (57,600 x 1.5) + (51,840 x 2) = 86,400 + 1,03,680 = 1,90,080 hours. (b) Since Time Available in Department A (1,87,200 hours) 780 Factory - Fed 35.679 -Fored 80 20 Administrative OH 30 100 10 180 Net Contribution before HO Charges (e) 150 520 64 260 Factory 4:40 16.67 120 60 Sub-Total Specific Fixed Costs Note: Ho expenses are considered apportioned and hence not restevant for decision making 2. Evaluation of Options 10 100 100 930 260 180 504 Option 1: Renew the Leaser Revised Net Contribution 504 (as above) less Extra Rent 24-480 Latches 750 . Option 28 3: Transfer of Output to Factory B and evaluated as under Note: Quantity produced in Factory "A" - 600 Lakhs Particulars Option 2: Transfer to "B" B (2,400+600) * PVR 32.5% (a) Contribution before Addnl VC = 975 (b) Additional Variable Costs (Note) 0.8*50= 40 (c) Revised Contribution (a - b) 935 (d) Fixed Costs: Given + Additional 520+100620 (e) Net On before HO Charges (c-d) 315 0.8 Lakh units. Option 3: Transfer to "C" B 440 780 (1,200+600) * PVR 36.67% -660 0.8 x 70-56 440 780 604 260 520 260+80-340 180 260 264 Decision: Net Cn (before Ho Charges) is highest in Option 3. Hence, the company may transfer output to Factory C. 495 524 RTP 12 6. 8 32 8 - 3.11 Evaluation of Alternatives - Profitability Analysis ABC Ltd has prepared the following budget estimates - Particulars Selling Price Product A (I unit) Product B RI unit) 64 Direct Material 40 22 Direct Wages 8 per Labour Hour 12 Variable Overheads 8 Fixed Overheads 4 12 Total Cost 5 Profit Sales Units 6,000 units 16,000 uni Capacity is linked with labour hours usage. After finalization of the above manufacturing programme, it was observed that o third of the capacity still remained idle. In order to improve the working in the Plant, the following proposals are put up for consideration -- 1. Discontinue Product A and capacity so released may be utilized for production of B. Selling Price of Product B however be decreased by *2 per unit to take care of increased volume of sale. 2. Discontinue Product B and use the capacity so released to produce Product C wiich has demand in export market. S Price and Cost of manufacturing per unit of C is given below: Selling Price 352 Direct Material 15 Direct Wages 10 Variable Overheads 5 9.44 The Cont De Pot Lonto per Quantity to the ce pot oferent you wsp +90 Creu 211.00. 4,00.000 17.3** uniew 31.00 10 Costo PR BEP The towing formation is given by Zad: (1) Margin of Satety 1.17.500 (3) Margin of Safety -7.500 units Calcutate Profil PV Rati, BEP Sales in (on) and Fixed Cont. Solutions 1. Sale Price pe 2 BES () =BEQ * Sale Price p.u. Total Sales MOS + BES Profit Total Sales - Total Cost Profit 5 Since MOS = PV Ratio PV Ratio Foxed Costs 6 Since BES = PV Ratio Fixed Cost BES PV Ratio = 62,500 30% Total cost-1,93,750 (4) Break Even Sates - 2,500 units Ons Particu 25 p MOS Value 1,87,500 MOSQU 7.500 units - 2,500 units x 25 -1,87,500 + ? 62,500 - = 2,50,000 -1,93,750 = Profit 56,250 MOS 31,87,500 62,500 =12,50,000 = 56,250 Les = 30% 13 Marginal Cost Sheet - Finding out missing figures, Shut Down Point = 18,750 M 01, N 03 Manager of the Company has informed that the Company has worked at a PV Ratio of 25% and Margin of Safety of 20%. But he Sumukha Ltd, which manufactures the component EXCEL, has achieved a turnover of 6,00,000 for the calendar Year 1. The feels due to severe competition, the Selling Price is to be reduced to maintain the same volume of sales for Year 2. He does not expect any change in variable costs. He expects that due to cost reduction programme, the PV Ratio and Margin of Safety Even if the Company prefers to shut down its operations for Year 2, it expects to incur a minimum Fixed Cost of 60,000 will be 20% and 30% respectively and considerable saving in Fixed Cost for Year 2. 1. 2. Present the comparative statement for the Years 1 and 2 showing under Marginal Costing. What will be minimum sales required, if it decides to shut down its unit in Year 2? Solution: Particulars 1. Marginal Cost Statement Computation Year 1 Year 2 Sales Given 6,00,000 = 35,62,500 Less: Variable Cost Contribution Less: Fixed Costs Profit Margin of Safety Profit = MOS x PVR 75% (bal. figure) 25% Given Balancing figure See below (MOS ~ PVR) 20% x 6,00,000 1,20,000 x 25% 4,50,000 1,50,000 1,20,000 * 30,000 1,20,000 * 30,000 Computation 4,50,000 80% Amount is same as Year 1 (80%) 20% Given Balancing figure See below (MOS x PVR) 30% x 5,62,500 1,68,750 x 20% 34,50,000 31,12,500 378,750 33,750 1,68,750 3 33,750 Avoidable Fixed Costs 2. Shut-Down Point for Year 2 = PV Ratio 78,750 - 60,000 20% 393,750 1.4 Cost Change over years - Simultaneous Equations The following information of a Company is available for Year 1 - M 9.22 Yo 10 Ft I becay or me MATURITY SALE INTRODITION DECLINE TIME Concept Illustration: Examine the validity of the following statements under Life Cycle Costing - Statement 1. the product easily accessible by target customers. 2 RTP Answer Valid 3. Valid end of the Introductory Stage. Invalid 4. In the Introduction Stage, usual marketing strategy is to strengthen the Supply Chain Relationships to make understand how the product works, so that they can develop the own similar, but different product. In the Introduction Stage, Competitors will purchase the product to carry out Reverse Engineering and In the Introduction Phase, the Firm will seek to avoid this competition by maintaining its Selling Price at the in the Growth Stage, if the product cannot be differentiated in other ways, the Firm may need further In the Maturity Stage, Firms are tempted to engage in costly promotional price wars to wean away market In the Decline Stage, falling Sales may induce Firms to slash marketing expenditure. Brand Loyalty will be reduction in Selling Price to maintain growth. Valid 5 share from Competitors. Valid 6. Valid 7. exploited to create profits. The Concept of Product Life Cycle is applicable only for well-established products. Invalid Concept Illustration: A Company's four products, M, N,O & P are in the market. Identify the phase of Product Life Cycle for each product with brief reasons. N 10 1. M: There is a lot of competition. Quantity sold has been increasing at 10%, 8% and 7% in the last 3 years. 2. However, N continues to have good sales. N: Until last year, N had no competition. Suddenly the company finds 4 new products very similar to N in the mark 3. O: There is intense competition. Achieving targeted sales is becoming increasingly difficult. Hence the Compan introducing slightly modified features in the market. 4. P: Huge Inventory of P is available. P is being sold but there are many products in the market which are priced lesser P, but have the same utility as P. 8.2Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


