Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
provide a critical analysis for this article Sources of Information and Beliefs About the Health Effects of Marijuana Julie H. Ishida, MD, MAS, Alysandra J.


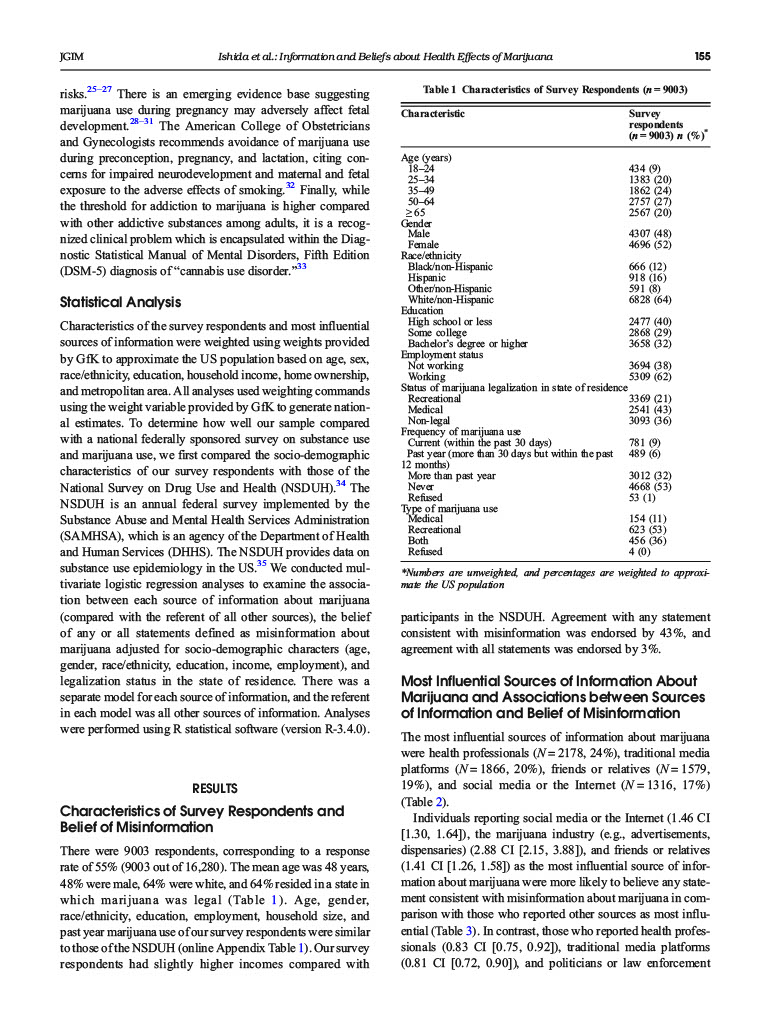
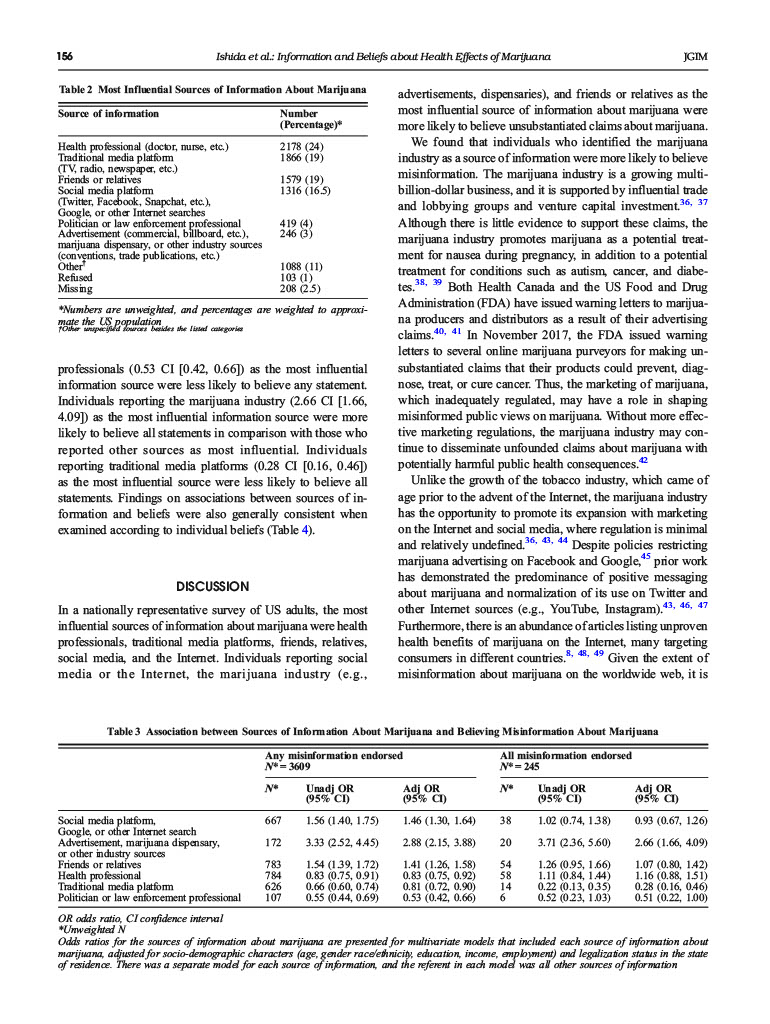
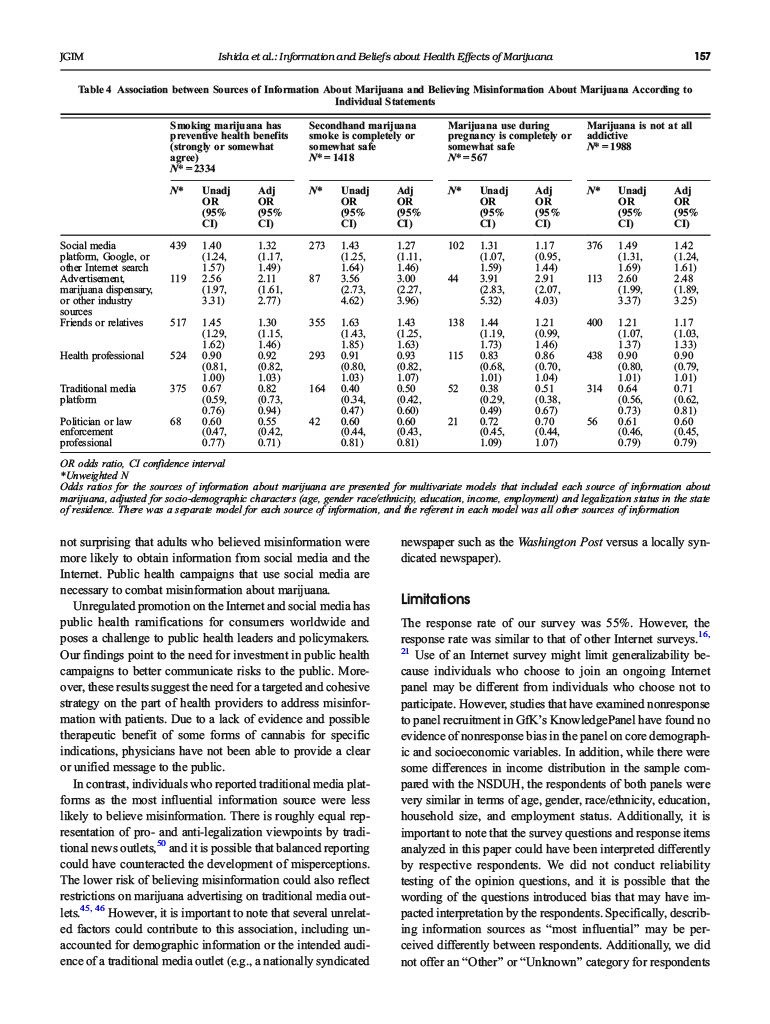


Sources of Information and Beliefs About the Health Effects of Marijuana Julie H. Ishida, MD, MAS, Alysandra J. Zhang, BA2, Stacey Steigerwald, MSSA, Beth E. Cohen, MD, MAS23, Marzieh Vali, MS, and Salomeh Keyhani, MD, MPH.3 Department of Medicine, Division of Nephrology, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA; 2San Francisco VA Medical Center, San Francisco, CA, USA; Department of Medicine, UCSF, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA. BACKGROUND: Marijuana is currently legal for recrea- tional use in 10 states and Washington DC while a total of 34 states have implemented varying degrees of medical marijuana. The commercialization of marijuana has been accompanied by a proliferation of false claims regarding the therapeutic potential of marijuana, which are popu- larized by several different information sources. To date, no study has examined where US adults get their infor- mation regarding marijuana. OBJECTIVE: To determine the sources of information associated with believing unsupported claims about marijuana. DESIGN: Probability-based online survey PARTICIPANTS: 16,820 adults, with a response rate of about 55% (N=9003) MAIN MEASURES: Most influential sources of informa- tion about marijuana and belief of statements consistent with misinformation, for example, smoking marijuana has preventative health benefits, secondhand marijuana smoke or use during pregnancy is completely or some- what safe, and marijuana is not at all addictive. KEY RESULTS: There were 9003 respondents (response rate 55%). Forty-three percent believed unsupported claims about marijuana. The most influential sources of information were health professionals, traditional media, friends/relatives, and social media/internet. Individuals reporting social media or the Internet (1.46 CI [1.30, 1.64]), the marijuana industry (e.g., advertisements, dis- pensaries) (2.88 CI [2.15, 3.88)), and friends or relatives (1.41 CI[1.26, 1.58]) as the most influential source of information about marijuana were more likely to believe any statement consistent with misinformation about marijuana in comparison with those who reported other sources as most influential. CONCLUSIONS: Individuals reporting the most signifi- cant source of information regarding marijuana was from social media or the Intemet, the marijuana industry, or friends or relatives were more likely to believe unsupport- ed claims about marijuana. Public health campaigns to counter the misinformation about marijuana to the pub- lic are needed. Electronic supplementary material The online version of this article (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-019-05335-6) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users. Check for updates Received October 31, 2018 Revised March 29, 2019 Accepted July 30, 2019 Published online October 21, 2019 KEY WORDS: marijuana; bellefs; information source. J Gen Intern Med 35(1):153-9 DOI: 10.1007/s11606-019-05335-6 Society of General Internal Medicine (This is a U.S. govemment work and not under copyright protection the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply) 2019 INTRODUCTION The prevalence of marijuana use has increased in the past decade in the United States (US) population and worldwide.. In tandem with increasing marijuana use, there has also been a substantial drop in the public's perception of risks from marijuana use in the US and other Western countries., 4 Moreover, the marijuana industry has experienced tremendous growth in the past decade and to exceed $57 and is projected billion in annual revenue within the next decade. In tandem with the growth in marijuana marketing, sales, and use, there has been a proliferation of misinformation.6-8 National surveys suggest the perception of "great risk" from weekly marijuana use has dropped from 50.4% in 2002 to 33.3% in 2014 and has dropped further since." A recent national survey demonstrated that the public attributes benefit to marijuana without any evidence to support such beliefs (e.g., improvement in sleep, focus, or concentration). More- over, recent data also suggests that many Americans believe that marit problemana has no risks and that it prevents health The main drivers of this favorable perception in the US are unclear, but it is likely multifactorial and includes the liberal- ization of medical marijuana laws 10 and promotion by advo- cacy organizations and business interests. For example, Busi- ness Insider, a website with an audience of over 100 million visitors a month," recently touted the ability of marijuana to "reverse carcinogenic effects of tobacco and improve lung health." The The source research article cited by Business Insider did not support such a claim.2 In addition, legalization has been accompanied by the commercialization of marijuana, with projections estimating that marijuana sales will exceed $25 billion by 2025.13 There is overt marketing to consumers of marijuana on the Internet and social media with inadequate regulatory oversight.", 14 It is possible that sources of infor- mation are playing a role in furthering misinformation among 153
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The study provides significant insights into the sources of information shaping beliefs about marijuana among adults in the United States Its findings ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


