Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
PSYC 3110 Problem Set #3 - t-test The faculty in the department of Psychology at a prestigious university are very concerned about the fact
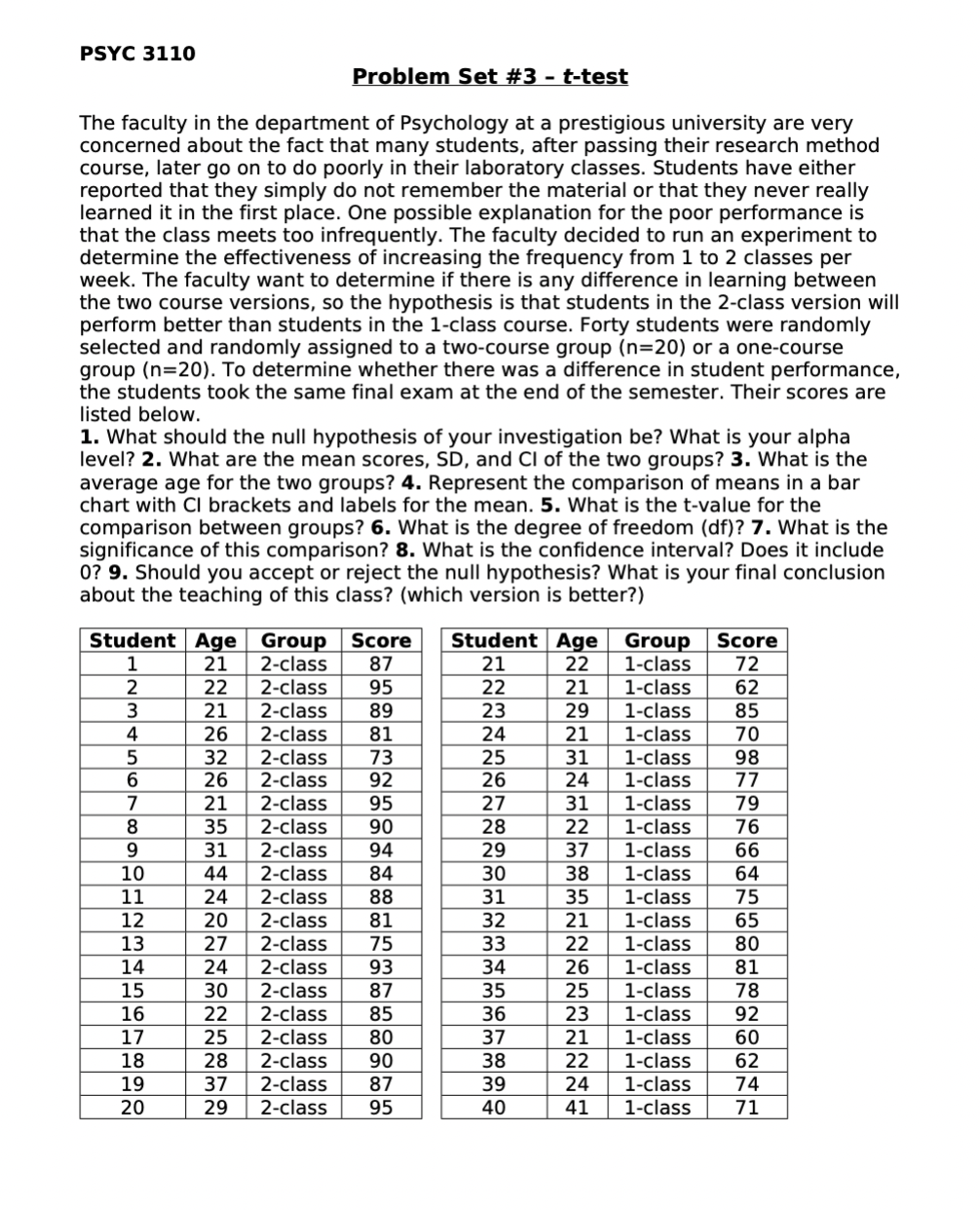

PSYC 3110 Problem Set #3 - t-test The faculty in the department of Psychology at a prestigious university are very concerned about the fact that many students, after passing their research method course, later go on to do poorly in their laboratory classes. Students have either reported that they simply do not remember the material or that they never really learned it in the first place. One possible explanation for the poor performance is that the class meets too infrequently. The faculty decided to run an experiment to determine the effectiveness of increasing the frequency from 1 to 2 classes per week. The faculty want to determine if there is any difference in learning between the two course versions, so the hypothesis is that students in the 2-class version will perform better than students in the 1-class course. Forty students were randomly selected and randomly assigned to a two-course group (n=20) or a one-course group (n=20). To determine whether there was a difference in student performance, the students took the same final exam at the end of the semester. Their scores are listed below. 1. What should the null hypothesis of your investigation be? What is your alpha level? 2. What are the mean scores, SD, and Cl of the two groups? 3. What is the average age for the two groups? 4. Represent the comparison of means in a bar chart with Cl brackets and labels for the mean. 5. What is the t-value for the comparison between groups? 6. What is the degree of freedom (df)? 7. What is the significance of this comparison? 8. What is the confidence interval? Does it include 0? 9. Should you accept or reject the null hypothesis? What is your final conclusion about the teaching of this class? (which version is better?) Student Age Group Score Student Age Group Score 1 21 2-class 87 21 22 1-class 2 22 2-class 95 22 21 1-class 3 21 2-class 89 23 29 1-class 4 26 2-class 81 24 21 1-class 5 32 2-class 73 25 31 1-class 6 26 2-class 92 26 24 1-class 7 21 2-class 95 27 31 8 35 2-class 90 28 22 9 31 2-class 94 29 37 10 44 2-class 84 30 38 11 24 2-class 88 31 35 12 20 2-class 81 32 21 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 134567890 27 2-class 75 33 22 24 2-class 93 34 26 30 2-class 87 35 25 22 2-class 85 36 25 2-class 80 37 21 28 2-class 90 38 37 2-class 87 39 24 29 2-class 95 40 12785-26537225 1-class 79 1-class 1-class 1-class 1-class 1-class 1-class 1-class 1-class 23 1-class 22 1-class 1-class 1-class 41 1-class 22508706645507022667F 72 98 81 92 71 On Your Own: Fujiwara-sensei read about this class study in his favorite Psychological journal and it sparks his curiosity as to whether dividing his twice a week, 2-hour lectures into 4 per week, 1-hour lectures can affect his student scores on an upcoming exam. He hypothesizes that number of meetings will have an impact on scores, despite meeting for the same total duration of time per week. The 40 students in his class are randomly assigned to the 2-class per week and 4-class per week groups, and their average scores on the exam are listed below. 1. What should the null hypothesis of your investigation be? What is your alpha level? 2. What are the mean scores, SD, and CI of the two groups? 3. What is the average age for the two groups? 4. Represent the comparison of means in a bar chart with Cl brackets and labels for the mean. 5. What is the t-value for the comparison between groups? 6. What is the degree of freedom (df)? 7. What is the significance of this comparison? 8. What is the confidence interval? Does it include 0? 9. Should you accept or reject the null hypothesis? What is your final conclusion about the teaching of this class? (which version is better?) Student Age Group Score Student Age Group Score 1 19 2/wk 82 21 16 4/wk 85 2 21 2/wk 94 22 31 4/wk 95 3 22 2/wk 85 23 22 4/wk 89 4 20 2/wk 87 24 26 4/wk 78 5 18 2/wk 98 25 24 4/wk 71 6 25 2/wk 81 26 27 4/wk 92 7 27 2/wk 95 27 17 4/wk 95 8 19 2/wk 76 28 18 4/wk 83 9 22 2/wk 76 29 21 4/wk 99 10 26 2/wk 90 30 27 4/wk 84 11 27 2/wk 95 31 12 23 2/wk 91 13 22 2/wk 80 33 14 28 2/wk 81 34 15 21 2/wk 78 35 16 18 2/wk 87 36 17 16 2/wk 70 18 22 2/wk 75 38 19 27 2/wk 74 20 29 2/wk 80 40 1234567890 25 4/wk 84 19 4/wk 81 23 4/wk 75 21 4/wk 93 20 4/wk 77 52 4/wk 85 21 4/wk 90 19 4/wk 90 22 4/wk 87 26 4/wk 91
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


