

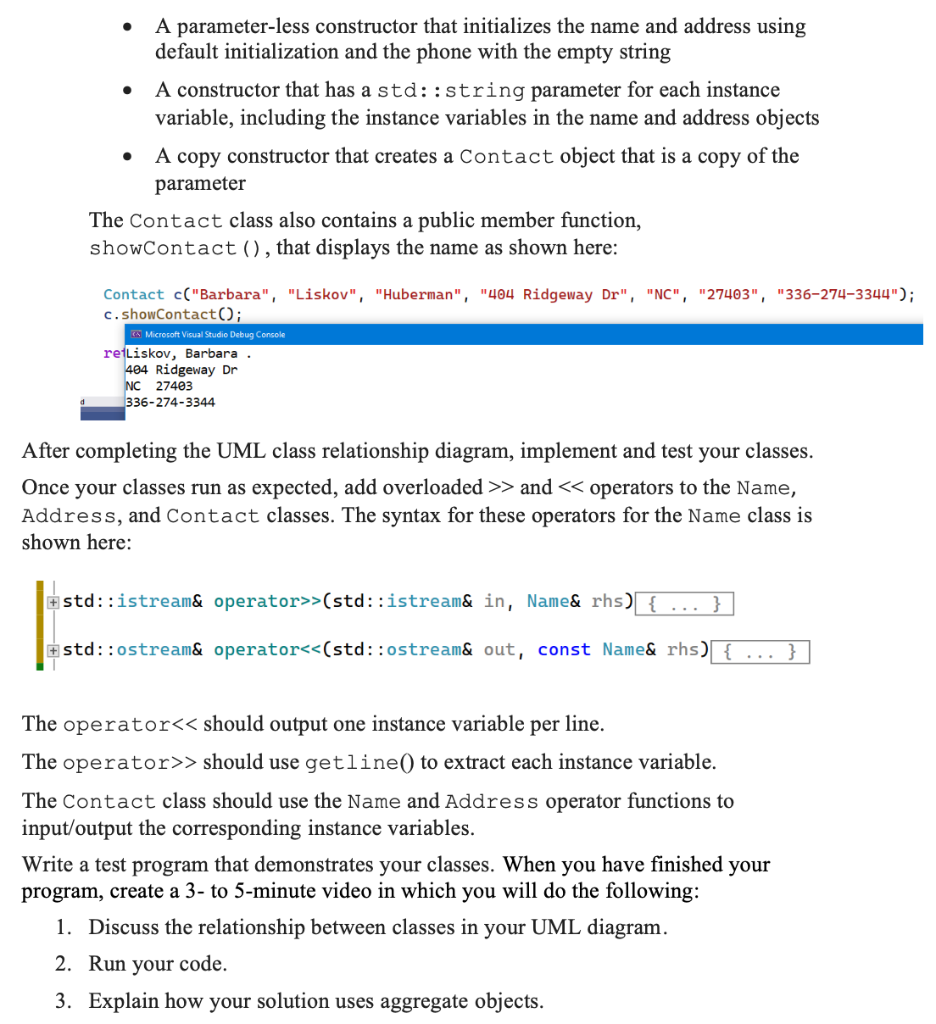
purpose of this assignment is to assess your ability to do the following: - Model aggregation relationships with UML class diagrams (utilize abstraction in software design). - Implement classes utilizing aggregating relationships. - Utilize aggregate objects in a software solution. - Utilize file input/output in a C++ program. this assignment, you will create a UML class relationship diagram for the following sses: 1. Name.h The Name class models a Name object. A Name object has the following private instance variables: - last_name : std: :string - first_name : std: :string - middle_name : std: :string The Name class should include setters and getters for all instance variables. The Name class has three constructors: - A parameter-less constructor that initializes all instance variables with the empty string - A constructor that has a parameter for each instance variable - A copy constructor that creates a Name object that is a copy of the parameter The Name class also contains a public member function, showName (), that displays the name as shown here: Name n("Barbara", "Liskov", "Huberman"); n. showName(); Cis Microsoft Visual Studio Debug Console Liskov, Barbara H. 2. Address.h The Address class models an Address object. An Address object has the following private instance variables: - streetAddress : std: string - state : std: string - zip : std: :string The Address class should include setters and getters for all instance variables. The Address class has three constructors: - A parameter-less constructor that initializes all instance variables with the empty string. - A constructor that has a parameter for each instance variable - A copy constructor that creates an Address object that is a copy of the parameter The Address class also contains a public member function, showAddress ( ), that displays the address as shown here: Address a("404 Ridgeway Dr", "NC", "27403"); a. showAddress(); return 0 ; 3. Contact.h The Contact class models a Contact object. A Contact object has the following private instance variables: - name : Name - address : Address - phone : std: string The Contact class should include setters and getters for all instance variables. The getters and setters should return/take string parameters. The string parameters will be used to update the Name and Address instance variables. The Contact class has three constructors: - A parameter-less constructor that initializes the name and address using default initialization and the phone with the empty string - A constructor that has a std: : string parameter for each instance variable, including the instance variables in the name and address objects - A copy constructor that creates a Contact object that is a copy of the parameter The Contact class also contains a public member function, showContact (), that displays the name as shown here: Contact c("Barbara", "Liskov", "Huberman", "404 Ridgeway Dr", "NC", "27403", "336-274-3344 c. showContact(); re-Liskov, Barbara . 404 Ridgeway Dr NC 27403 3362743344 After completing the UML class relationship diagram, implement and test your classes. Once your classes run as expected, add overloaded >> and > should use get line( to extract each instance variable. The Contact class should use the Name and Address operator functions to input/output the corresponding instance variables. Write a test program that demonstrates your classes. When you have finished your program, create a 3- to 5-minute video in which you will do the following: 1. Discuss the relationship between classes in your UML diagram. 2. Run your code. 3. Explain how your solution uses aggregate objects









