PYTHON 3..please help ASAP..




Here is the skeleton I have so far...
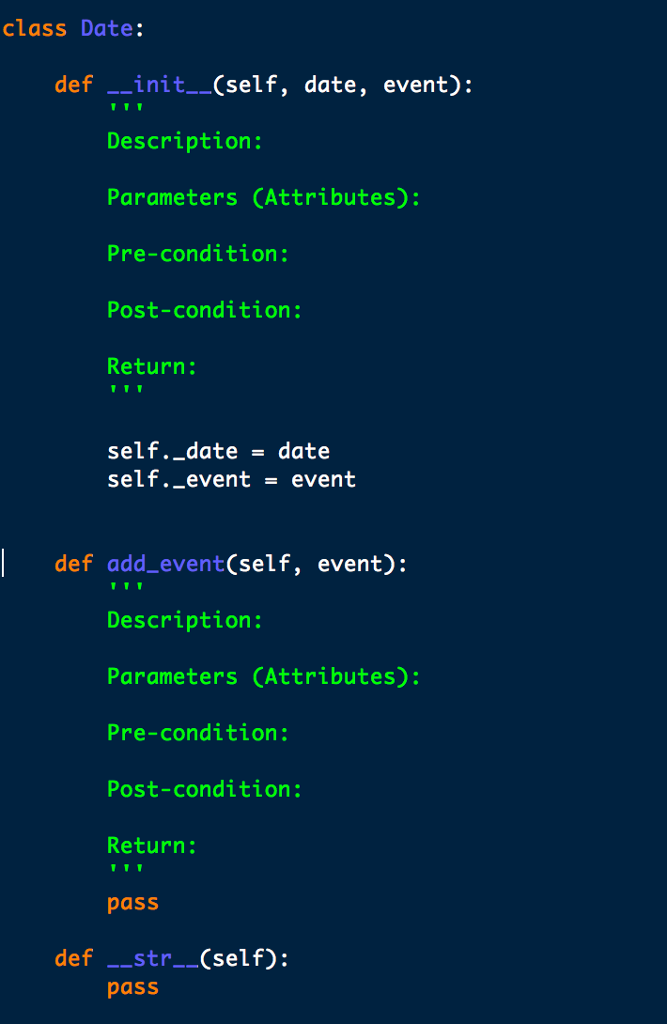
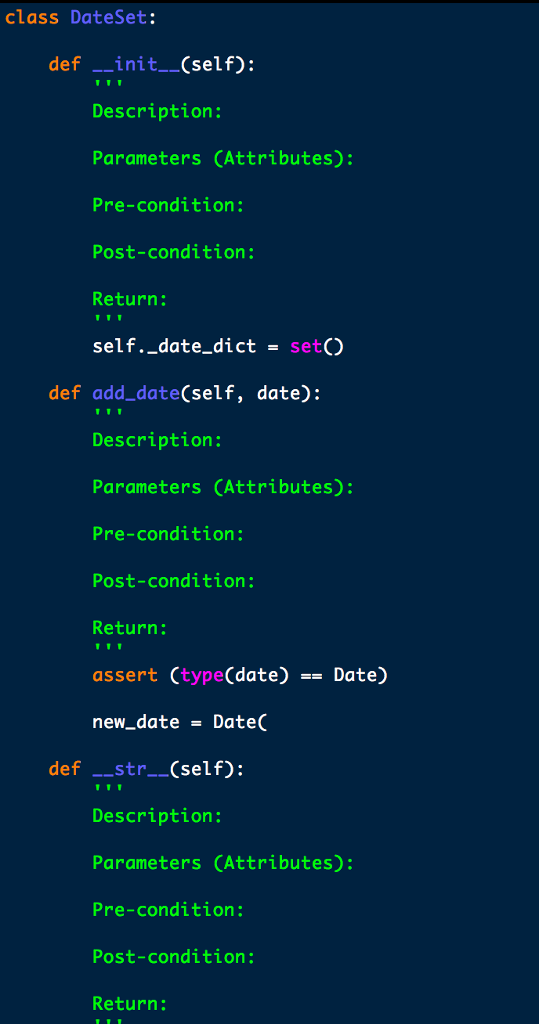
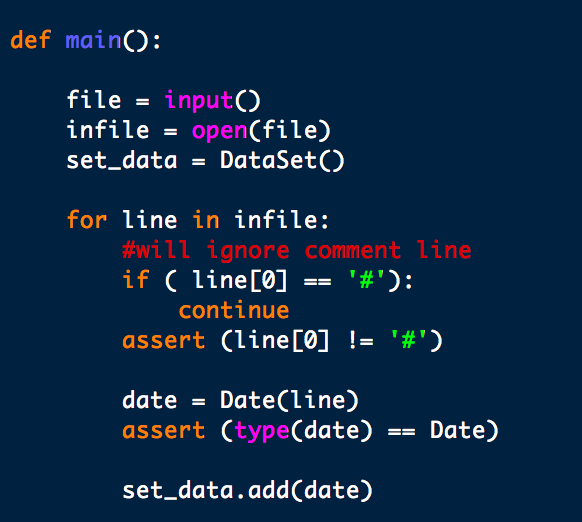
Problem Description Suppose you wanted to offer a website or app to manage a database of dates and events. Such a database might be used to look up dates in the past ("on this date in history...", as in the sites mentioned above); or they might be used as a calendar service to provide reminders for future events. In either case, you need a program that can record and look up strings (i.e., events) associated with dates One catch here is reasoning about dates. People use many different formats to write dates, e.g., "December 25, 2016" "2016-12-25", and "12/25/2016", all of which represent the same date. The format that was used to insert an event into the database may or may not be the same as the format used to look up up that date. Your program therefore needs a way to reason about dates in different formats. This problem involves writing a class to maintain information about dates and events and reason about dates in different formats. The idea is to read a file containing a series of operations, where each operation refers to a database of dates and events, and process each operation in turn nput Formats The input to the program is read from a file (see Expected Behavior below). Each line of the file is an operation, and is in one of the following two formats I Date:Event R Date The fields in an operation are as follow:s Date This specifies a date. It can be in any of the following three formats . yyyy-mm-dd, where yyyy is a 4-digit sequence giving the year, mm is a 1- or 2-digit sequence giving the month; and dd is a 1- or 2-digit sequence giving the date Example: 2017-02-31 * mm/dd/yyyy, where yyyy is a 4-digit sequence giving the year, mm is a 1- or 2-digit sequence giving the month; and dd is a 1- or 2-digit sequence giving the date Example: 02/31/2017. . MonthName dd yyyy, where MonthName is a three-letter sequence giving the name of a month (one of: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec); dd is a 1- or 2- digit sequence giving the date; and yyyy is a 4-digit sequence giving the year Example: Feb 31 2017 NOTE: To simplify programming, we will assume that all months have 31 days Event Problem Description Suppose you wanted to offer a website or app to manage a database of dates and events. Such a database might be used to look up dates in the past ("on this date in history...", as in the sites mentioned above); or they might be used as a calendar service to provide reminders for future events. In either case, you need a program that can record and look up strings (i.e., events) associated with dates One catch here is reasoning about dates. People use many different formats to write dates, e.g., "December 25, 2016" "2016-12-25", and "12/25/2016", all of which represent the same date. The format that was used to insert an event into the database may or may not be the same as the format used to look up up that date. Your program therefore needs a way to reason about dates in different formats. This problem involves writing a class to maintain information about dates and events and reason about dates in different formats. The idea is to read a file containing a series of operations, where each operation refers to a database of dates and events, and process each operation in turn nput Formats The input to the program is read from a file (see Expected Behavior below). Each line of the file is an operation, and is in one of the following two formats I Date:Event R Date The fields in an operation are as follow:s Date This specifies a date. It can be in any of the following three formats . yyyy-mm-dd, where yyyy is a 4-digit sequence giving the year, mm is a 1- or 2-digit sequence giving the month; and dd is a 1- or 2-digit sequence giving the date Example: 2017-02-31 * mm/dd/yyyy, where yyyy is a 4-digit sequence giving the year, mm is a 1- or 2-digit sequence giving the month; and dd is a 1- or 2-digit sequence giving the date Example: 02/31/2017. . MonthName dd yyyy, where MonthName is a three-letter sequence giving the name of a month (one of: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec); dd is a 1- or 2- digit sequence giving the date; and yyyy is a 4-digit sequence giving the year Example: Feb 31 2017 NOTE: To simplify programming, we will assume that all months have 31 days Event













