Question
PYTHON class LinkedList: def __init__(self): self.__head = None self.__tail = None self.__size = 0 # Return the head element in the list def getFirst(self): if
PYTHON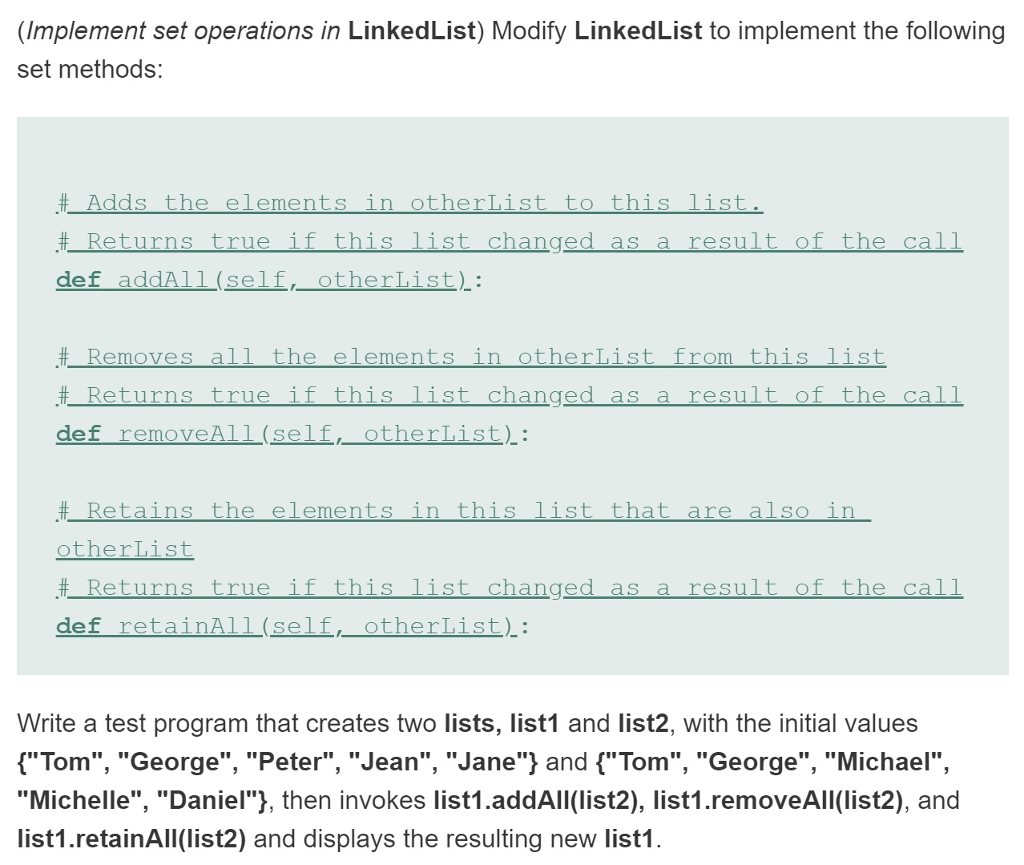
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.__head = None
self.__tail = None
self.__size = 0
# Return the head element in the list
def getFirst(self):
if self.__size == 0:
return None
else:
return self.__head.element
# Return the last element in the list
def getLast(self):
if self.__size == 0:
return None
else:
return self.__tail.element
# Add an element to the beginning of the list
def addFirst(self, e):
newNode = Node(e) # Create a new node
newNode.next = self.__head # link the new node with the head
self.__head = newNode # head points to the new node
self.__size += 1 # Increase list size
if self.__tail == None: # the new node is the only node in list
self.__tail = self.__head
# Add an element to the end of the list
def addLast(self, e):
newNode = Node(e) # Create a new node for e
if self.__tail == None:
self.__head = self.__tail = newNode # The only node in list
else:
self.__tail.next = newNode # Link the new with the last node
self.__tail = self.__tail.next # tail now points to the last node
self.__size += 1 # Increase size
# Same as addLast
def add(self, e):
self.addLast(e)
# Insert a new element at the specified index in this list
# The index of the head element is 0
def insert(self, index, e):
if index == 0:
self.addFirst(e) # Insert first
elif index >= self.__size:
self.addLast(e) # Insert last
else: # Insert in the middle
current = self.__head
for i in range(1, index):
current = current.next
temp = current.next
current.next = Node(e)
(current.next).next = temp
self.__size += 1
# Remove the head node and
# return the object that is contained in the removed node.
def removeFirst(self):
if self.__size == 0:
return None # Nothing to delete
else:
temp = self.__head # Keep the first node temporarily
self.__head = self.__head.next # Move head to point the next node
self.__size -= 1 # Reduce size by 1
if self.__head == None:
self.__tail = None # List becomes empty
return temp.element # Return the deleted element
# Remove the last node and
# return the object that is contained in the removed node
def removeLast(self):
if self.__size == 0:
return None # Nothing to remove
elif self.__size == 1: # Only one element in the list
temp = self.__head
self.__head = self.__tail = None # list becomes empty
self.__size = 0
return temp.element
else:
current = self.__head
for i in range(self.__size - 2):
current = current.next
temp = self.__tail
self.__tail = current
self.__tail.next = None
self.__size -= 1
return temp.element
# Remove the element at the specified position in this list.
# Return the element that was removed from the list.
def removeAt(self, index):
if index = self.__size:
return None # Out of range
elif index == 0:
return self.removeFirst() # Remove first
elif index == self.__size - 1:
return self.removeLast() # Remove last
else:
previous = self.__head
for i in range(1, index):
previous = previous.next
current = previous.next
previous.next = current.next
self.__size -= 1
return current.element
# Return true if the list is empty
def isEmpty(self):
return self.__size == 0
# Return the size of the list
def getSize(self):
return self.__size
def __str__(self):
result = "["
current = self.__head
for i in range(self.__size):
result += str(current.element)
current = current.next
if current != None:
result += ", " # Separate two elements with a comma
else:
result += "]" # Insert the closing ] in the string
return result
# Clear the list */
def clear(self):
self.__head = self.__tail = None
# Return true if this list contains the element o
def contains(self, e):
print("Implementation left as an exercise")
return True
# Remove the element and return true if the element is in the list
def remove(self, e):
print("Implementation left as an exercise")
return True
# Return the element from this list at the specified index
def get(self, index):
print("Implementation left as an exercise")
return None
# Return the index of the head matching element in this list.
# Return -1 if no match.
def indexOf(self, e):
print("Implementation left as an exercise")
return 0
# Return the index of the last matching element in this list
# Return -1 if no match.
def lastIndexOf(self, e):
print("Implementation left as an exercise")
return 0
# Replace the element at the specified position in this list
# with the specified element. */
def set(self, index, e):
print("Implementation left as an exercise")
return None
# Return elements via indexer
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.get(index)
# Return an iterator for a linked list
def __iter__(self):
return LinkedListIterator(self.__head)
# The Node class
class Node:
def __init__(self, element):
self.element = element
self.next = None
class LinkedListIterator:
def __init__(self, head):
self.current = head
def __next__(self):
if self.current == None:
raise StopIteration
else:
element = self.current.element
self.current = self.current.next
return element
(Implement set operations in LinkedList) Modify LinkedList to implement the following set methods: # Adds the elements in otherList to this 11st, # Returns true if this list changed as a I he call def addAll (self,,otherList): # Removes all the elements in otherList from this list Returns true if this list changed as a-resul t of the-ca11 def removeAlL (selfotherList)l: Retains the elements in this list that are also in otherList Returns true if this 11st changed as a result of the Call def retainA1L(self,_otherList): Write a test program that creates two lists, list1 and list2, with the initial values ("Tom", "George", "Pete", "Jean", "Jane"] and f" Tom", "George", "Michael", "Michelle", "Daniel"], then invokes list1.addAll(list2), list1.removeAll(list2), and list1.retainAll(list2) and displays the resulting new list1Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


