 *PYTHON COURSE* Can someone please help me answer this question for my class. I will 100% like you solving my answering. Thank you so much!!!!
*PYTHON COURSE* Can someone please help me answer this question for my class. I will 100% like you solving my answering. Thank you so much!!!!
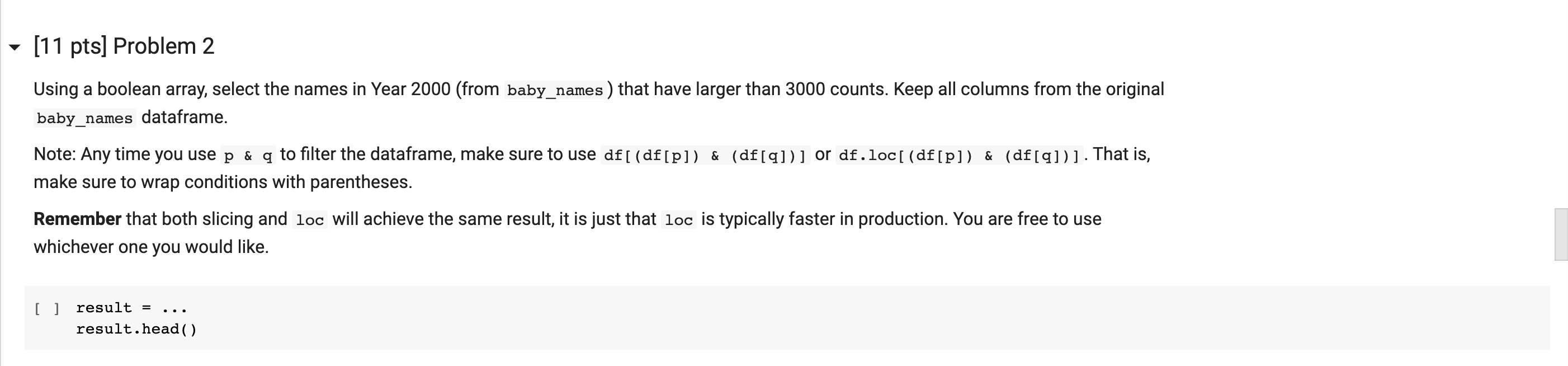
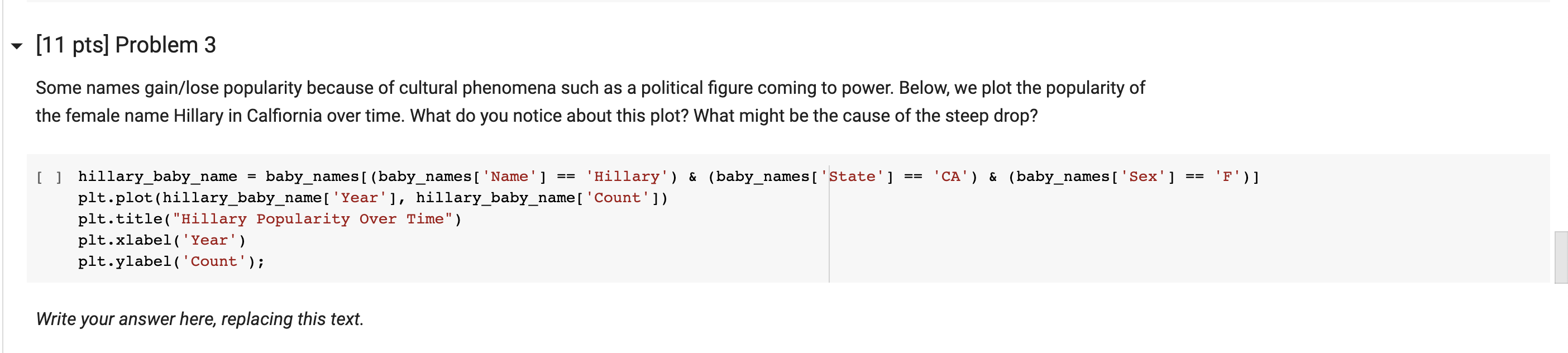
(11 pts] Problem 2 Using a boolean array, select the names in Year 2000 (from baby names ) that have larger than 3000 counts. Keep all columns from the original baby_names dataframe. Note: Any time you use p & q to filter the dataframe, make sure to use df[(df[p]) & (df[9])] or df.loc[ (df[p]) & (df[9])]. That is, make sure to wrap conditions with parentheses. Remember that both slicing and loc will achieve the same result, it is just that loc is typically faster in production. You are free to use whichever one you would like. [] result = result.head() (11 pts] Problem 3 Some names gain/lose popularity because of cultural phenomena such as a political figure coming to power. Below, we plot the popularity of the female name Hillary in Calfiornia over time. What do you notice about this plot? What might be the cause of the steep drop? == == 'CA') & (baby_names [ 'Sex'] == 'F')] [ ] hillary_baby_name = baby names [ (baby_names [ 'Name'] 'Hillary') & (baby_names [ 'State'] plt.plot(hillary_baby_name[ 'Year'], hillary_baby_name[ 'Count']) plt.title("Hillary Popularity Over Time") plt.xlabel('Year') plt.ylabel('Count'); Write your answer here, replacing this text. (11 pts] Problem 2 Using a boolean array, select the names in Year 2000 (from baby names ) that have larger than 3000 counts. Keep all columns from the original baby_names dataframe. Note: Any time you use p & q to filter the dataframe, make sure to use df[(df[p]) & (df[9])] or df.loc[ (df[p]) & (df[9])]. That is, make sure to wrap conditions with parentheses. Remember that both slicing and loc will achieve the same result, it is just that loc is typically faster in production. You are free to use whichever one you would like. [] result = result.head() (11 pts] Problem 3 Some names gain/lose popularity because of cultural phenomena such as a political figure coming to power. Below, we plot the popularity of the female name Hillary in Calfiornia over time. What do you notice about this plot? What might be the cause of the steep drop? == == 'CA') & (baby_names [ 'Sex'] == 'F')] [ ] hillary_baby_name = baby names [ (baby_names [ 'Name'] 'Hillary') & (baby_names [ 'State'] plt.plot(hillary_baby_name[ 'Year'], hillary_baby_name[ 'Count']) plt.title("Hillary Popularity Over Time") plt.xlabel('Year') plt.ylabel('Count'); Write your answer here, replacing this text

 *PYTHON COURSE* Can someone please help me answer this question for my class. I will 100% like you solving my answering. Thank you so much!!!!
*PYTHON COURSE* Can someone please help me answer this question for my class. I will 100% like you solving my answering. Thank you so much!!!!





