Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Python Only Write a function dimensionflip( ) that takes a list of observations in meters and outputs a list with the corresponding observations in centimeters.
Python Only
Write a function dimensionflip( ) that takes a list of observations in meters and outputs a list with the corresponding observations in centimeters. Your function should only convert dimensions of positive entries; therefore, a negative dimension in meters must not be changed. For example:
Input1: [1,4,5] Output1: [100,400,500]
Input2: [5,9,-8,6] Output2: [500,900,-8,600]
The values within the input list should not be changed following a call to this function.
# - I can't use append()

-------------------------------
Here is template
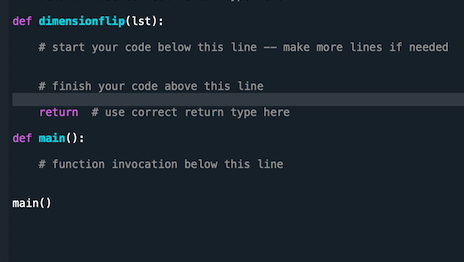
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


