Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
python please. no binary tree class was provided IMPORTANT: For this exercise, you will be defining a function which USES the BinarySearchTree ADT. A BinarySearchTree
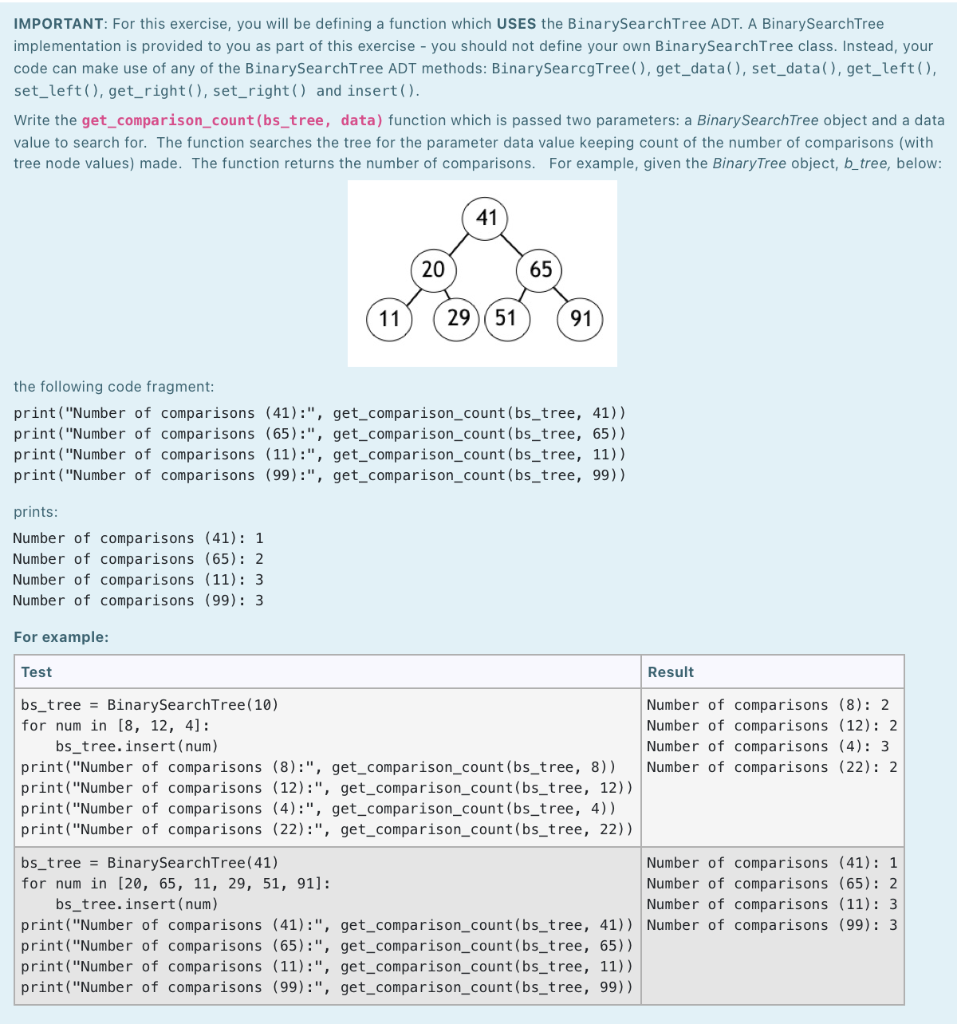 python please. no binary tree class was provided
python please. no binary tree class was provided
IMPORTANT: For this exercise, you will be defining a function which USES the BinarySearchTree ADT. A BinarySearchTree implementation is provided to you as part of this exercise - you should not define your own BinarySearchTree class. Instead, your code can make use of any of the BinarySearchTree ADT methods: BinarySearcgTree(), get_data(), set_data(), get_left(), set_left(), get_right(), set_right() and insert(). Write the get_comparison_count(bs_tree, data) function which is passed two parameters: a Binary Search Tree object and a data value to search for. The function searches the tree for the parameter data value keeping count of the number of comparisons (with tree node values) made. The function returns the number of comparisons. For example, given the Binary Tree object, b_tree, below: 41 20 65 11 29 (51 91 the following code fragment: print("Number of comparisons (41):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 41)) print("Number of comparisons (65):", get_comparison_count (bs_tree, 65)) print("Number of comparisons (11):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 11)) print("Number of comparisons (99):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 99)) prints: Number of comparisons (41): 1 Number of comparisons (65): 2 Number of comparisons (11): 3 Number of comparisons (99): 3 For example: Test Result bs_tree = BinarySearchTree (10) Number of comparisons (8): 2 for num in [8, 12, 4]: Number of comparisons (12): 2 bs_tree.insert (num) Number of comparisons (4): 3 print("Number of comparisons (8):", get_comparison_count (bs_tree, 8)) Number of comparisons (22): 2 print("Number of comparisons (12):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 12)) print("Number of comparisons (4):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 4)) print("Number of comparisons (22):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 22)) bs_tree = BinarySearchTree(41) Number of comparisons (41): 1 for num in [20, 65, 11, 29, 51, 91]: Number of comparisons (65): 2 bs_tree.insert(num) Number of comparisons (11): 3 print("Number of comparisons (41):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 41)) Number of comparisons (99): 3 print("Number of comparisons (65):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 65)) print("Number of comparisons (11):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 11)) print("Number of comparisons (99):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 99)) IMPORTANT: For this exercise, you will be defining a function which USES the BinarySearchTree ADT. A BinarySearchTree implementation is provided to you as part of this exercise - you should not define your own BinarySearchTree class. Instead, your code can make use of any of the BinarySearchTree ADT methods: BinarySearcgTree(), get_data(), set_data(), get_left(), set_left(), get_right(), set_right() and insert(). Write the get_comparison_count(bs_tree, data) function which is passed two parameters: a Binary Search Tree object and a data value to search for. The function searches the tree for the parameter data value keeping count of the number of comparisons (with tree node values) made. The function returns the number of comparisons. For example, given the Binary Tree object, b_tree, below: 41 20 65 11 29 (51 91 the following code fragment: print("Number of comparisons (41):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 41)) print("Number of comparisons (65):", get_comparison_count (bs_tree, 65)) print("Number of comparisons (11):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 11)) print("Number of comparisons (99):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 99)) prints: Number of comparisons (41): 1 Number of comparisons (65): 2 Number of comparisons (11): 3 Number of comparisons (99): 3 For example: Test Result bs_tree = BinarySearchTree (10) Number of comparisons (8): 2 for num in [8, 12, 4]: Number of comparisons (12): 2 bs_tree.insert (num) Number of comparisons (4): 3 print("Number of comparisons (8):", get_comparison_count (bs_tree, 8)) Number of comparisons (22): 2 print("Number of comparisons (12):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 12)) print("Number of comparisons (4):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 4)) print("Number of comparisons (22):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 22)) bs_tree = BinarySearchTree(41) Number of comparisons (41): 1 for num in [20, 65, 11, 29, 51, 91]: Number of comparisons (65): 2 bs_tree.insert(num) Number of comparisons (11): 3 print("Number of comparisons (41):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 41)) Number of comparisons (99): 3 print("Number of comparisons (65):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 65)) print("Number of comparisons (11):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 11)) print("Number of comparisons (99):", get_comparison_count(bs_tree, 99))
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


