
 python please
python please
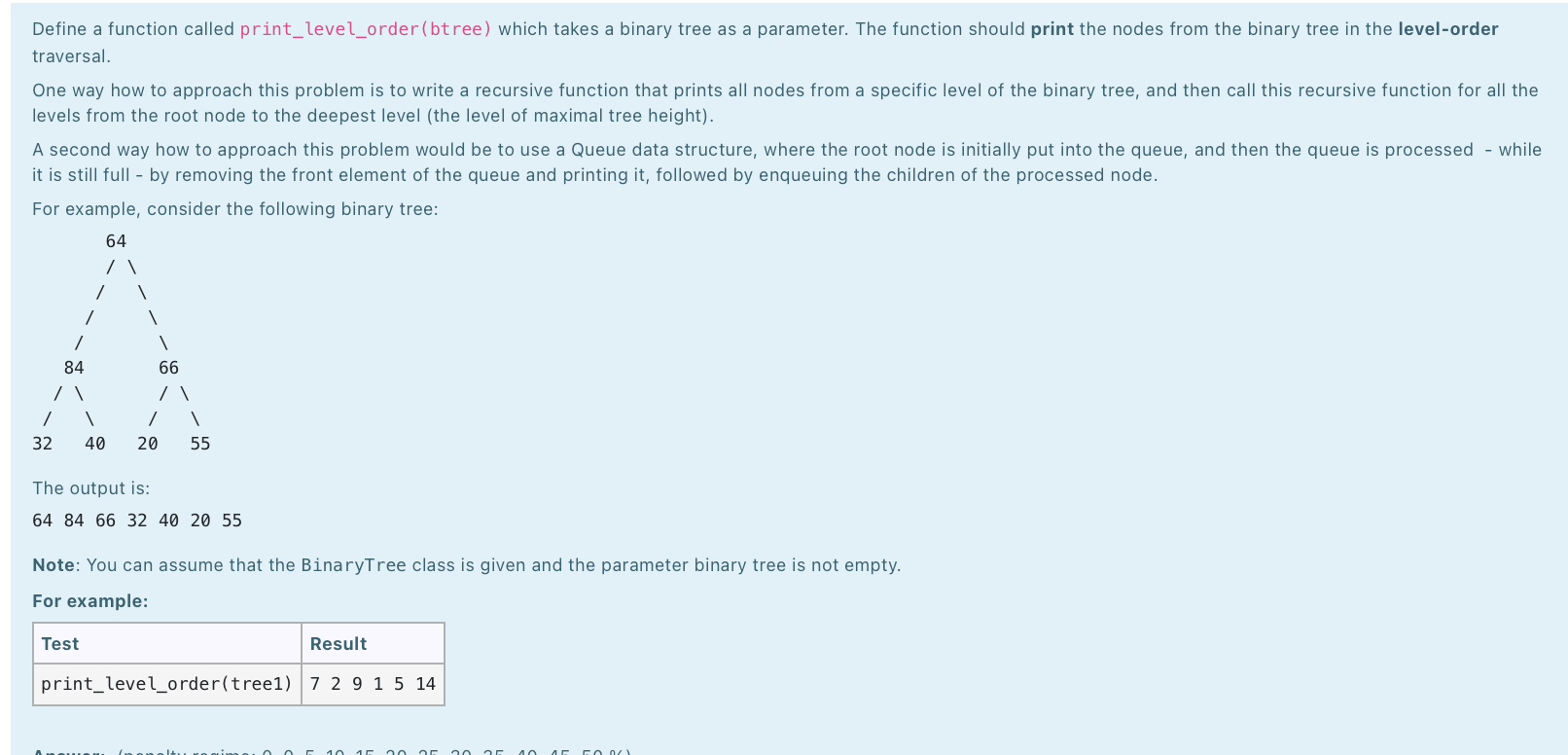
The purpose of this laboratory is for you to demonstrate your understanding of Binary Trees. The BinaryTree class definition is given as follows: class BinaryTree: def __init__(self, data, left=None, right=None): self.__data = data self._left = left self.__right = right def insert_left(self, new_data): if self._left == None: self._left = BinaryTree (new_data) else: tree = BinaryTree (new_data, left=self. __left) self._left = tree def insert_right (self, new_data): if self._right == None: self._right = BinaryTree(new_data) else: tree = BinaryTree (new_data, right=self.__right) self.__right = tree def get_left(self): return self._left def get_right (self): return self._right def set_data(self, data): self. __data = data def get_data(self): return self.__data def set_left(self, left): self._left = left def set_right(self, right): self._right = right IMPORTANT: For these exercises, you will be defining a function which USES the BinaryTree ADT. A BinaryTree implementation is provided to you as part of this exercise - you should not define your own BinaryTree class. Instead, your code can make use of any of the BinaryTree ADT methods: BinaryTree(), get_data(), set_data(), get_left(), set_left(), get_right(), set_right(), insert_left() and insert_right(). Define a function called print_level_order(btree) which takes a binary tree as a parameter. The function should print the nodes from the binary tree in the level-order traversal. One way how to approach this problem is to write a recursive function that prints all nodes from a specific level of the binary tree, and then call this recursive function for all the levels from the root node to the deepest level (the level of maximal tree height). A second way how to approach this problem would be to use a Queue data structure, where the root node is initially put into the queue, and then the queue is processed - while it is still full - by removing the front element of the queue and printing it, followed by enqueuing the children of the processed node. For example, consider the following binary tree: 64 / / / 66 84 / / 32 40 / / 20 55 The output is: 64 84 66 32 40 20 55 Note: You can assume that the BinaryTree class is given and the parameter binary tree is not empty. For example: Test Result print_level_order(tree1) 7 2 9 1 5 14 F

 python please
python please





