Question
Q1: choose the right answer for the following: (10 Marks) 1- The systems which allow only one process execution at a time, are called __________
Q1: choose the right answer for the following: (10 Marks) 1- The systems which allow only one process execution at a time, are called __________ a) uniprogramming systems b) uniprocessing systems c) unitasking systems d) none of the mentioned 2- In operating system, each process has its own __________ a) address space and global variables b) open files c) pending alarms, signals and signal handlers d) all of the mentioned 3- What is interprocess communication? a) Communication within the process b) communication between two process c) communication between two threads of same process d) none of the mentioned 4- In polling ____________ a) busy wait cycles wait for I/O from device b) interrupt handler receives interrupts c) interrupt-request line is triggered by I/O device d) all of the mentioned 5- The address of the next instruction to be executed for the current process is stored in a) cpu registers b) program counter c) process state d) process number 6- Once the process is allocated the cpu and is executing , which of several events could occur: 1- the process could issue an I/O request and then be placed in an I/O queue. 2- the process could create a new child process and wait for the Childs termination. 3- the process could forcibly from the cpu , as a result of an interrupt, and be put back in the ready queue. a) only 1. b) 1 and 2 c) 1,2,3 d) 2 and 3 7- What are the requirements for the solution to critical section problems? a) Mutual exclusion b) progress c) bounded waiting d) all of them 8- When a thread waits indefinitely for some resource, but other threads are actually using Information for Students: Examination paper with 4 questions in 3. pages, totaling 42Marks. Answer Three questions only, Q1 must be answered. 2 its called : a) starvation b)demand paging c)segmentation d) all of them 9- What is the full name of FAT? a) File attribute table b) File allocation table c) Font attribute table d) Format allocation table 10- Who provides the interface to access the services of the operating system? a) API b) System call c) Library d) Assembly instruction
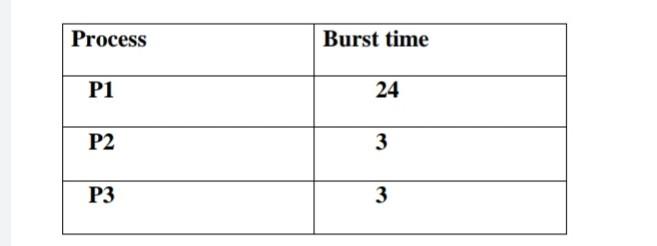
Q2 : A- BY using round robin (RR) scheduling algorithm , draw gantt chart and calculate the average waiting time for the following (quantum = 4) Process Burst time
B- Compare and contrast IPC using signals and message passing.
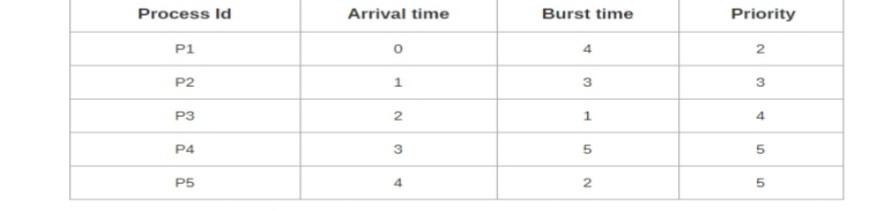
Q3 :A- If the CPU scheduling policy is priority preemptive, draw gantt chart and calculate the average waiting time. (Higher number represents higher priority)
B- Explain why the following statement is false:When several threads access shared information in main memory, mutual exclusion must be enforced to prevent the production of indeterminate results.
C- Explain how the disabling and enabling of interrupts is useful in implementing mutual exclusion primitives on uniprocessor systems.
Q4: Accurately, Answer all the below questions (10 Marks) 1- Why is the term firmware appropriate for describing microcode that is part of a hardware device? 2- In a block/wakeup mechanism, a process blocks itself to wait for an event to occur. Another process must detect that the event has occurred, and wake up the blocked process. 3 a- Can the operating system detect that a blocked process is waiting for an event that will never occur?
b- What reasonable safeguards might be built into an operating system to prevent processes from waiting indefinitely for an event? 3- Compare and contrast thread dispatching in kernel-level threads and in user-level threads. 4- Suppose the two threads in the following figure operate concurrently. What are the possible outcomes?

\begin{tabular}{|c|c|} \hline Process & Burst time \\ \hline P1 & 24 \\ \hline P2 & 3 \\ \hline P3 & 3 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|} \hline Process Id & Arrival time & Burst time & Priority \\ \hline P1 & 0 & 4 & 2 \\ \hline P2 & 1 & 3 & 3 \\ \hline P3 & 2 & 1 & 4 \\ \hline P4 & 3 & 5 & 5 \\ \hline P5 & 4 & 2 & 5 \\ \hline \end{tabular} Thread T, Thread Tz 1234567enterMutua1Exclusion(a);enterMutua1Exclusion(b);exitMutua1Exclusion(b);exitMutua1Exclusion(a);1234567enterMutua1Exclusion(b);enterMutua1Exclusion(a);exitMutua1Exclusion(a);exitMutua1Exclusion(b)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


