Q1/ On page 20 of the report, East Asia was identified as the region with the highest EPIC score. Try to compare and contrast the the following three countries, China, Japan and South Korea.
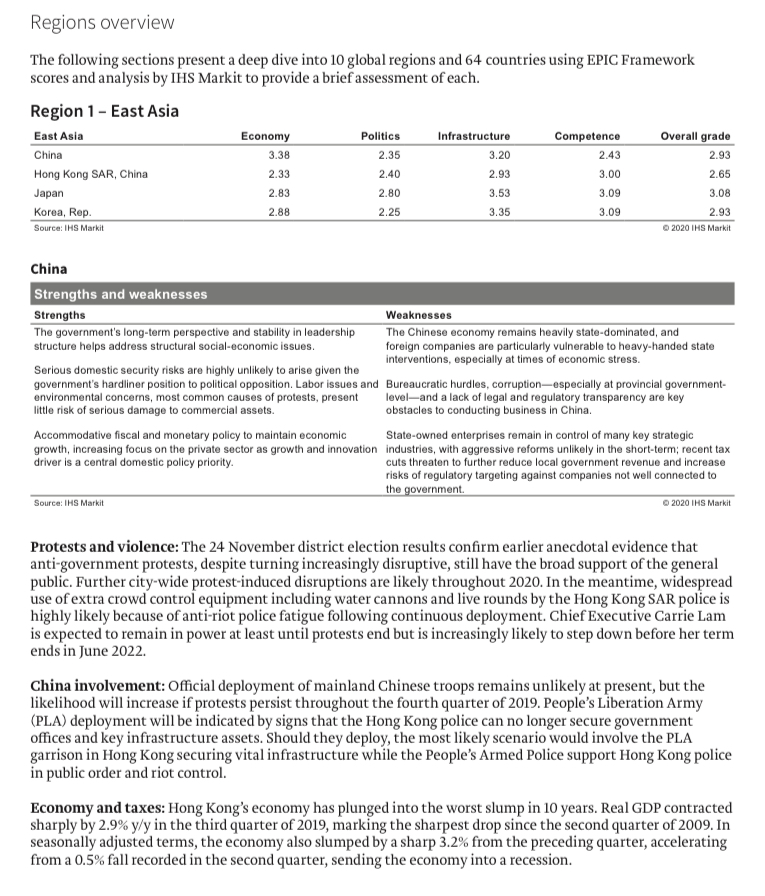
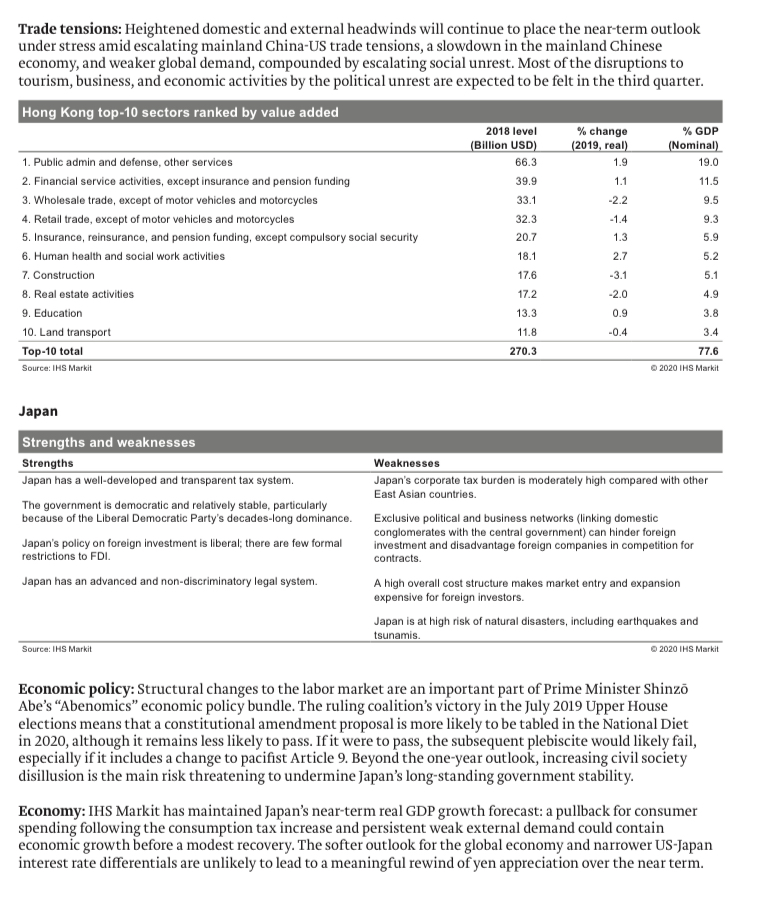
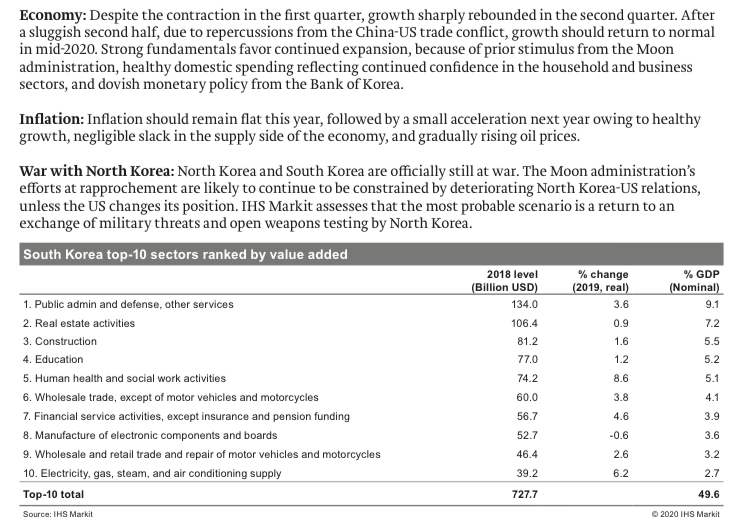
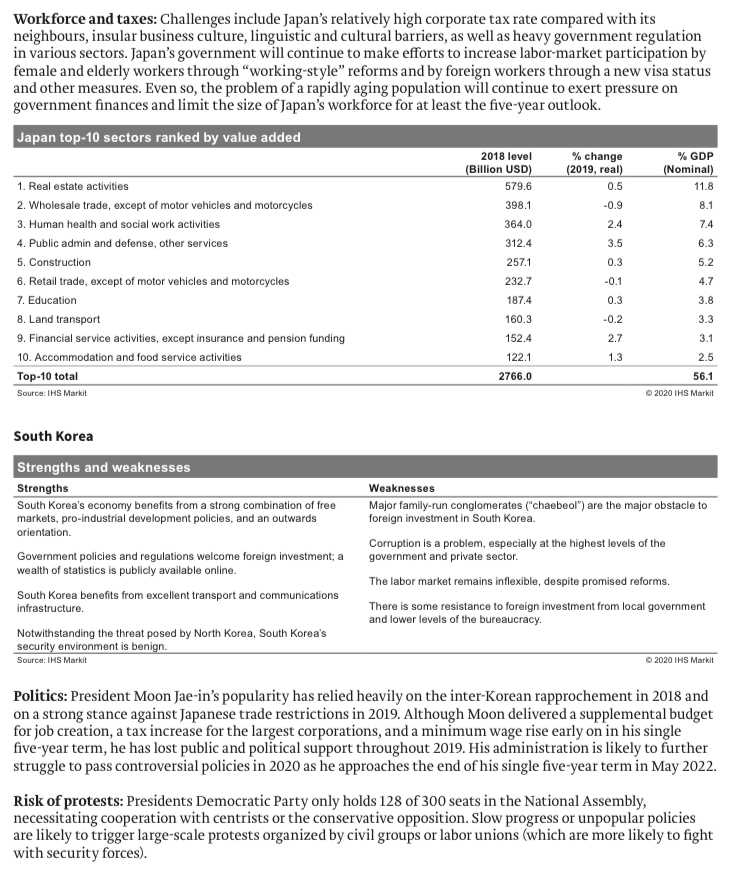
Regions overview The following sections present a deep dive into 10 global regions and 64 countries using EPIC Framework scores and analysis by IHS Markit to provide a brief assessment of each. Region 1 - East Asia East Asia Economy Politics Infrastructure Competence Overall grade China 3.38 2.35 3.20 2.43 2.93 Hong Kong SAR, China 2.33 2.40 2.93 3.00 2.65 Japan 2.83 2.80 3.53 3.09 3.08 Korea, Rep. 2.88 2.25 3.35 3.09 2.93 Source: IHS Markit 2020 IHS Markit China Strengths and weaknesses Strengths Weaknesses The government's long-term perspective and stability in leadership The Chinese economy remains heavily state-dominated, and structure helps address structural social-economic issues. foreign companies are particularly vulnerable to heavy-handed state interventions, especially at times of economic stress. Serious domestic security risks are highly unlikely to arise given the government's hardliner position to political opposition. Labor issues and Bureaucratic hurdles, corruption-especially at provincial government- environmental concerns, most common causes of protests, present level-and a lack of legal and regulatory transparency are key little risk of serious damage to commercial assets. obstacles to conducting business in China. Accommodation fiscal and monetary policy to maintain economic State-owned enterprises remain in control of many key strategic growth, increasing focus on the private sector as growth and innovation industries, with aggressive reforms unlikely in the short-term; recent tax driver is a central domestic policy priority. cuts threaten to further reduce local government revenue and increase risks of regulatory targeting against companies not well connected to the government. Source: IHS Markit 2020 IHS Markit Protests and violence: The 24 November district election results confirm earlier anecdotal evidence that anti-government protests, despite turning increasingly disruptive, still have the broad support of the general public. Further city-wide protest-induced disruptions are likely throughout 2020. In the meantime, widespread use of extra crowd control equipment including water cannons and live rounds by the Hong Kong SAR police is highly likely because of anti-riot police fatigue following continuous deployment. Chief Executive Carrie Lam is expected to remain in power at least until protests end but is increasingly likely to step down before her term ends in June 2022. China involvement: Official deployment of mainland Chinese troops remains unlikely at present, but the likelihood will increase if protests persist throughout the fourth quarter of 2019. People's Liberation Army (PLA) deployment will be indicated by signs that the Hong Kong police can no longer secure government offices and key infrastructure assets. Should they deploy, the most likely scenario would involve the PLA garrison in Hong Kong securing vital infrastructure while the People's Armed Police support Hong Kong police in public order and riot control. Economy and taxes: Hong Kong's economy has plunged into the worst slump in 10 years. Real GDP contracted sharply by 2.9% y/y in the third quarter of 2019, marking the sharpest drop since the second quarter of 2009. In seasonally adjusted terms, the economy also slumped by a sharp 3.2% from the preceding quarter, accelerating from a 0.5% fall recorded in the second quarter, sending the economy into a recession.Trade tensions: Heightened domestic and external headwinds will continue to place the near-term outlook under stress amid escalating mainland China-US trade tensions, a slowdown in the mainland Chinese economy, and weaker global demand, compounded by escalating social unrest. Most of the disruptions to tourism, business, and economic activities by the political unrest are expected to be felt in the third quarter. Hong Kong top-10 sectors ranked by value added 2018 level change % GDP (Billion USD) (2019, real) (Nominal) 1. Public admin and defense, other services 66.3 1.9 19.0 2. Financial service activities, except insurance and pension funding 39.9 1.1 11.5 3. Wholesale trade, except of motor vehicles and motorcycles 33.1 -2.2 9.5 4. Retail trade, except of motor vehicles and motorcycles 32.3 -1.4 9.3 5. Insurance, reinsurance, and pension funding, except compulsory social security 20.7 1.3 5.9 6. Human health and social work activities 18.1 2.7 5.2 7. Construction 17.6 -3.1 5.1 B. Real estate activities 17.2 -2.0 4.9 9. Education 13.3 0.9 3.8 10. Land transport 11.8 -0.4 3.4 Top-10 total 270.3 77.6 Source: IHS Markit Q 2020 THS Markit Japan Strengths and weaknesses Strengths Weaknesses Japan has a well-developed and transparent tax system. Japan's corporate tax burden is moderately high compared with other East Asian countries. The government is democratic and relatively stable, particularly because of the Liberal Democratic Party's decades-long dominance. Exclusive political and business networks (linking domestic conglomerates with the central government) can hinder foreign Japan's policy on foreign investment is liberal; there are few formal investment and disadvantage foreign companies in competition for restrictions to FDI. contracts Japan has an advanced and non-discriminatory legal system. A high overall cost structure makes market entry and expansion expensive for foreign investors. Japan is at high risk of natural disasters, including earthquakes and tsunamis. Source: IHS Markit 2020 IHS Markit Economic policy: Structural changes to the labor market are an important part of Prime Minister Shinzo Abe's "Abenomics" economic policy bundle. The ruling coalition's victory in the July 2019 Upper House elections means that a constitutional amendment proposal is more likely to be tabled in the National Diet in 2020, although it remains less likely to pass. If it were to pass, the subsequent plebiscite would likely fail, especially if it includes a change to pacifist Article 9. Beyond the one-year outlook, increasing civil society disillusion is the main risk threatening to undermine Japan's long-standing government stability. Economy: IHS Markit has maintained Japan's near-term real GDP growth forecast: a pullback for consumer spending following the consumption tax increase and persistent weak external demand could contain economic growth before a modest recovery. The softer outlook for the global economy and narrower US-Japan interest rate differentials are unlikely to lead to a meaningful rewind of yen appreciation over the near term.Economy: Despite the contraction in the first quarter, growth sharply rebounded in the second quarter. After a sluggish second half, due to repercussions from the China-US trade conflict, growth should return to normal in mid-2020. Strong fundamentals favor continued expansion, because of prior stimulus from the Moon administration, healthy domestic spending reflecting continued confidence in the household and business sectors, and dovish monetary policy from the Bank of Korea. Inflation: Inflation should remain flat this year, followed by a small acceleration next year owing to healthy growth, negligible slack in the supply side of the economy, and gradually rising oil prices. War with North Korea: North Korea and South Korea are officially still at war. The Moon administration's efforts at rapprochement are likely to continue to be constrained by deteriorating North Korea-US relations, unless the US changes its position. IHS Markit assesses that the most probable scenario is a return to an exchange of military threats and open weapons testing by North Korea. South Korea top-10 sectors ranked by value added 2018 level change % GDP (Billion USD) (2019, real) (Nominal) 1. Public admin and defense, other services 134.0 3.6 9.1 2. Real estate activities 106.4 0.9 7.2 3. Construction 81.2 1.6 5.5 4. Education 77.0 1.2 5.2 5. Human health and social work activities 74.2 8.6 5.1 6. Wholesale trade, except of motor vehicles and motorcycles 60.0 3.8 4.1 7. Financial service activities, except insurance and pension funding 56.7 4.6 3.9 8. Manufacture of electronic components and boards 52.7 -0.6 3.6 9. Wholesale and retail trade and repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles 46.4 2.6 3.2 10. Electricity, gas, steam, and air conditioning supply 39.2 6.2 2.7 Top-10 total 727.7 49.6 Source: IHS Markit 3 2020 IHS MarkitWorkforce and taxes: Challenges include Japan's relatively high corporate tax rate compared with its neighbours, insular business culture, linguistic and cultural barriers, as well as heavy government regulation in various sectors. Japan's government will continue to make efforts to increase labor-market participation by female and elderly workers through "working-style" reforms and by foreign workers through a new visa status and other measures. Even so, the problem of a rapidly aging population will continue to exert pressure on government finances and limit the size of Japan's workforce for at least the five-year outlook. Japan top-10 sectors ranked by value added 2018 level change % GDP (Billion USD) (2019, real) (Nominal) 1. Real estate activities 579.6 0.5 11.8 2. Wholesale trade, except of motor vehicles and motorcycles 398.1 -0.9 8.1 3. Human health and social work activities 364.0 2.4 7.4 4. Public admin and defense, other services 312.4 3.5 6.3 5. Construction 257.1 0.3 5.2 6. Retail trade, except of motor vehicles and motorcycles 232.7 -0.1 4.7 7. Education 187.4 0.3 3.8 8. Land transport 160.3 0.2 3.3 9. Financial service activities, except insurance and pension funding 152.4 2.7 3.1 10. Accommodation and food service activities 122.1 13 2.5 Top-10 total 2766.0 56.1 Source: IHS Markit 2020 IHS Markit South Korea Strengths and weaknesses Strengths Weaknesses South Korea's economy benefits from a strong combination of free Major family-run conglomerates ("chaebeol") are the major obstacle to markets, pro-industrial development policies, and an outwards foreign investment in South Korea orientation. Corruption is a problem, especially at the highest levels of the Government policies and regulations welcome foreign investment; a government and private sector. wealth of statistics is publicly available online. The labor market remains inflexible, despite promised reforms. South Korea benefits from excellent transport and communications infrastructure. There is some resistance to foreign investment from local government and lower levels of the bureaucracy. Notwithstanding the threat posed by North Korea, South Korea's security environment is benign. Source: IHS Markit 2020 IHS Markit Politics: President Moon Jae-in's popularity has relied heavily on the inter-Korean rapprochement in 2018 and on a strong stance against Japanese trade restrictions in 2019. Although Moon delivered a supplemental budget for job creation, a tax increase for the largest corporations, and a minimum wage rise early on in his single five-year term, he has lost public and political support throughout 2019. His administration is likely to further struggle to pass controversial policies in 2020 as he approaches the end of his single five-year term in May 2022. Risk of protests: Presidents Democratic Party only holds 128 of 300 seats in the National Assembly, necessitating cooperation with centrists or the conservative opposition. Slow progress or unpopular policies are likely to trigger large-scale protests organized by civil groups or labor unions (which are more likely to fight with security forces)