Question
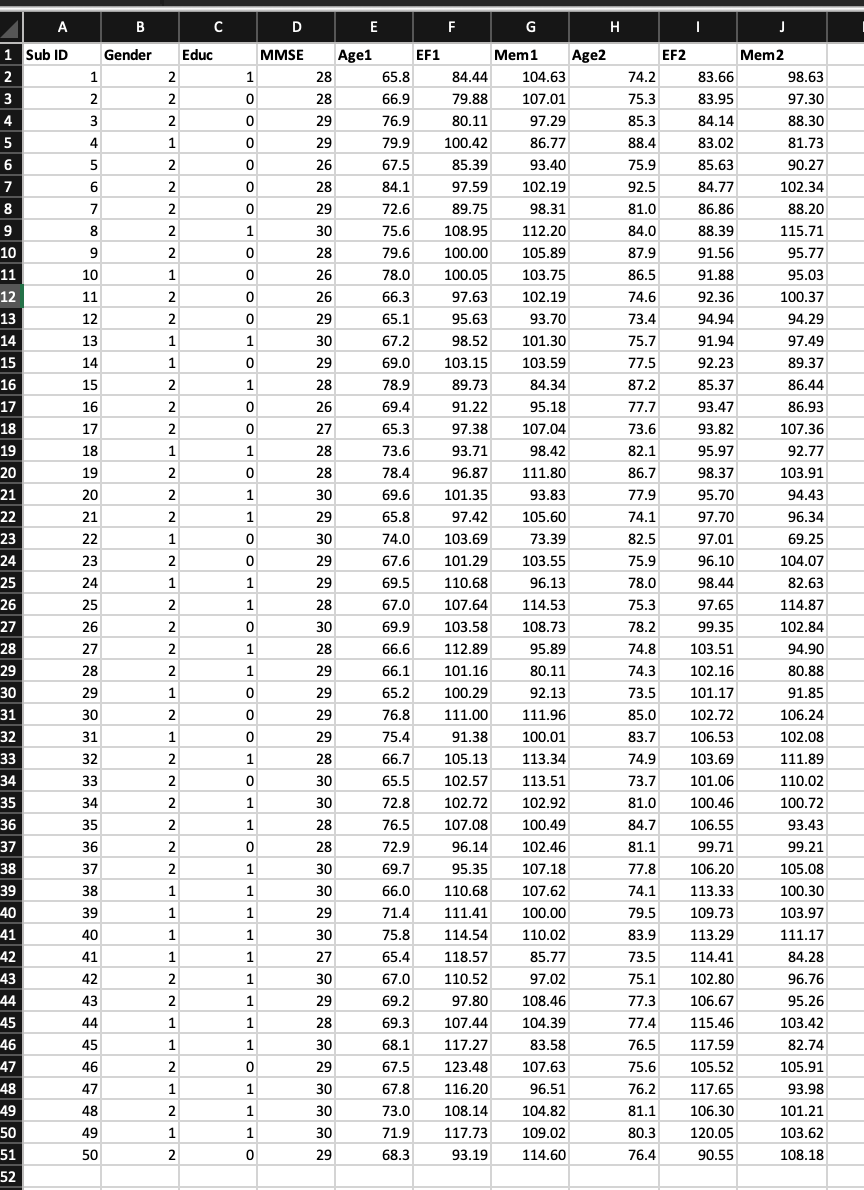
Q1. Perform and Interpret a t Test with SPSS (11 points total) The researchers want to examine the participant demographic information collected from the first
Q1. Perform and Interpret a t Test with SPSS (11 points total)
The researchers want to examine the participant demographic information collected from the first testing session. Run a two-tailed t test with ? = .05 to answer the following question:
Are the females and males significantly different in age at the first testing session ("Age1")?
A. What type of t test should be performed to answer this question? What is your rationale?
(2 points total: 1 for each question)
B. Create alternative hypothesis and null hypothesis from the research question. Type the hypotheses out both in words and in symbol notations.
Hint: The hypotheses should be non-directional for the two-tailed test.
(2 points total: 1 for each hypothesis. If symbol notation or written format is missing or incorrect for a hypothesis, deduct .5)
C. Run the analysis in SPSS and answer the following questions based on the analysis results.
1. Paste all the output tables from SPSS for this test. No point will be earned for the rest of the questions in Q1 if the output tables are not pasted or are incomplete.
2. Use the SPSS output to calculate effect size, Cohen's d. Must show the calculation process.
(2 points: deduct 1 if the process is correct but the calculation has errors.)
3. Report the t test result in symbols according to the APA standards, including t statistic with degree of freedom, p value, and effect size d.
-Present all the items in one single line, separated by commas, with the symbols italicized.
-Report "p
(2 points: deduct .5 for each error in value or format up to 3 total)
4. What is your decision about the null hypothesis (reject or fail to reject)? What is your rationale? (2 points total: 1 for each answer)
5. What is the answer to the research question? (1 point)
Q2. Perform and Interpret a t Test with SPSS (11 points total)
The researcher would like to know if memory function changes significantly from the first testing session (Mem1) to the second testing session (Mem2). Perform a two-tailed t test with ? = .05 to answer the following question:
Is memory in the second testing session significantly different from memory in the first testing session?
A. What type of t test should be performed to answer this question? What is your rationale?
(2 points total: 1 for each question)
B. Create (alternative hypothesis and null hypothesis) from the research question. Type the hypotheses out both in words and in symbol notations.
Hint: The hypotheses should be non-directional for the two-tailed test.
(2 points total: 1 for each hypothesis. If symbol notation or written format is missing or incorrect for a hypothesis, deduct .5)
C. Run the analysis in SPSS and answer the following questions based on the analysis results.
1. Paste all the output tables from SPSS for this test. No point will be earned for the rest of the questions in Q2 if the output tables are not pasted or are incomplete.
2. Use the SPSS output to calculate effect size, Cohen's d. Must show the calculation process.
(2 points: deduct 1 if the process is correct but the calculation has errors.)
3. Report the t test result in symbols according to the APA standards, including t statistic with degree of freedom, p value, and effect size d.
-Present all the items in one single line, separated by commas, with the symbols italicized.
-Report "p
(2 points: deduct .5 for each error in value or format up to 3 total)
4. What is your decision about the null hypothesis (reject or fail to reject)? What is your rationale? (2 points total: 1 for each answer)
5. What is the answer to the research question? What was the direction of change in memory function from the first session to the second session? (1 point: .5 for each question)
Q3. Select, perform, and interpret a t test with SPSS (11 points total)
The researcher would like to examine the potential relationship between education and executive function assessed during the first testing session (EF1). In this data set, education is indicated by either having no college degree or having a college degree or above. Perform a two-tailed t test with ? = .05 to answer the following question:
Is there a significant difference in executive function between people without a college degree and those with a college degree or above?
A. What type of t test should be performed to answer this question? What is your rationale?
(2 points total: 1 for each question)
B. Create (alternative hypothesis and null hypothesis) from the research question. Type the hypotheses out both in words and in symbol notations.
Hint: The hypotheses should be non-directional for the two-tailed test.
(2 points total: 1 for each hypothesis. If symbol notation or written format is missing or incorrect for a hypothesis, deduct .5)
C. Run the analysis in SPSS and answer the following questions based on the analysis results.
1. Paste all the output tables from SPSS for this test. No point will be earned for the rest of the questions in Q3 if the output tables are not pasted or are incomplete.
2. Use the SPSS output to calculate effect size, Cohen's d. Must show the calculation process.
(2 points: deduct 1 if the process is correct but the calculation has errors.)
3. Report the t test result in symbols according to the APA standards, including t statistic with degree of freedom, p value, and effect size d.
-Present all the items in one single line, separated by commas, with the symbols italicized.
-Report "p
(2 points: deduct .5 for each error in value or format up to 3 total)
4. What is your decision about the null hypothesis (reject or fail to reject)? What is your rationale? (2 points total: 1 for each answer)
5. What is the answer to the research question? What was the direction of the difference between these two groups? (1 point: .5 for each question)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


