Q1:9

Required A1
Required A2
Required B1
Required B2
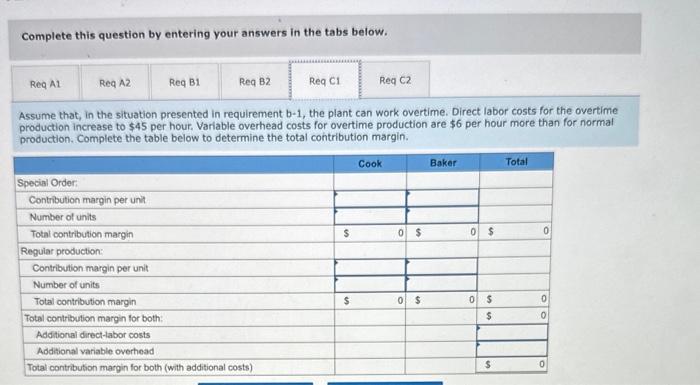
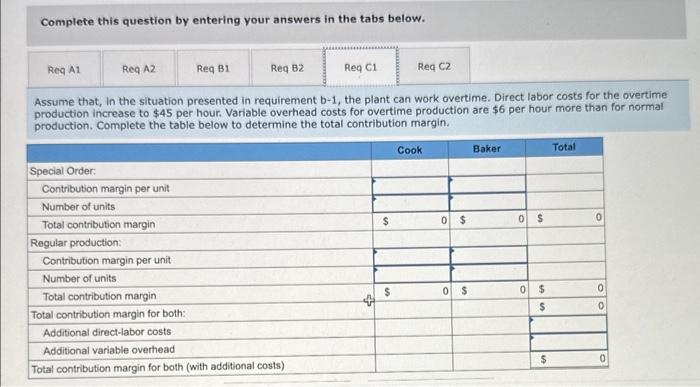
Required C1
Required C2
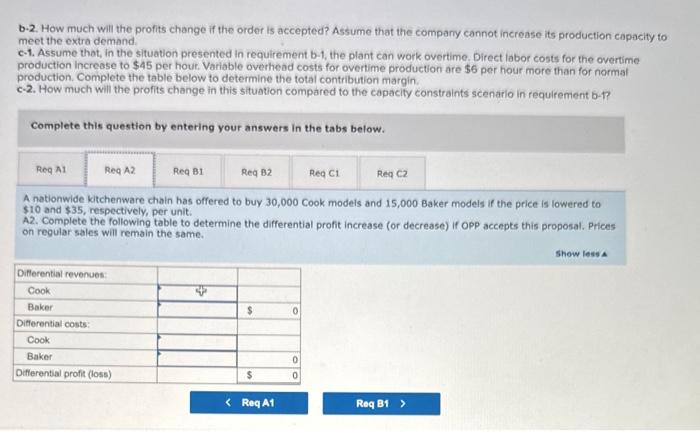
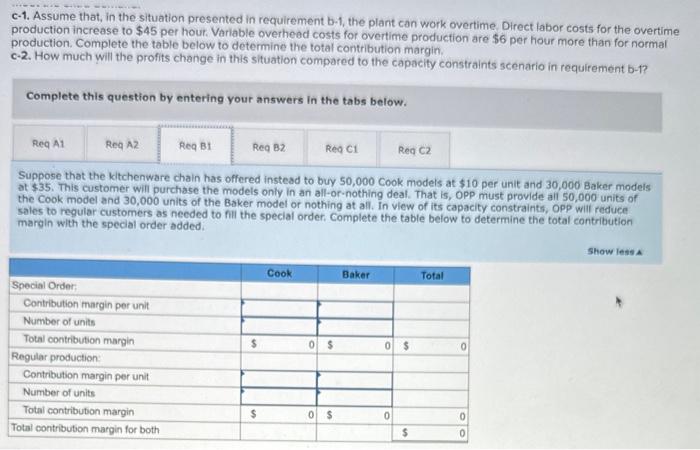
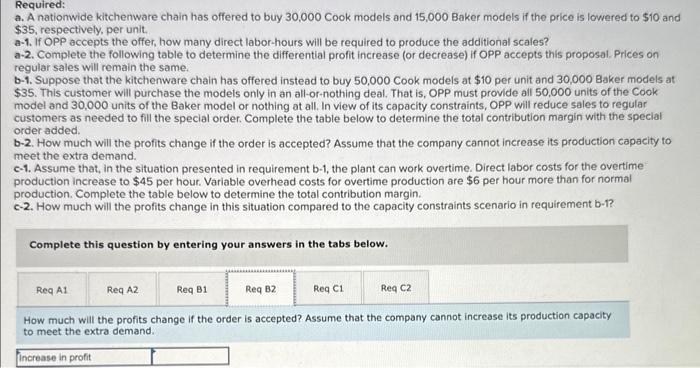
Oakland Precision Products (OPP) manufactures and sells a variety of scales for the kitchen and office. OPP sells primarily to kitchenware stores, discount stores, and so on. Two of the scales it produces for kitchen use are the Cook and Baker. The Cook is a basic food scale. The Baker has a greater capacity and special features that facilitate adjusting baking recipes for more or fewer people. The following information is available: The average wage rate is $32 per hour. Variable overhead varies with the quantity of direct labor-hours. The plant has a capacity of 20,000 direct labor-hours, but current production uses only 17,750 direct labor-hours. Required: a. A nationwide kitchenware chain has offered to buy 30,000 Cook models and 15,000 Baker models if the pricetis lowered to $10 and $35, respectively, per unit. a-1. If OPP accepts the offer, how many direct labor-hours will be required to produce the additional scales? a-2. Complete the following table to determine the differential profit increase (or decrease) if OPP accepts this proposal. Prices on regular sales will remain the same. b-1. Suppose that the kitchenware chain has offered instead to buy 50,000 Cook models at $10 per unit and 30,000 Baker models at $35. This customer will purchase the models only in an all-or-nothing deal. That is, OPP must provide all 50,000 units of the Cook model and 30,000 units of the Baker model or nothing at all. In view of its capacity constraints, OPP will reduce sales to regular customers as needed to fill the special order. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin with the special order added. b-2. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extra demand. c-1. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime required: a. A nationwide kitchenware chain has offered to bury 30,000 Cook models and 15,000 Baker models if the price is lowered to $10 and $35, respectively, per unit. a-1. If OPP accepts the offer, how many direct labor-hours will be required to produce the additional scales? a-2. Complete the following table to determine the differential profit increase (or decrease) if OPP accepts this proposal. Prices on regular sales will remain the same b-1. Suppose that the kitchenware chain has offered instead to buy 50,000 Cook models at $10 per unit and 30,000 Baker models at $35. This customer will purchase the models only in an all-or-nothing deal. That is, OPP must provide all 50,000 units of the Cook model and 30,000 units of the Baker model or nothing at all. In view of its capacity constraints, OPP will reduce sales to regular customers as needed to fill the special order. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin with the special order added. b-2. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extra demand. c-1. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hour. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. c-2. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario in requirement b-1? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. A nationwide kitchenware chain has offered to buy 30,000 Cook models and 15,000 Baker models if the price is lowered to $10 and $35, respectively, per unit. A1. If OPP accepts the offer, how many direct labor-hours will be required to produce the additional scales? b-2. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the compary cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extre demand c-1. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hout. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. c-2. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario in requirement b-1? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. A nationwide kitchenware chain has offered to buy 30,000 Cook models and 15,000 Baker models if the price is lowered to $10 and $35, respectively, per unit. A2. Complete the following table to determine the differential profit increase (or decrease) if OPP accepts this proposal. Prices on regular sales will remain the same. c-1. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hour. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. c-2. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario in requirement b-1? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Suppose that the kitchenware chain has offered instead to buy 50,000 Cook models at $10 per unit and 30,000 Baker models at \$35. This customer will purchase the models only in an all-or-nothing deal. That is, OPP must provide all 50,000 units of the Cook model and 30,000 units of the Baker model or nothing at all. in view of its capacity constraints, 0 Pp will reduce. sales to regular customers as needed to fill the special order. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution maroin with the special order added. b-2. How much will the profits change if the order is ccepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity order added. meet the extra demand. c-1. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hour. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. c-2. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario in requirement b-1? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extra demand. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hour. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. customers as needed to fill the special ordet. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin with the special order added. b-2. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extra demand c-1. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hour. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. c-2. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario in requirement b-1? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario in requirement b1 ? a. A nationwide kitchenware chain has offered to buy 30.000 Cook models and 15.000 Baker models if the price is lowered to $10 and $35, respectively, per unit. a-1. If OPP accepts the offer, how many direct labor-hours will be required to produce the additional scales? a-2. Complete the following table to determine the differential profit increase (or decrease) if OPP accepts this proposal. Prices on regular sales will remain the same. b-1. Suppose that the kitchenware chain has offered instead to buy 50,000 Cook models at $10 per unit and 30,000 Baker models at $35. This customer will purchase the models only in an all-or-nothing deal. That is, OPP must provide all 50,000 units of the Cook model and 30,000 units of the Baker model or nothing at all. In view of its capacity constraints, OPP will reduce sales to regular. customers as needed to fill the special order. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin with the speciai order added. b-2. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extra demand. c-1. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hour. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. c-2. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario in requirement b-1? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extra demand. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hour. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. ktchehware stores, ascourt stores. vha so on. wwo of the scmes it produces for kitchen use are me cook and Baker, ine Look is a basic food scale. The Boker has a grebter crpacity and special foatures that facllitate adjusting baking reelpes for more or fewee people. The following information is tivelloble: The average wage tate is $32 per hout. Variable overhead varies with the quantity of direct labor-hours. The plant has a capacity of 20,000 direct labor-hours, but current production uses only 17.750 direct tabor-hours. Required: a. A nationwide kitchemware chain has offered to buy 30,000 Cook models and 15,000 Baker models if the price is lowered to $10 and \$35, respectively, per unit. a-1. If OPP accepts the offec, how many direct labor-hours wili be required to produce the additional scales? a-2. Complete the following table to determine the differential profit increase (or decrease) if OPP accepts this proposal. Prices on regular sales will remain the same. b-1. Suppose that the kitchenware chain has offered instead to buy 50.000 Cook models at $10 per unit and 30,000 Baker models at 535. This customer will purchase the models only in an all-or-nothing deat. That is, OPP must provide all 50,000 units of the Cook modet and 30,000 units of the Baker model or nothing at all. In view of its capacity constraints, OPP will reduce sales to regular custamers as needed to fill the special order. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin with the special order added. b-2. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extra demand. c-1. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hout. Variable overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. c-2. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario in requirement b-1? The average wage tate is $32 per hout. Variable ovechoed varlos with the quantify of direct labor-hours. The plant has a capacity of 20,000 direct iabor-hours, but current production uses only 17,750 direct labor-hours. Required: a. A nationwide kitchenware chain has offered to buy 30,000 Cook models and 15,000 Baker models if the price is lowered to $10 and $35, respecthely, per unit. a-1. If OpP accepts the offer, how many direct labor-hours will be required to produce the additional scates? a-2. Complete the following thble to determine the differential profit increase (or decrease) ir opp accepts this proposal. Prices on regular sales will remain the same. b-1. Suppose that the kitchenware chain has offered instead to buy 50,000 Cook models at $10 per unit and 30,000 Baker models at 535. This customer will purchase the models only in an all-or-nothing deal. That is, OPP must provide all 50,000 units of the Cook model and 30,000 units of the Baker model or nothing at all. In view of its capacity constraints, opp will reduce sales to regutar customers as needed to hill the special order. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin with the special order added b-2. How much will the profits change if the order is accepted? Assume that the company cannot increase its production capacity to meet the extra demand c-1. Assume that, in the situation presented in requirement b-1, the plant can work overtime. Direct labor costs for the overtime production increase to $45 per hour. Varioble overhead costs for overtime production are $6 per hour more than for normal. production. Complete the table below to determine the total contribution margin. c-2. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario ingequirement b-i? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. How much will the profits change in this situation compared to the capacity constraints scenario in requirement b- 1