Question
Q2. As shown in Fig. 2, the person A is standing on the merry-go-round (i.e. not moving relative to it), which is rotating at
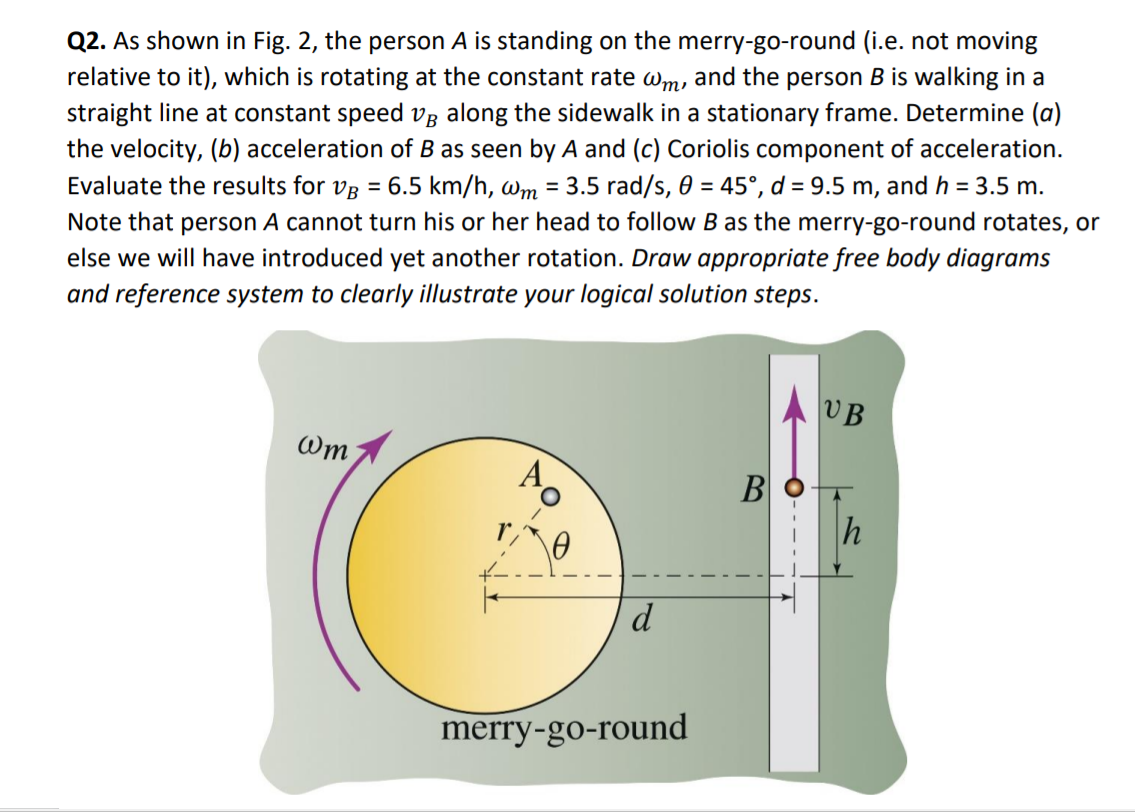
Q2. As shown in Fig. 2, the person A is standing on the merry-go-round (i.e. not moving relative to it), which is rotating at the constant rate wm, and the person B is walking in a straight line at constant speed v along the sidewalk in a stationary frame. Determine (a) the velocity, (b) acceleration of B as seen by A and (c) Coriolis component of acceleration. Evaluate the results for VB = 6.5 km/h, wm = 3.5 rad/s, 0 = 45, d = 9.5 m, and h = 3.5 m. Note that person A cannot turn his or her head to follow B as the merry-go-round rotates, or else we will have introduced yet another rotation. Draw appropriate free body diagrams and reference system to clearly illustrate your logical solution steps. Wm Ao re d merry-go-round B UB
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get StartedRecommended Textbook for
Vector Mechanics for Engineers Statics and Dynamics
Authors: Ferdinand Beer, E. Russell Johnston, Jr., Elliot Eisenberg, William Clausen, David Mazurek, Phillip Cornwell
8th Edition
73212229, 978-0073212227
Students also viewed these Mechanical Engineering questions
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
Question
Answered: 1 week ago
View Answer in SolutionInn App



