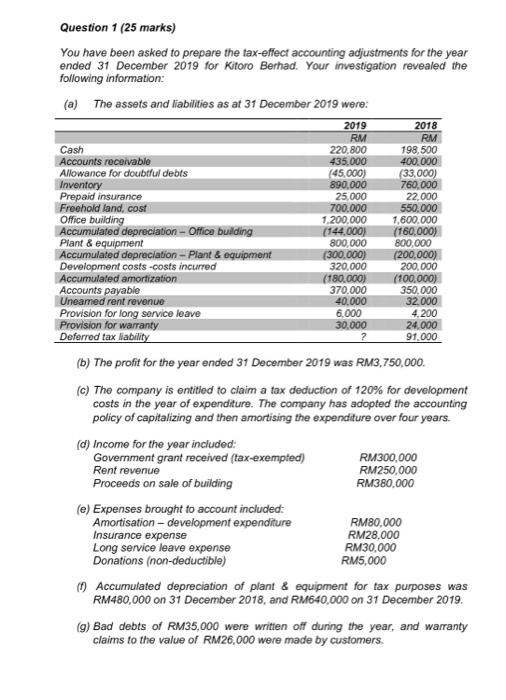
Question 1 (25 marks) You have been asked to prepare the tax-effect accounting adjustments for the year ended 31 December 2019 for Kitoro Berhad. Your investigation revealed the following information: (a) The assets and liabilities as at 31 December 2019 were: 2019 2018 RM RM Cash 220.800 198,500 Accounts receivable 435.000 400.000 Allowance for doubtful debts (45.000) (33,000) Inventory 890.000 760,000 Prepaid insurance 25,000 22,000 Freehold land, cost 700.000 550.000 Office building 1.200.000 1,600.000 Accumulated depreciation - Office building (144,000) (160.000) Plant & equipment 800,000 800,000 Accumulated depreciation - Plant & equipment (300.000) (200,000) Development costs -costs incurred 320,000 200,000 Accumulated amortization (180.000) (100.000) Accounts payable 370.000 350.000 Uneamed rent revenue 40.000 32.000 Provision for long service leave 6.000 4.200 Provision for warranty 30.000 24.000 Deferred tax lability ? 91.000 (b) The profit for the year ended 31 December 2019 was RM3,750,000 (c) The company is entitled to claim a tax deduction of 120% for development costs in the year of expenditure. The company has adopted the accounting policy of capitalizing and then amortising the expenditure over four years. (d) Income for the year included: Government grant received (tax-exempted) RM300,000 Rent revenue RM250,000 Proceeds on sale of building RM380,000 (e) Expenses brought to account included: Amortisation development expenditure RM80,000 Insurance expense RM28,000 Long service leave expense RM30,000 Donations (non-deductible) RM5,000 Accumulated depreciation of plant & equipment for tax purposes was RM480,000 on 31 December 2018, and RM640,000 on 31 December 2019. (9) Bad debts of RM35,000 were written off during the year, and warranty claims to the value of RM26,000 were made by customers. (h) The company's accounting policy is to depreciate building over 50 years with no residual value. No deduction is allowed for tax purpose. The building sold during the year had a cost of RM400,000 when acquired 5 years ago. Any gain (loss) on sale of building is not taxable (deductible). No disposal of other non-current assets. () In September 2018, the government increased the company tax rate from 24% to 25%, effective from 1 January 2019. Required: i. Prepare the worksheets to calculate and record the current tax liability and any movements in deferred tax assets/liabilities in accordance with IAS 12/MFRS 112 for the year ended 31 December 2019. [20 marks) ii. Prepare journal entries to record the current tax liability and deferred tax assets/liabilities in accordance with IAS 12/MFRS 112 for the year ended 31 December 2019. [2 marks] iii. Give an example of temporary difference for Kitoro Bhd and discuss its tax effect [3 marks) Question 1 (25 marks) You have been asked to prepare the tax-effect accounting adjustments for the year ended 31 December 2019 for Kitoro Berhad. Your investigation revealed the following information: (a) The assets and liabilities as at 31 December 2019 were: 2019 2018 RM RM Cash 220.800 198,500 Accounts receivable 435.000 400.000 Allowance for doubtful debts (45.000) (33,000) Inventory 890.000 760,000 Prepaid insurance 25,000 22,000 Freehold land, cost 700.000 550.000 Office building 1.200.000 1,600.000 Accumulated depreciation - Office building (144,000) (160.000) Plant & equipment 800,000 800,000 Accumulated depreciation - Plant & equipment (300.000) (200,000) Development costs -costs incurred 320,000 200,000 Accumulated amortization (180.000) (100.000) Accounts payable 370.000 350.000 Uneamed rent revenue 40.000 32.000 Provision for long service leave 6.000 4.200 Provision for warranty 30.000 24.000 Deferred tax lability ? 91.000 (b) The profit for the year ended 31 December 2019 was RM3,750,000 (c) The company is entitled to claim a tax deduction of 120% for development costs in the year of expenditure. The company has adopted the accounting policy of capitalizing and then amortising the expenditure over four years. (d) Income for the year included: Government grant received (tax-exempted) RM300,000 Rent revenue RM250,000 Proceeds on sale of building RM380,000 (e) Expenses brought to account included: Amortisation development expenditure RM80,000 Insurance expense RM28,000 Long service leave expense RM30,000 Donations (non-deductible) RM5,000 Accumulated depreciation of plant & equipment for tax purposes was RM480,000 on 31 December 2018, and RM640,000 on 31 December 2019. (9) Bad debts of RM35,000 were written off during the year, and warranty claims to the value of RM26,000 were made by customers. (h) The company's accounting policy is to depreciate building over 50 years with no residual value. No deduction is allowed for tax purpose. The building sold during the year had a cost of RM400,000 when acquired 5 years ago. Any gain (loss) on sale of building is not taxable (deductible). No disposal of other non-current assets. () In September 2018, the government increased the company tax rate from 24% to 25%, effective from 1 January 2019. Required: i. Prepare the worksheets to calculate and record the current tax liability and any movements in deferred tax assets/liabilities in accordance with IAS 12/MFRS 112 for the year ended 31 December 2019. [20 marks) ii. Prepare journal entries to record the current tax liability and deferred tax assets/liabilities in accordance with IAS 12/MFRS 112 for the year ended 31 December 2019. [2 marks] iii. Give an example of temporary difference for Kitoro Bhd and discuss its tax effect [3 marks)