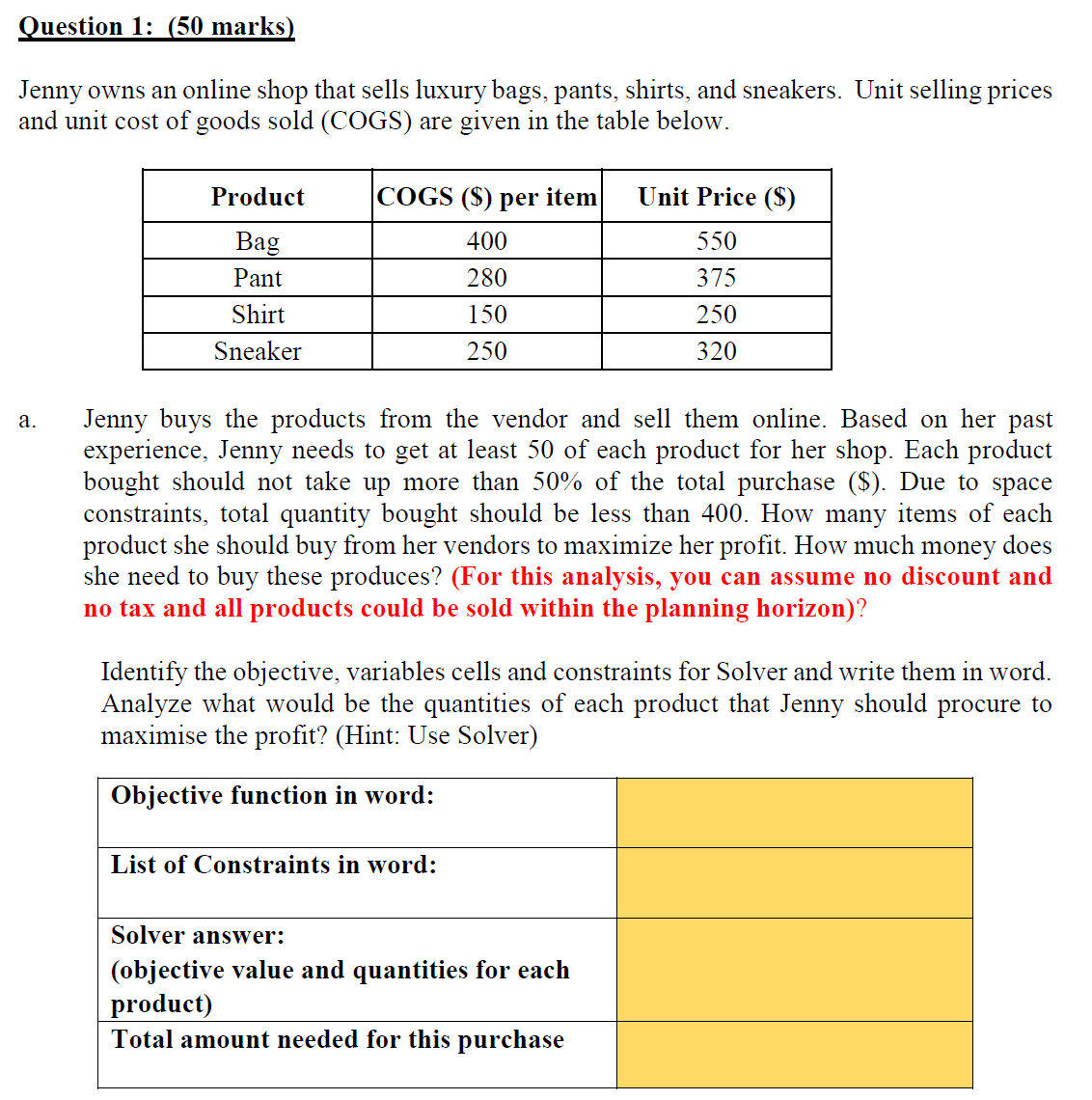
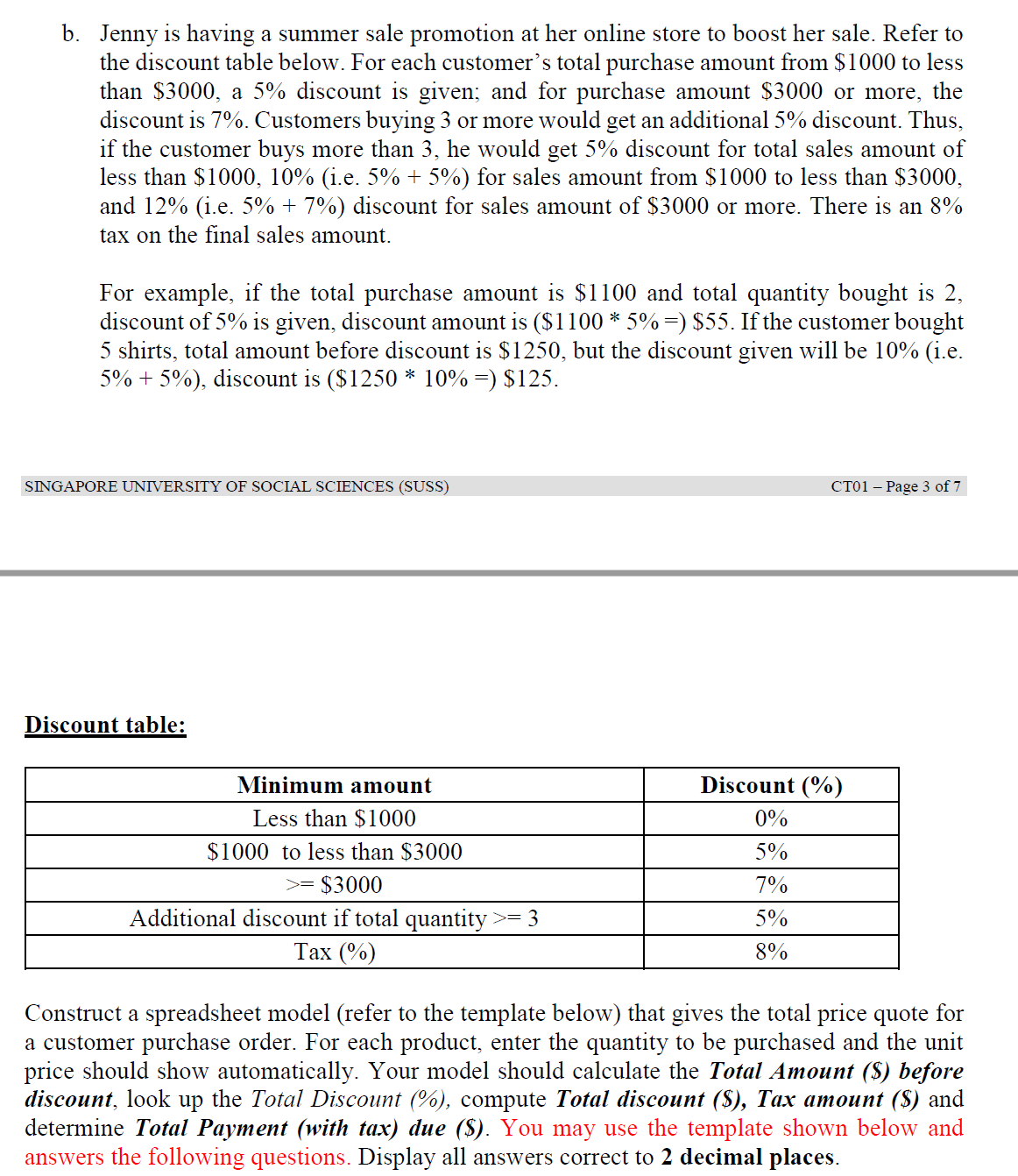
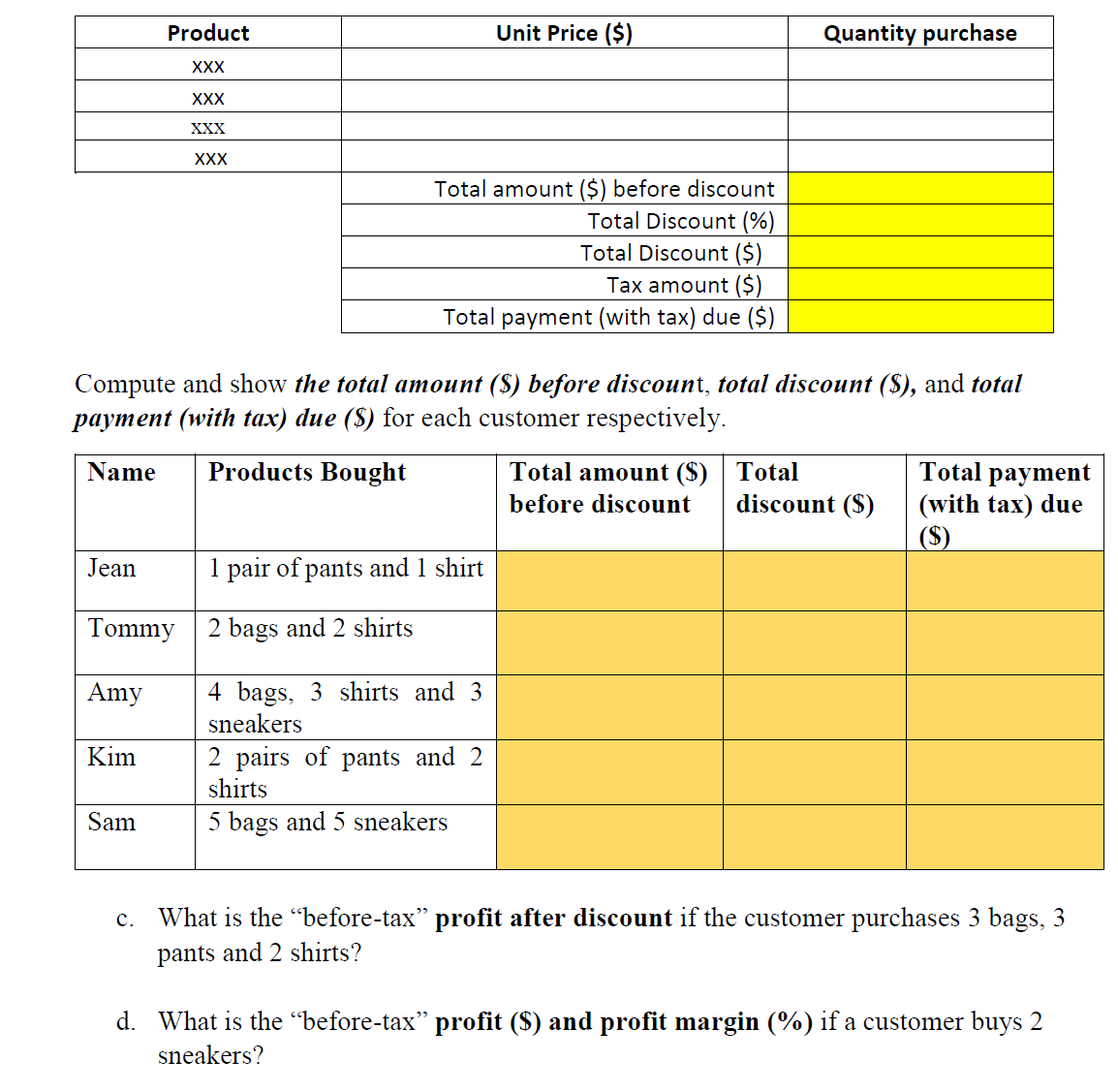
Question 1: [50 marks] Jenny owns an online shop that sells luxury bags, pants, shirts, and sneakers. Unit selling prices and unit cost of goods sold (COGS) are given in the table below. COGS ($) per item Unit Price ($) Bag 550 375 250 Sneaker 250 320 a. Jenny buys the products from the vendor and sell them online. Based on her past experience, Jenny needs to get at least 50 of each product for her shop. Each product bought should not take up more than 50% of the total purchase ($). Due to space constraints, total quantity bought should be less than 400. How many items of each product she should buy from her vendors to maximize her profit. How much money does she need to buy these produces? (For this analysis, you can assume no discount and no tax and all products could be sold Within the planning horizon)? Identify the objective, variables cells and constraints for Solver and write them in word. Analyze what would be the quantities of each product that Jenny should procure to maximise the prot? (Hint: Use Solver) Objective function in word: List of Constraints in word: Solver answer: (objective value and quantities for each product) Total amount needed for this purchase b. Jenny is having a summer sale promotion at her online store to boost her sale. Refer to the discount table below. For each customer's total purchase amount from $1000 to less than $3000, a 5% discount is given; and for purchase amount $3000 or more, the discount is 7%. Customers buying 3 or more would get an additional 5% discount. Thus, if the customer buys more than 3, he would get 5% discount for total sales amount of less than $1000, 10% (i.e. 5% + 5%) for sales amount from $1000 to less than $3000, and 12% (i.e. 5% + 7%) discount for sales amount of $3000 or more. There is an 8% tax on the nal sales amount. For example, if the total purchase amount is $1100 and total quantity bought is 2, discount of 5% is given, discount amount is ($1 100 * 5% :) $55. If the customer bought 5 shirts, total amount before discount is $1250, but the discount given will be 10% (i.e. 5% + 5%), discount is ($1250 * 10% :) $125. SINGAPORE UNIVERSITY OF SOCIAL SCIENCES (SUSS) CTOl 7 Page 3 of 7 Discount table: lVIiuimum amount Discount (%) Less than $1000 0% $1000 to less than $3000 5% >: $3000 7% Additional discount if total quantity >: 3 5% Tax (%) 8% Construct a spreadsheet model (refer to the template below) that gives the total price quote for a customer purchase order. For each product, enter the quantity to be purchased and the unit price should show automatically. Your model should calculate the Total Amount (5) before discount, look up the Total Discount (%), compute Total discount ($), Tax amount ($) and determine Total Payment (with tax) due ($). You may use the template shown below and answers the following questions. Display all answers correct to 2 decimal places. Product Unit Price (5) Quantity purchase XXX XXX XXX Total amount (S) before discount Total Discount (%) Total Discount (3) Tax amount ($) Total payment (with tax) due (S) Compute and show the total amount (3) before discount, total discount (5), and total payment (with tax) due ($) for each customer respectively. Name Products Bought Total amount ($) Total Total payment before discount discount ($) (with tax) due (35) Jean 1 pair of pants and l shirt Tommy 2 bags and 2 shirts Amy 4 bags, 3 shirts and 3 sneakers Kim 2 pairs of pants and 2 shirts Sam 5 bags and 5 sneakers c. What is the \"beforetax\" prot after discount if the customer purchases 3 bags, 3 pants and 2 shirts? d. What is the \"before-tax\" prot ($) and prot margin (%) if a customer buys 2 sneakers