Question 1
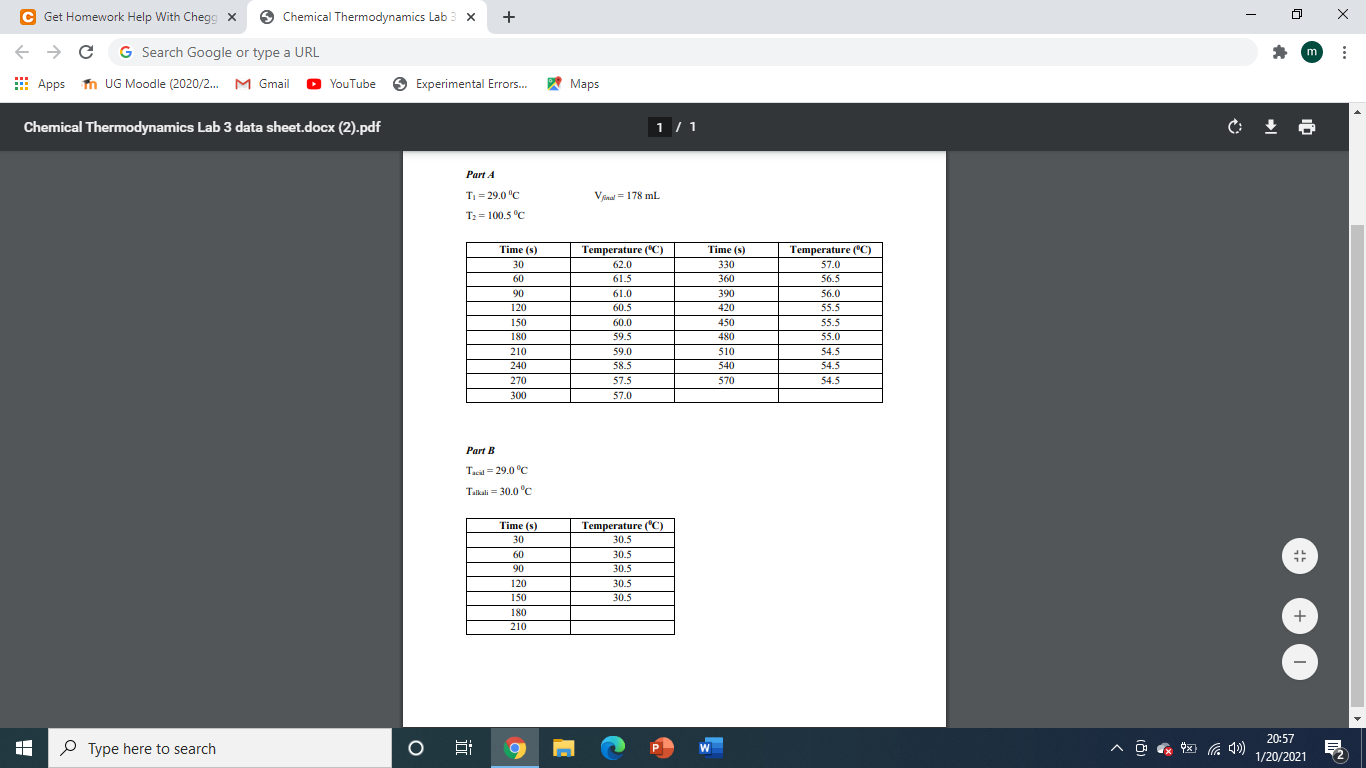
a) calculate the determination of heat capacity of calorimeter and enthalpy of neutralization
b) Construct a Graph of Cp vs lnT for solid water including determination of molar entropy
c) Construct a Graph of Cp vs lnT for liquid water including determination of molar entropy
d) Calculate the entropy of neutralization, Gibb's energy of neutralization, and the ionic product of water including two reasons why the experimental Kw differs from the accepted value of 1.0x10-14.
Ps. This is one question 
C Get Homework Help With Chegg X Chemical Thermodynamics Lab 3 X + { m C G Search Google or type a URL Apps UG Moodle (2020/2... M Gmail YouTube Experimental Errors... Maps Chemical Thermodynamics Lab 3 data sheet.docx (2).pdf 1/1 Part 4 T = 29.0C V = 178 mL T2 = 100.5 C Time (5) 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 Temperature (C) 62.0 61.5 61.0 60.5 60.0 59.5 59.0 58.5 57.5 Time (s) 330 360 390 420 450 480 510 540 570 Temperature (C) 57.0 56.5 56.0 55.5 55.5 55.0 54.5 54.5 54.5 57.0 Part B Tid=29.0C Talkali = 30.0C 1 Time (s) 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 Temperature (C) 30.5 30.5 30.5 30.5 30.5 + Type here to search 3 P W 20:57 1/20/2021 C Get Homework Help With Chegg X Chemical Thermodynamics Lab + e G * Apps m UG Moodle (2020/2... M Gmail YouTube Experimental Errors... Maps Part 1 - Determination of the heat capacity of the calorimeter Place exactly 100 mL of water (using a measuring cylinder) into the inner beaker of the calorimeter. Place about 100 mL of water into the conical flask and heat to boil. Measure and record the temperature (T2) of the boiling water in the conical flask over a period of five minutes. Remove the thermometer and cool it to room temperature (under tap water) while the water continues to boil in the flask. Measure and record the temperature (T) of the water in the inner beaker of the calorimeter over a period of 5 minutes while stirring with a wire stirrer. Remove the conical flask from the heating arrangement and quickly add the boiling water into the water in the inner beaker of the calorimeter. Stir with the wire stirrer and record the temperature at 30 s intervals until the temperature is steady. Measure the total volume of the water in the inner beaker now using the measuring cylinder. Part B - Determination of the enthalpy change associated with a neutralisation Place exactly 100 mL of 0.1 M H2SO4 using a measuring cylinder into a clean, dry inner beaker of the calorimeter used in Part A. Place exactly 100 mL of 0.2 N KOH into a clean dry conical flask. Measure the temperature of the acid in the beaker over a period of 5 min while stirring with a wire stirrer. Record the average temperature of the acid. Remove the thermometer, rinse it under the tap water and dry it. Measure the temperature of the alkali in the flask at 60 s intervals over a period of 5 minutes. Record the average temperature of the alkali. Place the thermometer in the acid in the beaker, start the stop clock and QUICKLY pour the alkali from the flask into the acid in the beaker. Stir the contents of the beaker gently with the wire stirrer. Record the temperature at 30 s intervals until the temperature is steady. Type here to search 21:28 1/20/2021 C Get Homework Help With Chegg X Chemical Thermodynamics Lab 3 X + { m C G Search Google or type a URL Apps UG Moodle (2020/2... M Gmail YouTube Experimental Errors... Maps Chemical Thermodynamics Lab 3 data sheet.docx (2).pdf 1/1 Part 4 T = 29.0C V = 178 mL T2 = 100.5 C Time (5) 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 Temperature (C) 62.0 61.5 61.0 60.5 60.0 59.5 59.0 58.5 57.5 Time (s) 330 360 390 420 450 480 510 540 570 Temperature (C) 57.0 56.5 56.0 55.5 55.5 55.0 54.5 54.5 54.5 57.0 Part B Tid=29.0C Talkali = 30.0C 1 Time (s) 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 Temperature (C) 30.5 30.5 30.5 30.5 30.5 + Type here to search 3 P W 20:57 1/20/2021 C Get Homework Help With Chegg X Chemical Thermodynamics Lab + e G * Apps m UG Moodle (2020/2... M Gmail YouTube Experimental Errors... Maps Part 1 - Determination of the heat capacity of the calorimeter Place exactly 100 mL of water (using a measuring cylinder) into the inner beaker of the calorimeter. Place about 100 mL of water into the conical flask and heat to boil. Measure and record the temperature (T2) of the boiling water in the conical flask over a period of five minutes. Remove the thermometer and cool it to room temperature (under tap water) while the water continues to boil in the flask. Measure and record the temperature (T) of the water in the inner beaker of the calorimeter over a period of 5 minutes while stirring with a wire stirrer. Remove the conical flask from the heating arrangement and quickly add the boiling water into the water in the inner beaker of the calorimeter. Stir with the wire stirrer and record the temperature at 30 s intervals until the temperature is steady. Measure the total volume of the water in the inner beaker now using the measuring cylinder. Part B - Determination of the enthalpy change associated with a neutralisation Place exactly 100 mL of 0.1 M H2SO4 using a measuring cylinder into a clean, dry inner beaker of the calorimeter used in Part A. Place exactly 100 mL of 0.2 N KOH into a clean dry conical flask. Measure the temperature of the acid in the beaker over a period of 5 min while stirring with a wire stirrer. Record the average temperature of the acid. Remove the thermometer, rinse it under the tap water and dry it. Measure the temperature of the alkali in the flask at 60 s intervals over a period of 5 minutes. Record the average temperature of the alkali. Place the thermometer in the acid in the beaker, start the stop clock and QUICKLY pour the alkali from the flask into the acid in the beaker. Stir the contents of the beaker gently with the wire stirrer. Record the temperature at 30 s intervals until the temperature is steady. Type here to search 21:28 1/20/2021








