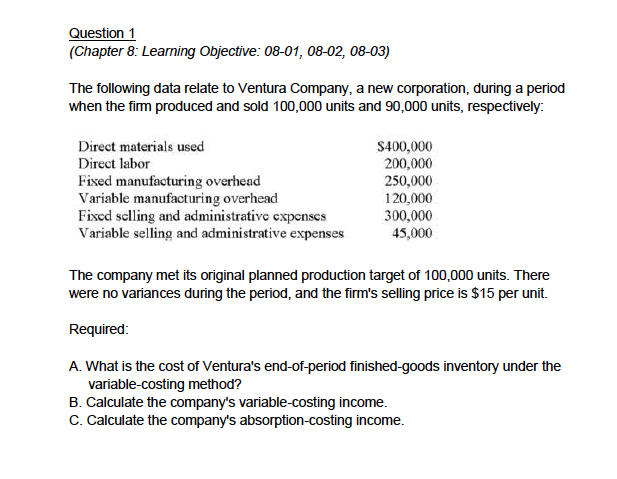



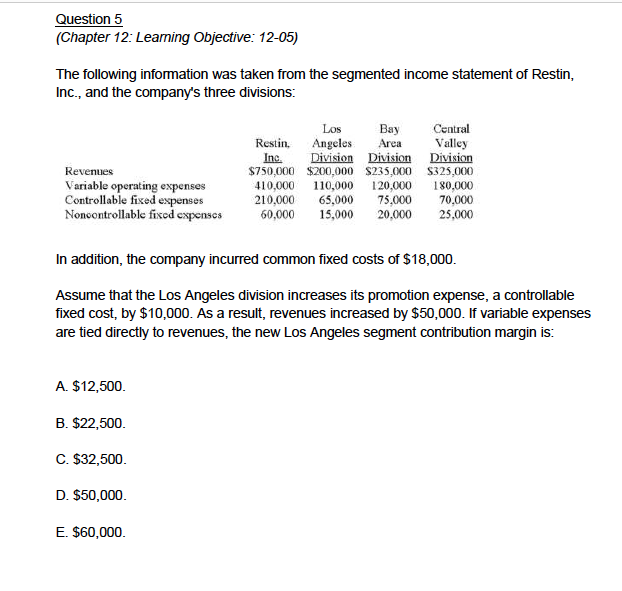
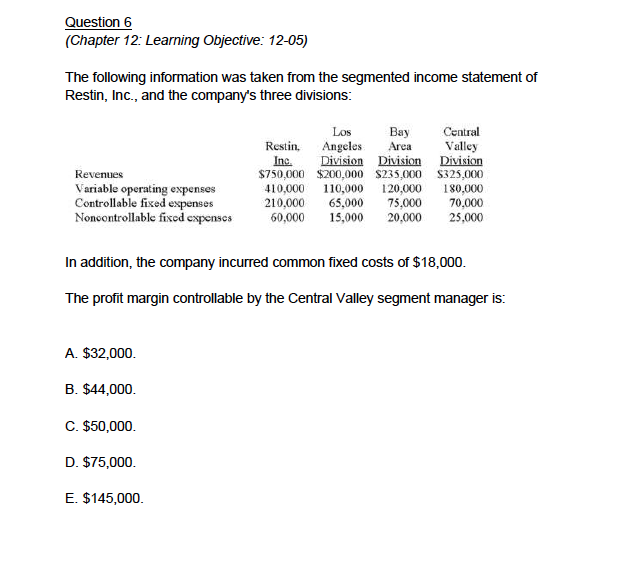

Question 1 (Chapter 8 Learning Objective: 08-01, 08-02, 08-03) The following data relate to Ventura Company, a new corporation, during a period when the firm produced and sold 100,000 units and 90,000 units, respectively: Direct materials used Direct labor Fixed manufacturing overhead Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed sclling and administrativc cxpcnscs Variable selling and administrative expenses $400,000 200,000 250,000 120,000 300,000 45,000 The company met its original planned production target of 100,000 units. There were no variances during the period, and the firm's selling price is $15 per unit. Required A. What is the cost of Ventura's end-of-period finished-goods inventory under the variable-costing method? B. Calculate the company's variable-costing income C. Calculate the company's absorption-costing income Question 2 Consider the statements that follow. 1. Variable selling costs are expensed when incurred. 2. The income statement discloses a company's contribution margin. 5. Sales revenue minus cost of goods sold equals contribution margin. 6. This method must be used for extemal financial reporting. 7. Fixed selling and administrative expenses are treated in the same manner as fixed manufacturing overhead. 8. This method is sometimes called full costing. 9. This method requires the calculation of a fixed manufacturing cost per unit. rting. 7. Fixed selling and administratveeal Required: Determine which of the nine statements: A. Relate only to absorption costing. B. Relate only to variable costing. C. Relate to both absorption costing and variable costing. D. Relate to neither absorption costing nor variable costing. Question 3 (Chapter 12: Leaning Objectives 12-4, 12-5) Pretty Lady is an upscale boutique that operates various stores throughout Florida. The company, which has three divisions (Miami, Naples, and Tampa), reported the following information for the year just ended (in thousands): Miami Naples Tampa S9,000 S6,000 $5,000 ,400 3,500 Profit margin controllable by division manager 900 1000 200 Sales revenue Divisional contribution margin 000 1,9003,s0 700 6,400 Divisional profit margin Pretty Lady also reported $600 of common fixed expenses that top management wants to allocate to the divisions on the basis of sales revenue. As the company's chief executive officer notes, "Each division helped to incur a portion of these costs and, as a result, each should absorb its fair share." The firm has adopted various responsibility accounting procedures to evaluate division personnel Required A. Compute the company's total sales B. Calculate the amount of variable operating expense incurred by the Naples Division C. Calculate the fixed costs controllable by Miami's management. D. Calculate the fixed costs traceable to the Tampa Division but controllable by others. E. Pretty Lady desires to promote a division manager to the corporate office to oversee selected operations. In determining which individual to promote should Pretty Lady's top management focus on the profit margin controllable by the division manager or the overall divisional profit margin? Briefly explain F. If the company follows the desires of top management, how much of the common fixed expenses would be allocated to the Tampa Division? G. Do cost allocations such as those in part "F" typically appear on a segmented income statement? Question 4 (Chapter 12: Learning Objective: 12-07) Balanced scorecards contain a number of factors that are important to the success of a business. These factors are often divided into four categories: financial, internal operations, customer, and leaning and growth? Consider the twelve factors that follow 1. Market share 2. Eamings per share 3. Manufacturing cycle efficiency 4. Machine downtime 5. Number of patents held 6. Employee suggestions 7. Number of repeat sales 8. Levels of inventories held 9. Number of vendors used 10. Cash flow from operations 11. Employee training hours 12. Gross margin Required Determine the proper classification (financial, internal operations, customer, and learning and growth?) for each of the twelve factors listed. Question5 (Chapter 12: Leaming Objective: 12-05) The following information was taken from the segmented income statement of Restin, Inc., and the company's three divisions: Bay Central Resi Angeles AreaValley Inc Division Division Division $750,000 $200,000 S235,000 S325,000 10,000 10,000 120,000 180,000 210,000 65,000 75,000 70,000 0,000 ,00 20,000 25,000 Los Revenues Variable operating expenses Controllable fixed espenses Nonoontrollable fixod espenses In addition, the company incurred common fixed costs of $18,000 Assume that the Los Angeles division increases its promotion expense, a controllable fixed cost, by $10,000. As a result, revenues increased by $50,000. If variable expenses are tied directly to revenues, the new Los Angeles segment contribution margin is: A. $12,500. B. $22,500. C. $32,500. D. $50,000. E. $60,000. Question 6 (Chapter 12 Learning Objective: 12-05) The following information was taken from the segmented income statement of Restin, Inc., and the company's three divisions: Bay ral Resi Angeles AreaValley Inc Division Divon Division $750,000 $200,000 S235,000 S325,000 10,000 110,000 120,000 180,000 210,000 65,000 75,000 70,000 0,000 ,00 20,000 25,000 Los Revenues Variable operating expenses Controllable fixed espenses Nonoontrollable fixod espenses in addition, the company incurred common fixed costs of $18,000. The profit margin controllable by the Central Valley segment manager is: A. $32,000. B. $44,000. C. $50,000. D. $75,000. E. $145,000. Question 7 (Chapter 12: Learning Objective: 12-02) Decentralized firms can delegate authority by structuring an organization into responsibility centers. Which of the following organizational segments is most like a totally independent, standalone business where managers are expected to "make it on their own"? A. Cost center B. Revenue center C. Profit center D. Investment center E. Contribution center Question 1 (Chapter 8 Learning Objective: 08-01, 08-02, 08-03) The following data relate to Ventura Company, a new corporation, during a period when the firm produced and sold 100,000 units and 90,000 units, respectively: Direct materials used Direct labor Fixed manufacturing overhead Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed sclling and administrativc cxpcnscs Variable selling and administrative expenses $400,000 200,000 250,000 120,000 300,000 45,000 The company met its original planned production target of 100,000 units. There were no variances during the period, and the firm's selling price is $15 per unit. Required A. What is the cost of Ventura's end-of-period finished-goods inventory under the variable-costing method? B. Calculate the company's variable-costing income C. Calculate the company's absorption-costing income Question 2 Consider the statements that follow. 1. Variable selling costs are expensed when incurred. 2. The income statement discloses a company's contribution margin. 5. Sales revenue minus cost of goods sold equals contribution margin. 6. This method must be used for extemal financial reporting. 7. Fixed selling and administrative expenses are treated in the same manner as fixed manufacturing overhead. 8. This method is sometimes called full costing. 9. This method requires the calculation of a fixed manufacturing cost per unit. rting. 7. Fixed selling and administratveeal Required: Determine which of the nine statements: A. Relate only to absorption costing. B. Relate only to variable costing. C. Relate to both absorption costing and variable costing. D. Relate to neither absorption costing nor variable costing. Question 3 (Chapter 12: Leaning Objectives 12-4, 12-5) Pretty Lady is an upscale boutique that operates various stores throughout Florida. The company, which has three divisions (Miami, Naples, and Tampa), reported the following information for the year just ended (in thousands): Miami Naples Tampa S9,000 S6,000 $5,000 ,400 3,500 Profit margin controllable by division manager 900 1000 200 Sales revenue Divisional contribution margin 000 1,9003,s0 700 6,400 Divisional profit margin Pretty Lady also reported $600 of common fixed expenses that top management wants to allocate to the divisions on the basis of sales revenue. As the company's chief executive officer notes, "Each division helped to incur a portion of these costs and, as a result, each should absorb its fair share." The firm has adopted various responsibility accounting procedures to evaluate division personnel Required A. Compute the company's total sales B. Calculate the amount of variable operating expense incurred by the Naples Division C. Calculate the fixed costs controllable by Miami's management. D. Calculate the fixed costs traceable to the Tampa Division but controllable by others. E. Pretty Lady desires to promote a division manager to the corporate office to oversee selected operations. In determining which individual to promote should Pretty Lady's top management focus on the profit margin controllable by the division manager or the overall divisional profit margin? Briefly explain F. If the company follows the desires of top management, how much of the common fixed expenses would be allocated to the Tampa Division? G. Do cost allocations such as those in part "F" typically appear on a segmented income statement? Question 4 (Chapter 12: Learning Objective: 12-07) Balanced scorecards contain a number of factors that are important to the success of a business. These factors are often divided into four categories: financial, internal operations, customer, and leaning and growth? Consider the twelve factors that follow 1. Market share 2. Eamings per share 3. Manufacturing cycle efficiency 4. Machine downtime 5. Number of patents held 6. Employee suggestions 7. Number of repeat sales 8. Levels of inventories held 9. Number of vendors used 10. Cash flow from operations 11. Employee training hours 12. Gross margin Required Determine the proper classification (financial, internal operations, customer, and learning and growth?) for each of the twelve factors listed. Question5 (Chapter 12: Leaming Objective: 12-05) The following information was taken from the segmented income statement of Restin, Inc., and the company's three divisions: Bay Central Resi Angeles AreaValley Inc Division Division Division $750,000 $200,000 S235,000 S325,000 10,000 10,000 120,000 180,000 210,000 65,000 75,000 70,000 0,000 ,00 20,000 25,000 Los Revenues Variable operating expenses Controllable fixed espenses Nonoontrollable fixod espenses In addition, the company incurred common fixed costs of $18,000 Assume that the Los Angeles division increases its promotion expense, a controllable fixed cost, by $10,000. As a result, revenues increased by $50,000. If variable expenses are tied directly to revenues, the new Los Angeles segment contribution margin is: A. $12,500. B. $22,500. C. $32,500. D. $50,000. E. $60,000. Question 6 (Chapter 12 Learning Objective: 12-05) The following information was taken from the segmented income statement of Restin, Inc., and the company's three divisions: Bay ral Resi Angeles AreaValley Inc Division Divon Division $750,000 $200,000 S235,000 S325,000 10,000 110,000 120,000 180,000 210,000 65,000 75,000 70,000 0,000 ,00 20,000 25,000 Los Revenues Variable operating expenses Controllable fixed espenses Nonoontrollable fixod espenses in addition, the company incurred common fixed costs of $18,000. The profit margin controllable by the Central Valley segment manager is: A. $32,000. B. $44,000. C. $50,000. D. $75,000. E. $145,000. Question 7 (Chapter 12: Learning Objective: 12-02) Decentralized firms can delegate authority by structuring an organization into responsibility centers. Which of the following organizational segments is most like a totally independent, standalone business where managers are expected to "make it on their own"? A. Cost center B. Revenue center C. Profit center D. Investment center E. Contribution center













