Question
Question 1: Customer Profitability Analysis (40 marks) Taylors Cheesecakes supplies cheesecakes to three large supermarket chains. Management has become concerned about the rising costs associated
Question 1: Customer Profitability Analysis (40 marks)
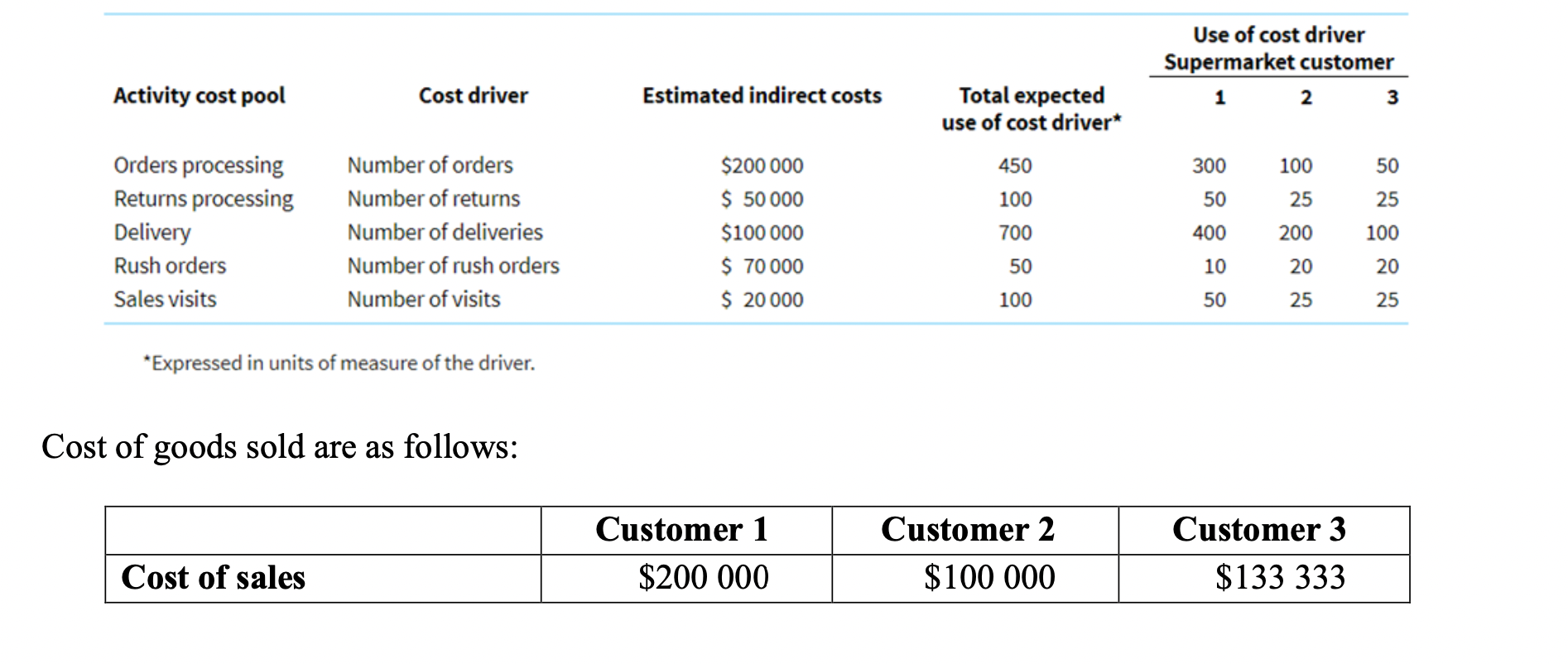
Taylors Cheesecakes supplies cheesecakes to three large supermarket chains. Management has become concerned about the rising costs associated with the processing and dispatch of orders. An activity analysis of the indirect costs identified the following customer-related costs:
Required (a) Calculate the activity cost driver rate for each activity. (10 marks).
-
(b) Assign the overhead costs to each of the three customers using the activity cost driver rates.
(10 marks).
-
(c) Calculate the net profit of each customer if the sales revenue pattern for each customer is as follows: Customer 1 $300 000; Customer 2 $150 000; Customer 3 $200 000. (10 marks).
-
(d) AdvisethemanagementofTaylorsCheesecakesastowhetheranychangesshouldbemade in the management of its relationships with customers and suggestion possible strategies for how to best manage unprofitable customers. In your response, weigh up the pros and cons of divesting unprofitable customers (10 marks).
Question 2: Working Capital (30 marks)
Reina Ltd has a payables deferral period of 40 days, an inventory turnover ratio of 6.9 times and an accounts receivable balance of $78,164. The total sales for the year are $300,000 whilst its cash conversion cycle is 108 days. The company uses a 365 day calendar year for its working capital calculations.
The company has a gross profit margin of 40% and fixed operating expenses of $50,000 per year. It has total assets of $900,000 and its cost of debt is 5% before tax on both short term and long term liabilities. It has a policy of funding 50% of assets by equity and a tax rate of 40%.
(Please use SALES, not COGS, to calculate the inventory conversion period.)
Required:
-
Based on the above information calculate the cash conversion cycle, return on equity and return on assets for Reina Ltd.
(10 marks)
-
Assuming that all the information given above remains constant other than the accounts receivable balance which drops from $78,164 to $39,802, recalculate the cash conversion cycle, the return on assets and return on equity.
(14 marks)
-
Discuss any other policy options for the management and improvement of working capital that may be available to Reina Ltd, other than considering the accounts receivable balance. You must provide two examples.
(6 marks)
Question 3: Variance Analysis (30 marks)
Part A Black Industries has a static budget based on production and sales of 24 000 units. Sales revenue is expected to be $96 000, variable costs $36 000 and fixed costs $32 000. Actual production and sales were 30 000 units with a profit of $50 000.
Required (a) Calculate the amount of profit in the flexible budget. (10 marks).
(b) Calculate the overall variance between the flexible budget and actual results. (5 marks). (c) Discuss the different types of variances that can be calculated using different types of
budgets. What are the advantages of using a flexible budget? (5 marks)
Part B: Sherry North is the supply manager for West Industries, a manufacturer of garden furniture for the major department store in Australia. As part of her bonus plan, Sherry must meet the materials budget that was established at the beginning of the year. As West Industries manufactures three products in large volumes, standard costs are easily established for the factors of production. The reports for the first half of the year indicate that the materials variance is unfavourable. In an attempt to achieve her bonus target Sherry has been purchasing lower-grade materials at reduced costs for a new supplier. Management have been very pleased with the turnaround in the variance.
Required
Discuss what implications Sherrys actions have for West Industries as a whole? In your answer you must consider the implications in relation to other variances that may be reported in the production area. (10 marks).
Activity cost pool Cost driver Orders processing Number of orders Number of returns Returns processing Delivery Number of deliveries Rush orders Number of rush orders Number of visits Sales visits *Expressed in units of measure of the driver. Cost of goods sold are as follows: Cost of sales Estimated indirect costs $200 000 $ 50 000 $100 000 $ 70 000 $ 20 000 Customer 1 $200 000 Total expected use of cost driver* 450 100 700 50 100 Customer 2 $100 000 Use of cost driver Supermarket customer 1 2 3 300 100 50 50 25 25 400 200 100 10 20 20 50 25 25 Customer 3 $133 333 Activity cost pool Cost driver Orders processing Number of orders Number of returns Returns processing Delivery Number of deliveries Rush orders Number of rush orders Number of visits Sales visits *Expressed in units of measure of the driver. Cost of goods sold are as follows: Cost of sales Estimated indirect costs $200 000 $ 50 000 $100 000 $ 70 000 $ 20 000 Customer 1 $200 000 Total expected use of cost driver* 450 100 700 50 100 Customer 2 $100 000 Use of cost driver Supermarket customer 1 2 3 300 100 50 50 25 25 400 200 100 10 20 20 50 25 25 Customer 3 $133 333Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


