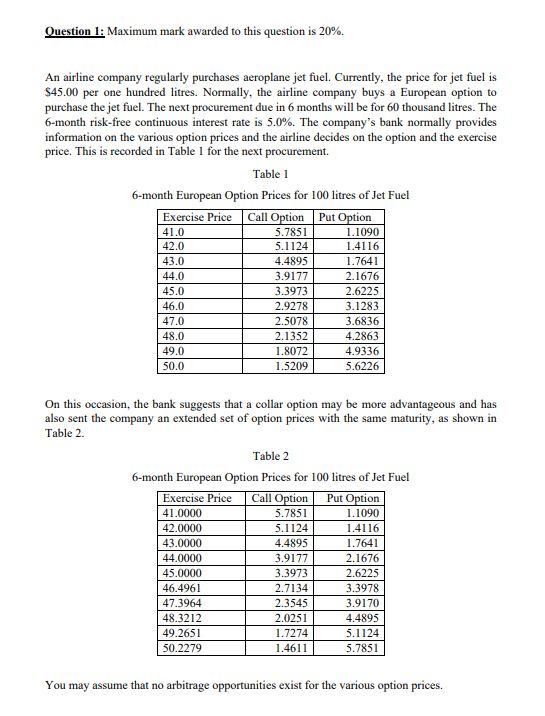

Question 1: Maximum mark awarded to this question is 20%. An airline company regularly purchases aeroplane jet fuel. Currently, the price for jet fuel is $45.00 per one hundred litres. Normally, the airline company buys a European option to purchase the jet fuel. The next procurement due in 6 months will be for 60 thousand litres. The 6-month risk-free continuous interest rate is 5.0%. The company's bank normally provides information on the various option prices and the airline decides on the option and the exercise price. This is recorded in Table 1 for the next procurement Table 1 6-month European Option Prices for 100 litres of Jet Fuel Exercise Price Call Option Put Option 41.0 5.7851 42.0 5.1124 1.4116 43.0 4.4895 1.7641 44.0 3.9177 2.1676 45.0 3.3973 2.6225 46.0 2.9278 3.1283 47.0 2.5078 3.6836 2.1352 4.2863 49.0 1.8072 4.9336 50.0 1.5209 5.6226 1.1090 48.0 On this occasion, the bank suggests that a collar option may be more advantageous and has also sent the company an extended set of option prices with the same maturity, as shown in Table 2. Table 2 6-month European Option Prices for 100 litres of Jet Fuel Exercise Price Call Option Put Option 41.0000 5.7851 1.1090 42.0000 5.1124 1.4116 43.0000 4.4895 1.7641 44.0000 3.9177 2.1676 45.0000 3.3973 2.6225 46.4961 2.7134 3.3978 47.3964 2.3545 3.9170 48.3212 2.0251 4.4895 49.2651 1.7274 5.1124 50.2279 1.4611 5.7851 You may assume that no arbitrage opportunities exist for the various option prices. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a collar option compared with its plain vanilla equivalent. b) Draw the spot price outturn profiles for the two alternatives and discuss their key similarities and differences. c) Although the airline company contracted an option for procuring 60 thousand litres of jet fuel, instead because of a market upturn the company on the maturity date now requires to purchase 80 thousand litres. How does this change your answers to parts (a) and (b)? Discuss the implications. d) Although the airline company contracted an option for procuring 60 thousand litres of jet fuel, instead because of a market upturn the company on the maturity date now requires to purchase 40 thousand litres. How does this change your answers to parts (a) and (b)? Discuss the implications. Question 1: Maximum mark awarded to this question is 20%. An airline company regularly purchases aeroplane jet fuel. Currently, the price for jet fuel is $45.00 per one hundred litres. Normally, the airline company buys a European option to purchase the jet fuel. The next procurement due in 6 months will be for 60 thousand litres. The 6-month risk-free continuous interest rate is 5.0%. The company's bank normally provides information on the various option prices and the airline decides on the option and the exercise price. This is recorded in Table 1 for the next procurement Table 1 6-month European Option Prices for 100 litres of Jet Fuel Exercise Price Call Option Put Option 41.0 5.7851 42.0 5.1124 1.4116 43.0 4.4895 1.7641 44.0 3.9177 2.1676 45.0 3.3973 2.6225 46.0 2.9278 3.1283 47.0 2.5078 3.6836 2.1352 4.2863 49.0 1.8072 4.9336 50.0 1.5209 5.6226 1.1090 48.0 On this occasion, the bank suggests that a collar option may be more advantageous and has also sent the company an extended set of option prices with the same maturity, as shown in Table 2. Table 2 6-month European Option Prices for 100 litres of Jet Fuel Exercise Price Call Option Put Option 41.0000 5.7851 1.1090 42.0000 5.1124 1.4116 43.0000 4.4895 1.7641 44.0000 3.9177 2.1676 45.0000 3.3973 2.6225 46.4961 2.7134 3.3978 47.3964 2.3545 3.9170 48.3212 2.0251 4.4895 49.2651 1.7274 5.1124 50.2279 1.4611 5.7851 You may assume that no arbitrage opportunities exist for the various option prices. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a collar option compared with its plain vanilla equivalent. b) Draw the spot price outturn profiles for the two alternatives and discuss their key similarities and differences. c) Although the airline company contracted an option for procuring 60 thousand litres of jet fuel, instead because of a market upturn the company on the maturity date now requires to purchase 80 thousand litres. How does this change your answers to parts (a) and (b)? Discuss the implications. d) Although the airline company contracted an option for procuring 60 thousand litres of jet fuel, instead because of a market upturn the company on the maturity date now requires to purchase 40 thousand litres. How does this change your answers to parts (a) and (b)? Discuss the implications








