Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 1 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 P Flag question In a perfectly competitive market, the price of the good equals its marginal
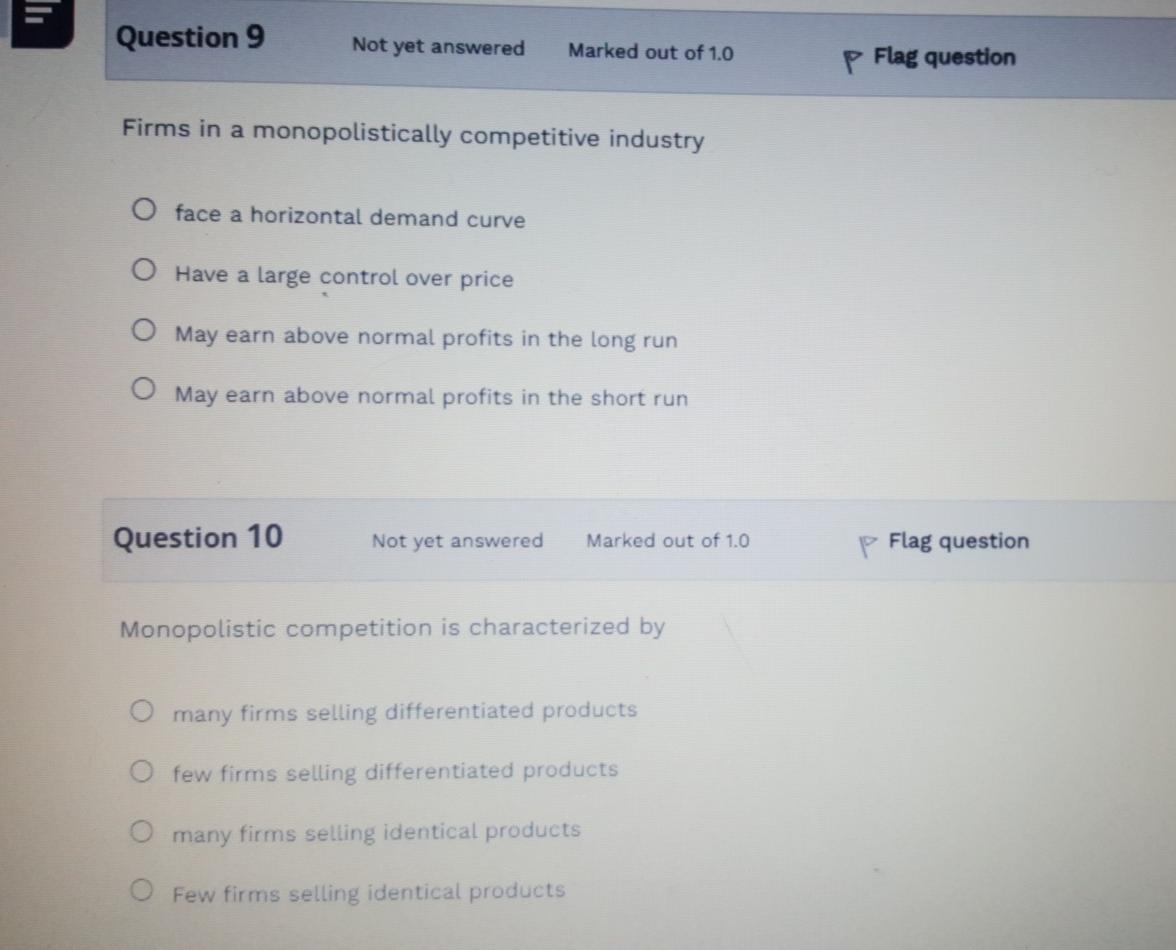
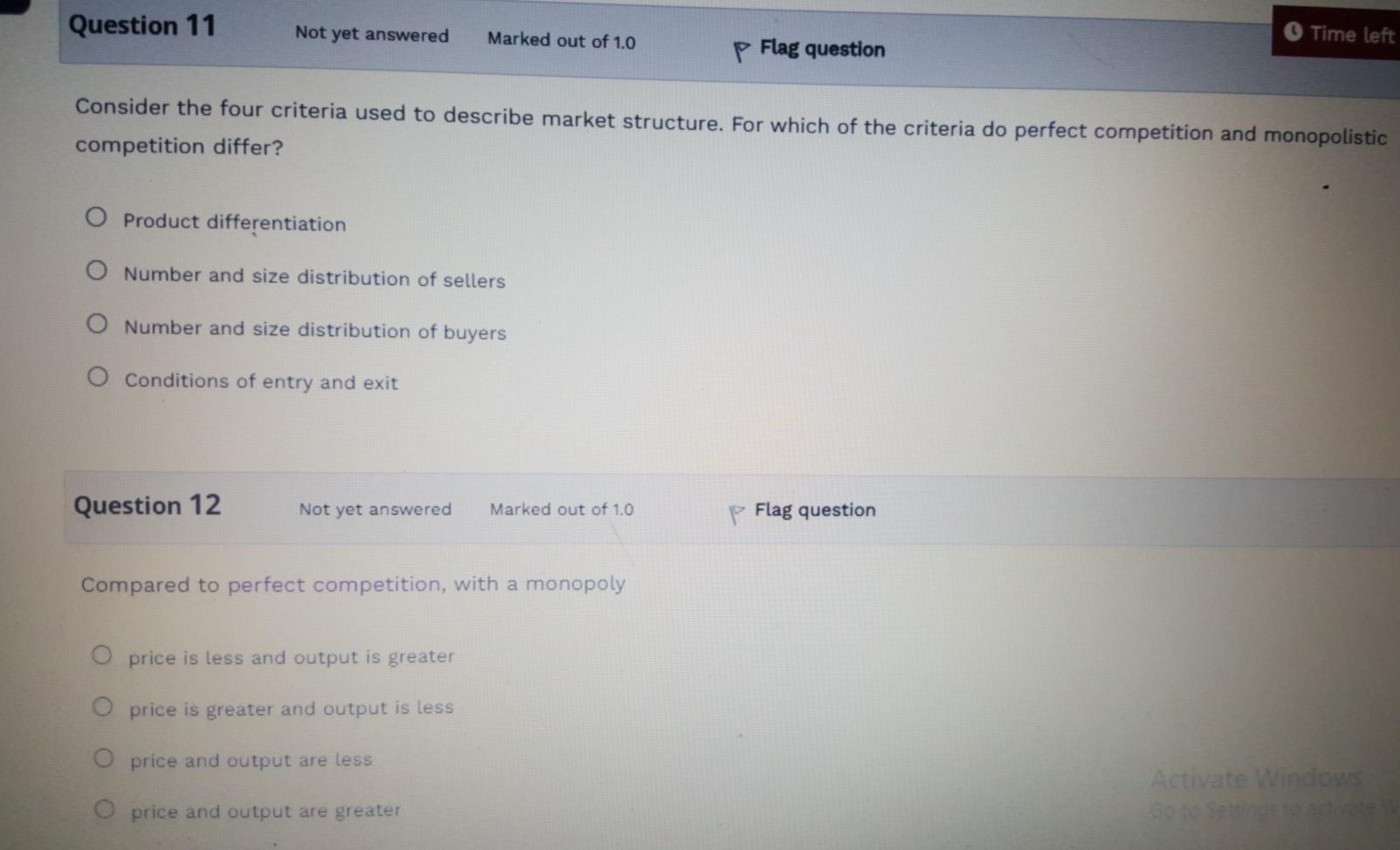
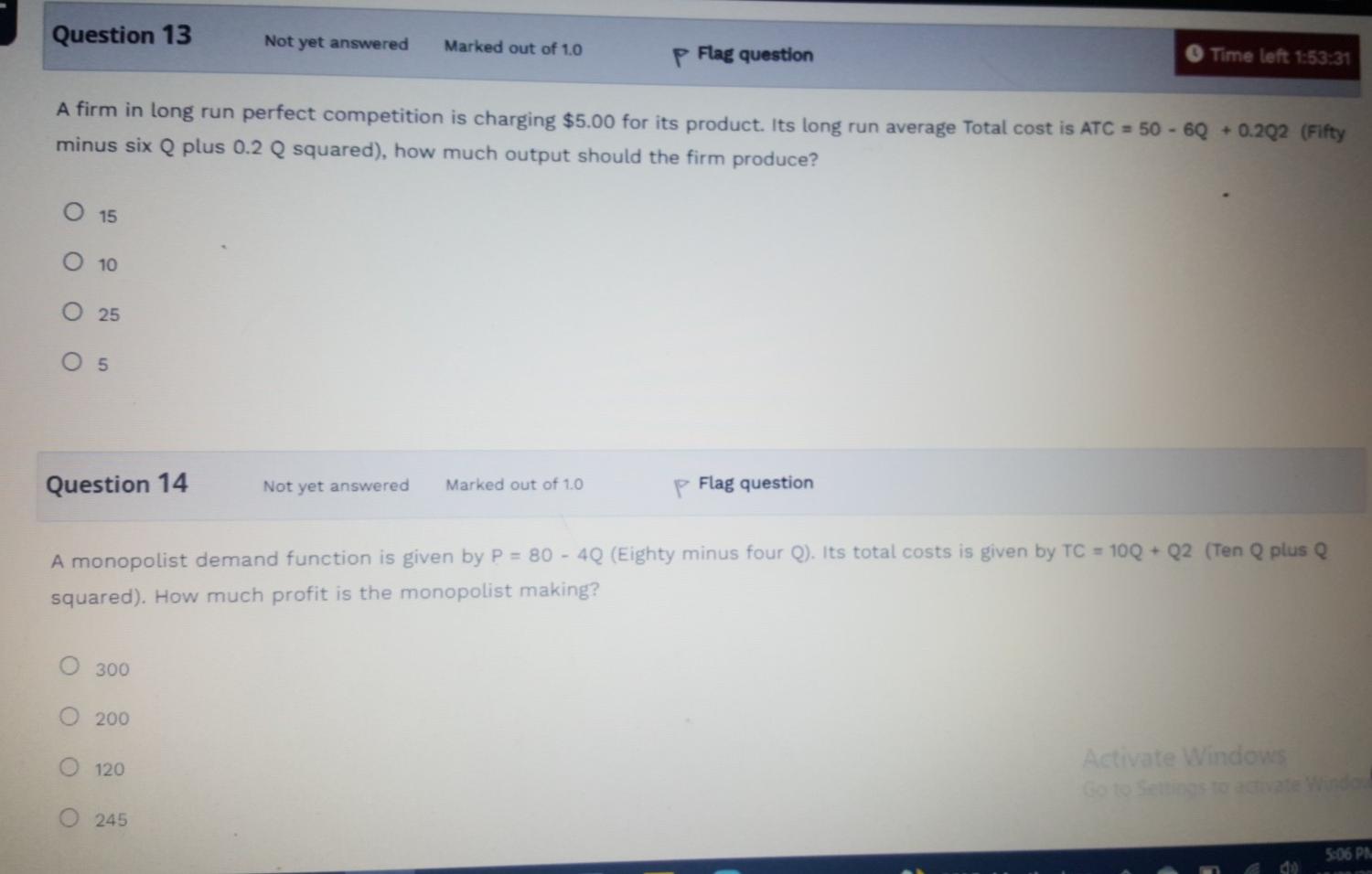
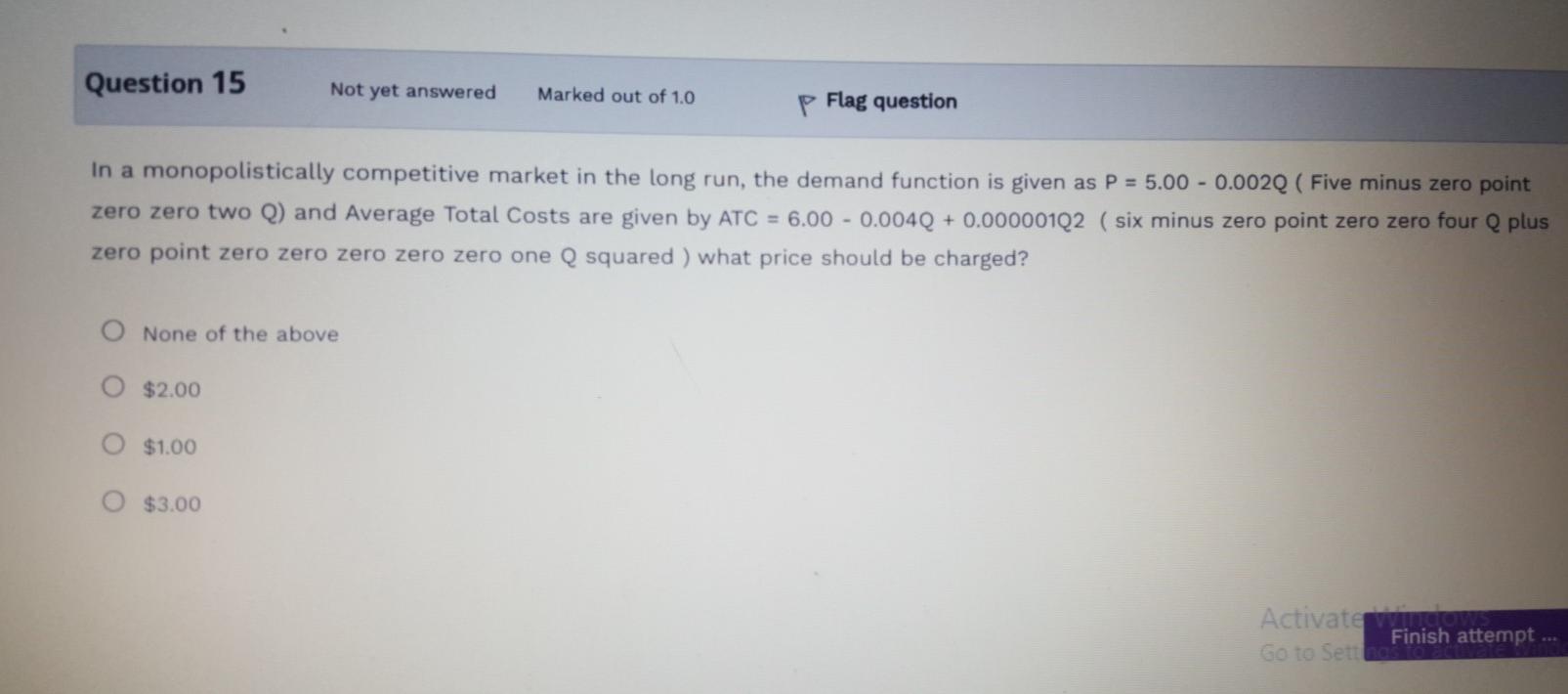
Question 1 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 P Flag question In a perfectly competitive market, the price of the good equals its marginal cost because O that is the price that the Government will allow producers to sell at O that is the price that allows firms to maximize profits O Price is less than marginal revenue O price is greater than marginal revenue Question 2 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 P Flag question The requirement for profit maximization under perfect competition is O Marginal revenue should be equal to marginal cost Average revenue should be equal to price. Marginal revenue should be less than marginal cost O Marginal Revenue should be greater than marginal cost Question 3 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 p Flag question In the long run, a perfectly competitive firm will always have negative above normal profits O zero above normal profits O Positive above normal profits O Either a profit or a loss Question 4 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 P Flag question If marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, increasing output will O All of the above reduce profits O have no impact on profits O Increase profits Question 5 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 P Flag question A monopolist's marginal revenue curve is always O above its demand curve O below its demand curve O the same as its demand curve O upward sloping Question 6 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 P Flag question The models of perfect competition and monopoly describe most real world markets are useful for establishing benchmarks to evaluate real world situations all of the above O provide few insights into the real world Question 7 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 P Flag question The behaviour of decision makers in perfectly competitive and monopoly firms in similar in the following respect? All of the above O in both cases, profits are maximized by setting price equal to marginal cost O in both cases, profits are maximized by setting marginal cost equal to marginal revenue O in both cases, profits are maximized by setting price equal to average cost Question 8 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 p Flag question Which of the following is true of both perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive firms? Both earn only a normal profit in the long run Both set price equal to marginal cost Both face slightly downward sloping demand curves Activate Go to Setti O Both sell a homogeneous product Question 9 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 p Flag question Firms in a monopolistically competitive industry face a horizontal demand curve O Have a large control over price May earn above normal profits in the long run O May earn above normal profits in the short run Question 10 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 Flag question Monopolistic competition is characterized by many firms selling differentiated products O few firms selling differentiated products O many firms selling identical products O Few firms selling identical products Question 11 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 Time left p Flag question Consider the four criteria used to describe market structure. For which of the criteria do perfect competition and monopolistic competition differ? O Product differentiation O Number and size distribution of sellers O Number and size distribution of buyers Conditions of entry and exit Question 12 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 Flag question Compared to perfect competition, with a monopoly O price is less and output is greater O price is greater and output is less O price and output are less Activate Windows Go to Set price and output are greater Question 13 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 p Flag question Time left 1:53:31 A firm in long run perfect competition is charging $5.00 for its product. Its long run average Total cost is ATC = 50 - 6Q + 0.202 (Fifty minus six Q plus 0.2 squared), how much output should the firm produce? O 15 O 10 O 25 O 5 Question 14 Not yet answered Marked out of 10 P Flag question A monopolist demand function is given by P = 80 - 4Q (Eighty minus four Q). Its total costs is given by TC = 10Q+Q2 (Ten plus Q squared). How much profit is the monopolist making? 300 0 200 120 Activate Windows Soto 245 5:06 PM Question 15 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.0 p Flag question In a monopolistically competitive market in the long run, the demand function is given as P = 5.00 -0.002Q (Five minus zero point zero zero two Q) and Average Total Costs are given by ATC = 6.00 - 0.004Q + 0.000001Q2 ( six minus zero point zero zero four plus zero point zero zero zero zero zero one Q squared ) what price should be charged? O None of the above O $2.00 $1.00 $3.00 Activate Go to Sett Finish attempt
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


