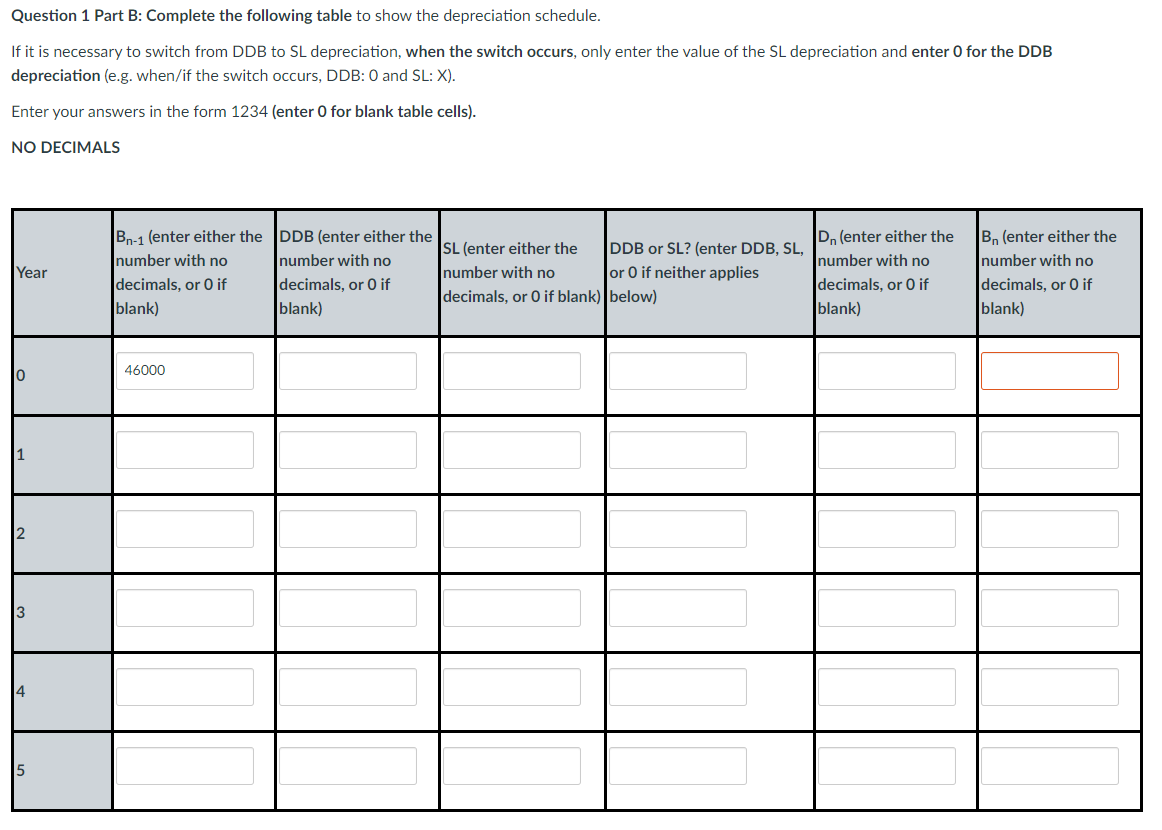

Question 1 Part B: Complete the following table to show the depreciation schedule. If it is necessary to switch from DDB to SL depreciation, when the switch occurs, only enter the value of the SL depreciation and enter 0 for the DDB depreciation (e.g. when/if the switch occurs, DDB: 0 and SL: X). Enter your answers in the form 1234 (enter 0 for blank table cells). NO DECIMALS Year B.-1 (enter either the DDB (enter either the SL (enter either the D. (enter either the DDB or SL? (enter DDB, SL, number with no number with no number with no number with no or 0 if neither applies decimals, or O if decimals, or if decimals, or O if decimals, or 0 if blank) below) blank) blank) blank) Bn (enter either the number with no decimals, or O if blank) 0 46000 3 4 5 Your company purchases a patent for $46,000 to attempt to compete in a usually restricted market. This patent does not have a salvage value at the end of its 5-year useful life. You are tasked with computing the depreciation schedule and book value for the patent using double declining balance with a switch to the straight-line method (if necessary). Question 7 Part A: Choose the correct formula for the Double-Declining Balance depreciation method. Depreciation, = (Initial Cost - Salvage Value)/(2*N) where N = the useful life of the project Depreciation, =Bn-1*(2/N) where N = the useful life of the project Depreciation - (Initial Cost - Salvage Value) / N where N = the useful life of the project Depreciation - (Bn-1)/N where N = the useful life of the project Question 1 Part B: Complete the following table to show the depreciation schedule. If it is necessary to switch from DDB to SL depreciation, when the switch occurs, only enter the value of the SL depreciation and enter 0 for the DDB depreciation (e.g. when/if the switch occurs, DDB: 0 and SL: X). Enter your answers in the form 1234 (enter 0 for blank table cells). NO DECIMALS Year B.-1 (enter either the DDB (enter either the SL (enter either the D. (enter either the DDB or SL? (enter DDB, SL, number with no number with no number with no number with no or 0 if neither applies decimals, or O if decimals, or if decimals, or O if decimals, or 0 if blank) below) blank) blank) blank) Bn (enter either the number with no decimals, or O if blank) 0 46000 3 4 5 Your company purchases a patent for $46,000 to attempt to compete in a usually restricted market. This patent does not have a salvage value at the end of its 5-year useful life. You are tasked with computing the depreciation schedule and book value for the patent using double declining balance with a switch to the straight-line method (if necessary). Question 7 Part A: Choose the correct formula for the Double-Declining Balance depreciation method. Depreciation, = (Initial Cost - Salvage Value)/(2*N) where N = the useful life of the project Depreciation, =Bn-1*(2/N) where N = the useful life of the project Depreciation - (Initial Cost - Salvage Value) / N where N = the useful life of the project Depreciation - (Bn-1)/N where N = the useful life of the project








