Question
Question #1 Question #2 Question #3 #4 Zentech Phone Gear Inc. produces high-quality, durable protective cases for a variety of cellular phones. The company just
Question #1
Question #2

Question #3
#4
Zentech Phone Gear Inc. produces high-quality, durable protective cases for a variety of cellular phones. The company just received a special order to produce 440 units of a modified case for a specific phone model. The unit cost for the regular case is $39 ($31 in total for variable costs and $8 for allocated fixed manufacturing overhead that is common to the company). A regular case is priced at $61/unit. Extra costs for the modified case would be as follows:
- Extra paint and plastic required for the modified case costs $1 per unit. - Adjustments to the design of the modified case costs $2,464 (a one-time cost). The price charged for a modified case is $63/unit. For each modified case produced and sold, the production and sale of a regular case must be given up. (i.e. Zentech Phone Gear is currently operating at full capacity). Should the company accept the order for the modified cases?
Do not enter dollar signs or commas in the input boxes.
Round Fixed Cost per Unit and Total Relevant Cost to 2 decimal places.
(Put answers here:)
FORGONE CONTRIBUTION MARGIN PER UNIT: $
VARIABLE COST PER UNIT: $
FIXES COST PER UNIT: $
TOTAL RELEVANT COSTS: $
ACCEPT OR REJECT:
QUESTION #5
Sparrow Rollers Company produces bikes. Each bike has the following costs:
| Direct Materials | $9.00 |
| Direct Labor | $12.00 |
| Variable Manufacturing Overhead | $5.00 |
| Allocated Fixed Manufacturing Overhead | $11.00 |
| Unit Cost | $37.00 |
Note: The fixed manufacturing overhead is common to the company. The production capacity is 347,000 units per year. However, Sparrow Rollers expects to produce only 246,000 units for the coming year. The company also has fixed selling costs of $613,000 per year and variable selling costs of $6 per unit sold. Each bike normally sells for $40 each. Recently, a customer offered to buy 49,000 bikes at a special price of $29 each. This order would not have any variable selling costs because no sales commissions are involved. Based on a quantitative analysis, should the company accept the special order?
Do not enter dollar signs or commas in the input boxes. Use the negative sign for values that must be subtracted and negative values.
| Total Revenues | $Answer |
| Total Direct Materials | $Answer |
| Total Direct Labor | $Answer |
| Total Variable Overhead | $Answer |
| Incremental Operating Income | $Answer |
The special order should be:
QUESTION # 6
Jenson Monitors Ltd., a manufacturer of computer monitors, currently produces a 19-inch LCD monitor. The company's accounting department has reported the following annual costs of producing the LCD monitor internally:
| Jenson Monitors Annual Production Costs for 19-inch LCD Monitor | ||
| Per Unit | 10,000 Units | |
| Direct Materials | $20.00 | $200,000 |
| Direct Labor | $14.00 | $140,000 |
| Variable Overhead | $5.00 | $50,000 |
| Production Supervisor's Salary | $15.00 | $150,000 |
| Depreciation of LCD manufacturing equipment | $4.00 | $40,000 |
| Allocated Fixed Overhead | $8.00 | $80,000 |
| Total Cost | $66.00 | $660,000 |
An external supplier has offered to provide Jenson Monitors 10,000 units of the same LCD monitor per year at a price of $46 each. Also consider the following information:
The LCD manufacturing equipment has no salvage value and has no other use aside from producing the 19-inch LCD monitors. It cannot be sold.
The fixed overhead costs allocated to the LCD monitors are common to all items produced in the factory.
The production supervisor will take over duties in another department if the monitors are purchased from the external supplier. If this is the case, his annual salary will drop to $135,000.
Should the company continue manufacturing the monitors internally or begin purchasing them from the external supplier? Do not enter dollar signs or commas in the input boxes. Round all answers to 2 decimal places.
| Jenson Monitors Make or Buy Analysis | |||||
| Production Cost Per Unit | Per Unit Differential Cost | Total Differential Cost (10,000 Units) | |||
| Make | Buy | Make | Buy | ||
| Direct Materials | $20.00 | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer |
| Direct Labor | $14.00 | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer |
| Variable Overhead | $5.00 | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer |
| Supervisor's Salary | $15.00 | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer |
| Depreciation of Equipment (sunk) | $4.00 | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer |
| Allocated Fixed Overhead (common) | $8.00 | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer |
| Outside Purchase Price | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer | |
| Total Relevant Cost | $66.00 | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer | $Answer |
The company should:
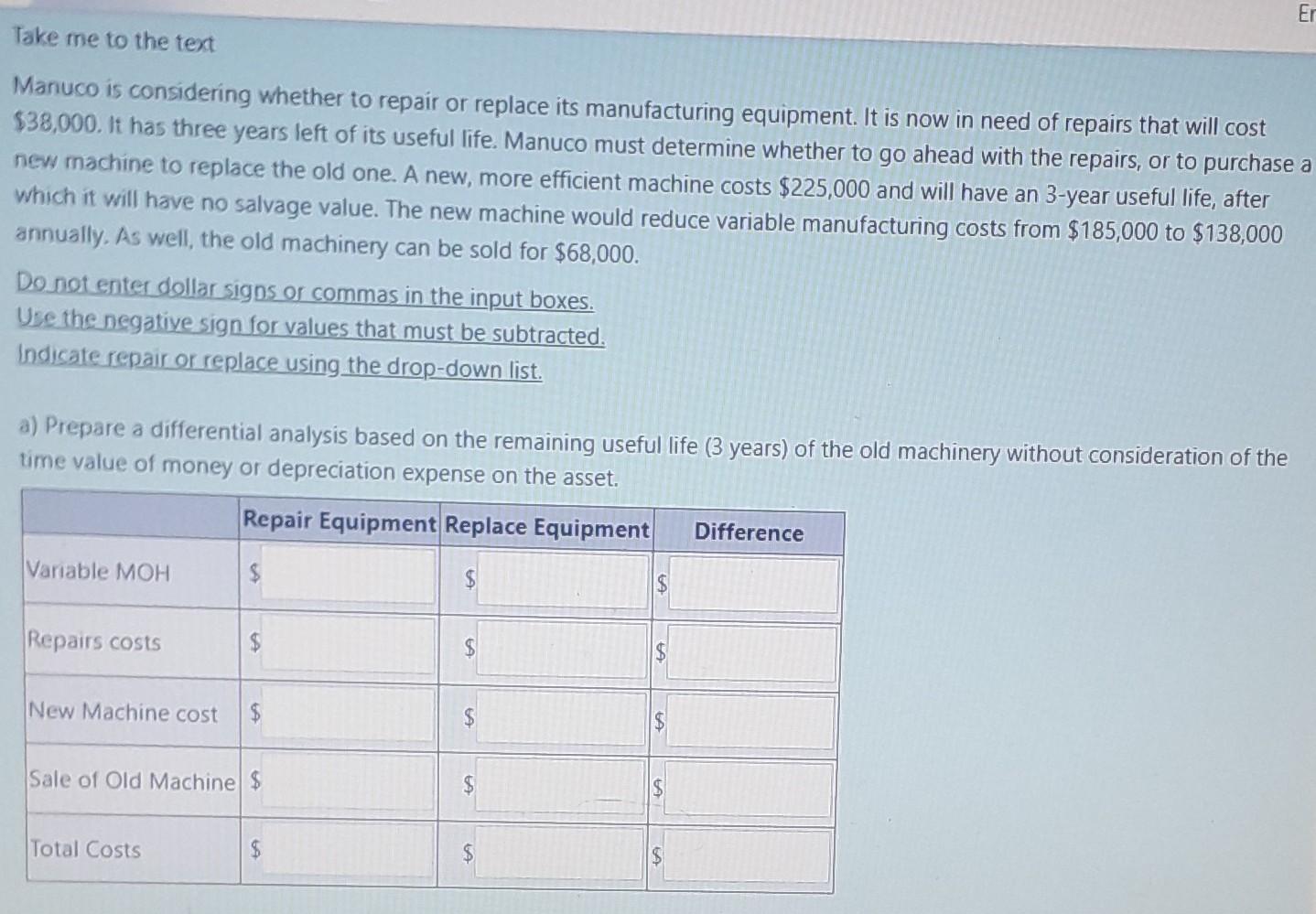
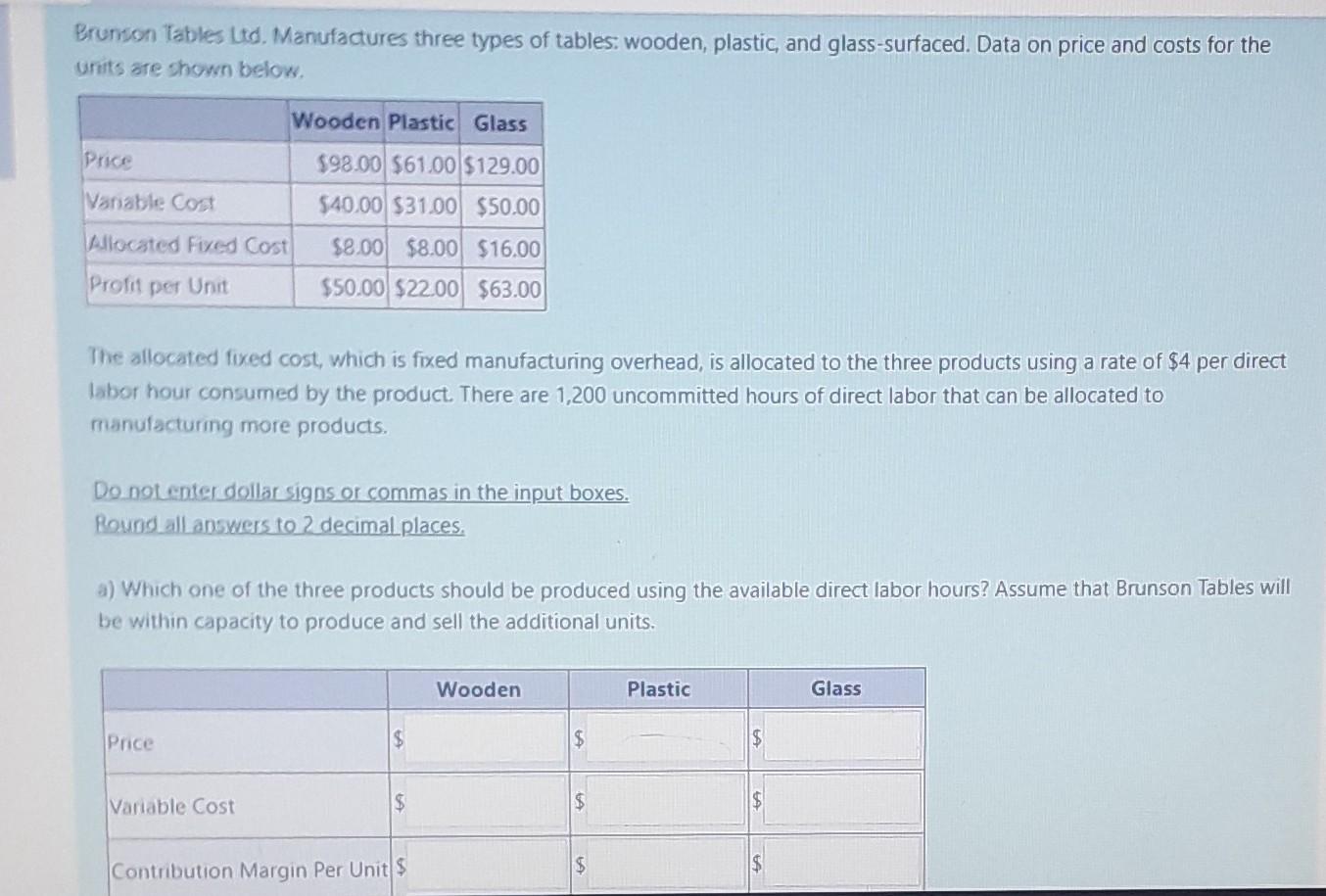
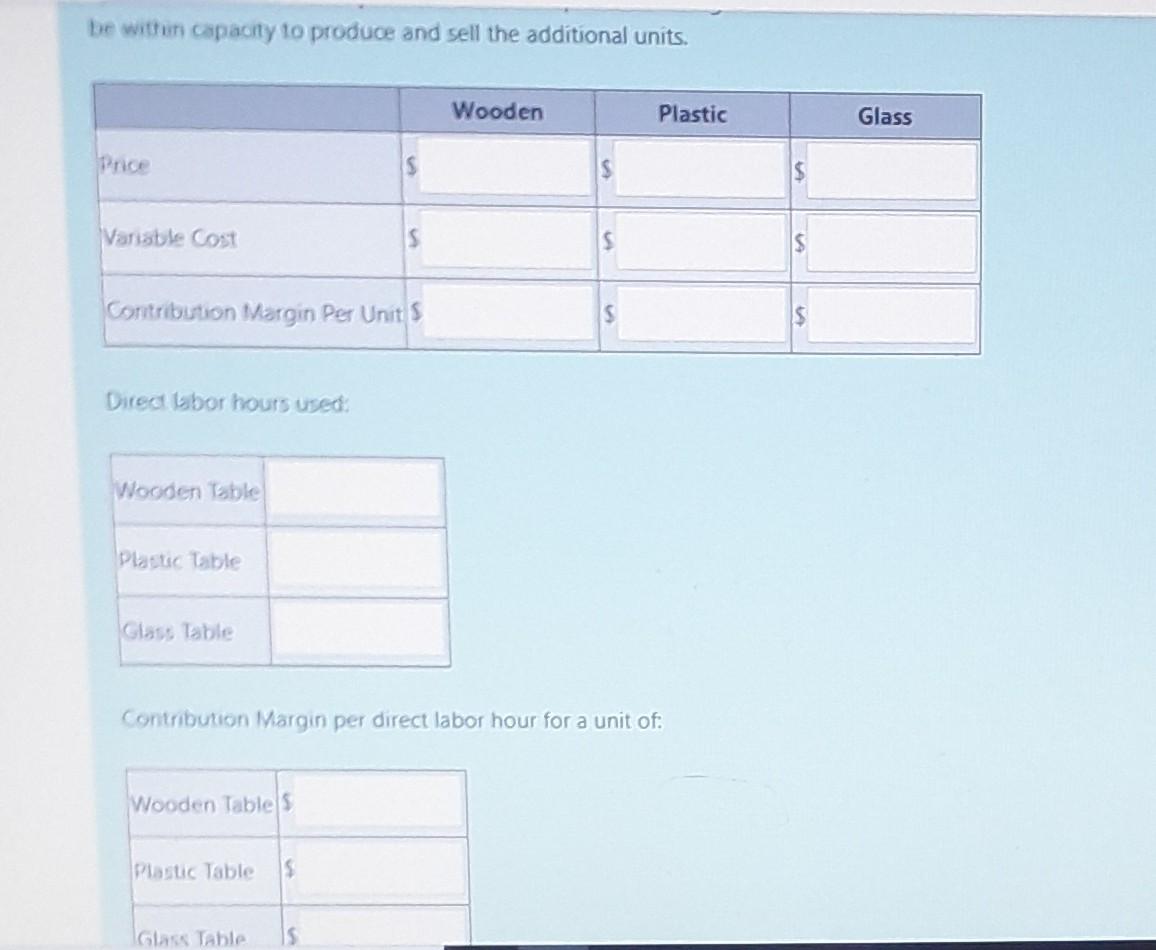
Take me to the text Manuco is considering whether to repair or replace its manufacturing equipment. It is now in need of repairs that will cost $38,000. It has three years left of its useful life. Manuco must determine whether to go ahead with the repairs, or to purchase a new machine to replace the old one. A new, more efficient machine costs $225,000 and will have an 3-year useful life, after which it will have no salvage value. The new machine would reduce variable manufacturing costs from $185,000 to $138,000 annually. As well, the old machinery can be sold for $68,000. Do not enter dollar signs or commas in the input boxes. Use the negative sign for values that must be subtracted. Indicate repair or replace using the drop-down list. a) Prepare a differential analysis based on the remaining useful life (3 years) of the old machinery without consideration of the time value of money or depreciation expense on the asset. Repair Equipment Replace Equipment Variable MOH Repairs costs New Machine cost $ Sale of Old Machine $ Total Costs $ LA $ $ LA LA Er Difference A company offers two versions of its main products: basic and luxury. The manufacturing process for these products is capital- intensive (e. primarily relies on the use of machines). The unit contribution margins for basic and luxury are $54.70 and $334.75 respectively. The company has 260 uncommitted hours of machine time that can be allocated to manufacturing more products. The machine hours used to produce one unit of basic is 0.5. The machine hours used per unit of luxury is 2.5. Do not enter dollar signs or commas in the input boxes. Bound your answers to 2 decimal places. a) Calculate the contribution margin per machine hour for each product. Basic S Luxury: $ b) Which product, basic or luxury, should be produced using the uncommitted machine hours? Assume that there are no capacity constraints. Item to be produced: c) How many units of the product selected in part b) above will be produced using the uncommitted machine time? Round the number of units to 2 decimal places. Number of units: d) What is the company's increase in contribution margin if the product selected in part b) will be produced using the uncommitted machine time? Increase in contribution margin: $ Brunson Tables Ltd. Manufactures three types of tables: wooden, plastic, and glass-surfaced. Data on price and costs for the units are shown below. Price Vanable Cost Allocated Fixed Cost Profit per Unit Wooden Plastic Glass $98.00 $61.00 $129.00 $40.00 $31.00 $50.00 $8.00 $8.00 $16.00 $50.00 $22.00 $63.00 The allocated fixed cost, which is fixed manufacturing overhead, is allocated to the three products using a rate of $4 per direct labor hour consumed by the product. There are 1,200 uncommitted hours of direct labor that can be allocated to manufacturing more products. Do not enter dollar signs or commas in the input boxes. Round all answers to 2 decimal places. a) Which one of the three products should be produced using the available direct labor hours? Assume that Brunson Tables will be within capacity to produce and sell the additional units. Price Variable Cost $ $ Contribution Margin Per Unit $ Wooden $ $ $ Plastic $ $ LA Glass be within capacity to produce and sell the additional units. Price Variable Cost Contribution Margin Per Unit S Direct labor hours used: Wooden Table Plastic Table Glass Table Wooden Table S S Plastic Table $ Contribution Margin per direct labor hour for a unit of: Glass Table IS Wooden Plastic SA S S GlassStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


