Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Please help solve these 3 questions BatCo makes baseball bats. Each bat requires 2.00 pounds of wood at $16
Question 1
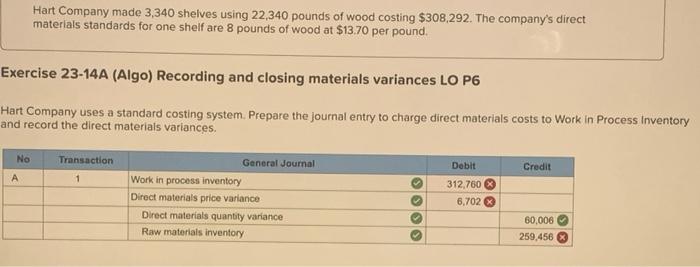
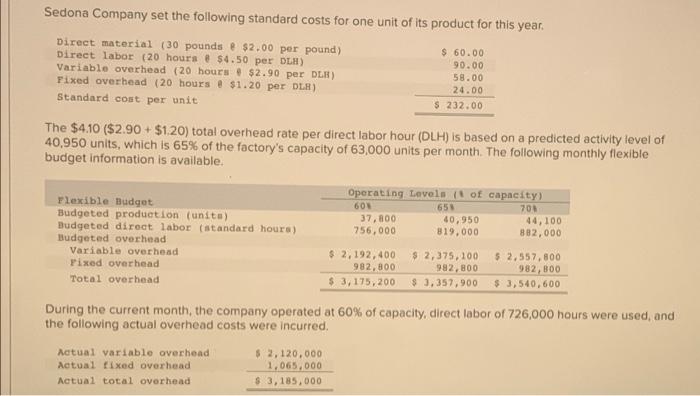
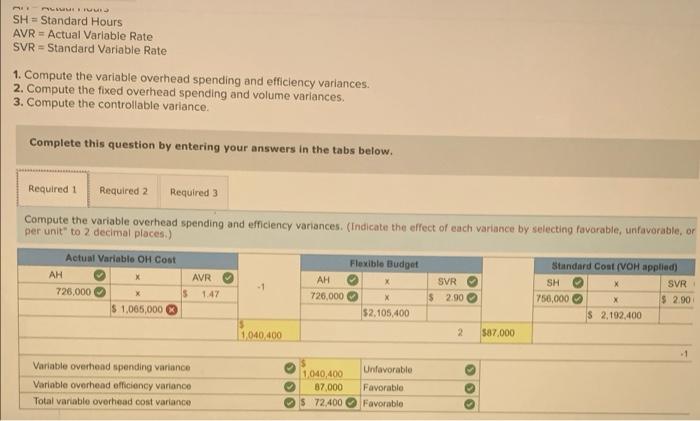
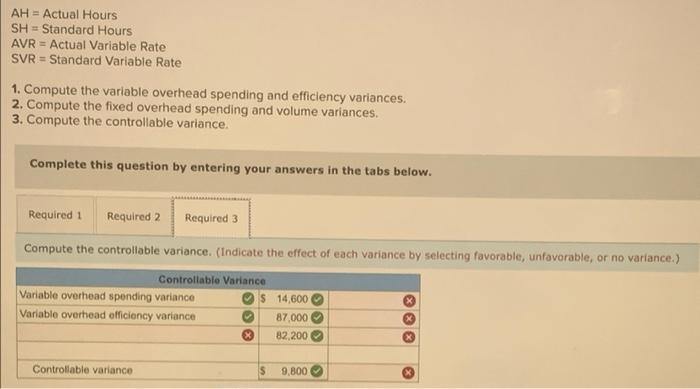
BatCo makes baseball bats. Each bat requires 2.00 pounds of wood at $16 per pound and 0.30 direct labor hour at $30 per hour. Overhead is assigned at the rate of $60 per direct labor hour. QS 23-6 (Algo) Total Cost variances LO P2 Assume the actual cost to manufacture 130 bats is $8,580.00, Compute the total cost variance and identify it as favorable on unfavorable. (Indicate the effect of the variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable or no variance.) Actual cost 7,670 3 Budgeted standard cost 8,580 Total cost variance (910) Unfavorable "led text indicates to response was peded in a cor a formulare con income deducted Hart Company made 3,340 shelves using 22,340 pounds of wood costing $308,292. The company's direct materials standards for one shelf are 8 pounds of wood at $13.70 per pound. Exercise 23-14A (Algo) Recording and closing materials variances LO P6 Hart Company uses a standard costing system. Prepare the journal entry to charge direct materials costs to Work in Process Inventory and record the direct materials variances No Transaction Credit 1 General Journal Work in process inventory Direct materials price variance Direct materials quantity variance Raw materials inventory Dobit 312,760 6.702 60,006 259,456 Sedona Company set the following standard costs for one unit of its product for this year. Direct material (30 pounds $2.00 per pound) $ 60.00 Direct labor (20 hours @ $4.50 per DLH) 90.00 Variable overhead (20 hours $2.90 per DLR) 58.00 Fixed overhead (20 hours a $1.20 per DLR) 24.00 Standard cost per unit $ 232.00 The $4.10 ($2.90 + $1.20) total overhead rate per direct labor hour (DLH) is based on a predicted activity level of 40,950 units, which is 65% of the factory's capacity of 63,000 units per month. The following monthly flexible budget information is available. Operating Levels of capacity) Flexible Budget 605 65 700 Budgeted production (unit) 37, 800 40,950 44,100 Budgeted direct labor (standard hours) 756,000 819.000 882,000 Budgeted overhead Variable overhead $ 2,192,400 $ 2,375,100 $ 2.557, 800 Pixed overhead 982,800 982,800 982,800 Total overhead $ 3,175,200 $ 3,357,900 $ 3,540,600 During the current month, the company operated at 60% of capacity, direct labor of 726,000 hours were used, and the following actual overhead costs were incurred. Actual variable overhead $ 2, 120,000 Actual fixed overhead 1,065,000 Actual total overhead $ 3,185,000 SH = Standard Hours AVR = Actual Variable Rate SVR = Standard Variable Rate 1. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. 2. Compute the fixed overhead spending and volume variances, 3. Compute the controllable variance. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable. per unit" to 2 decimal places.) Actual Variable OH Cost Flexible Budget Standard Cont(VOH applied) AH AVR AH -1 726,000 $ 1.47 726,000 $ 2.90 750,000 $ 2.90 $ 1,065,000 $2.105,400 $ 2,192,400 2 1.040.400 $87,000 X SVR SH SVR X 1 Variable overhead spending variance Variable overhead officiency variance Total variable overhead cost variance 1040,400 Unfavorable 87,000 Favorable $ 72,400 Favorable AH = Actual Hours SH - Standard Hours AVR = Actual Variable Rate SVR = Standard Variable Rate 1. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. 2. Compute the fixed overhead spending and volume variances. 3. Compute the controllable variance. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Compute the controllable variance. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no variance.) Controllable Variance Variable overhead spending variance $ 14,600 Variable overhead officiency variance 87.000 X 82,200 Controllable variance S 9,800 
Question 2

Question 3



Please help solve these 3 questions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


