Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 1: Question2: Question 3: Question 4: Question 5: Question 6: Question 7: Question 8: Question 9: Question 10: Question 11: Question 12: Question 13:
Question 1: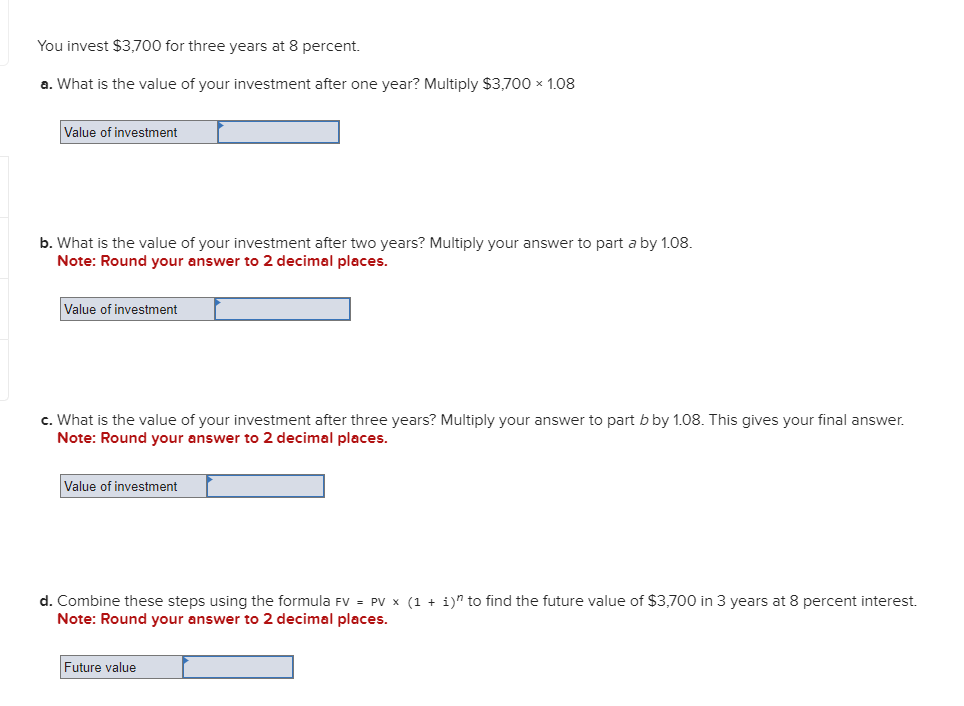
Question2:
Question 3:

Question 4:
Question 5:
Question 6:

Question 7:
Question 8:

Question 9:

Question 10:
Question 11:
Question 12:
Question 13:
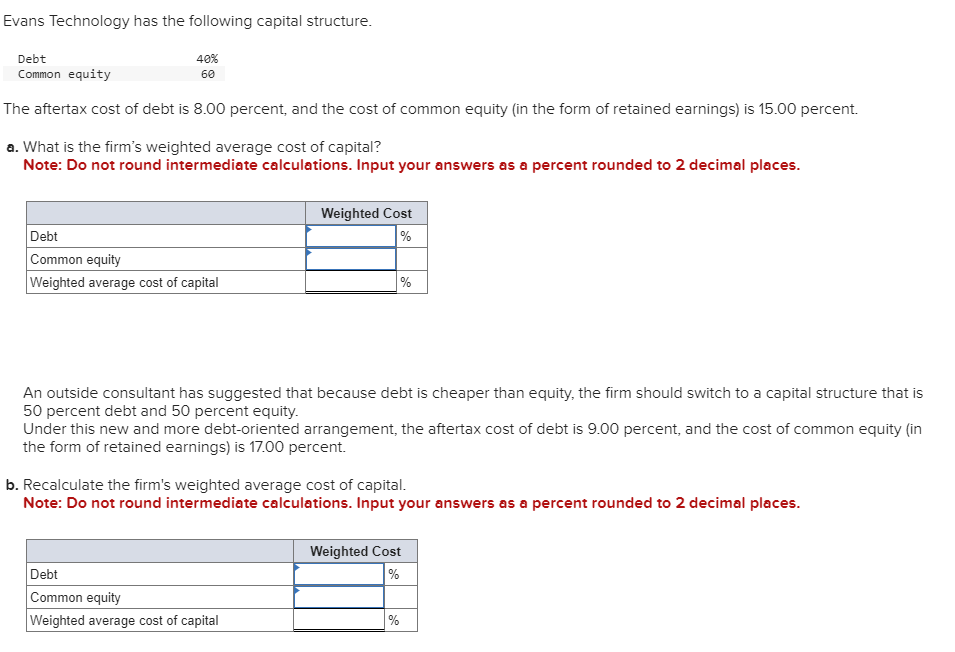
Question 14:
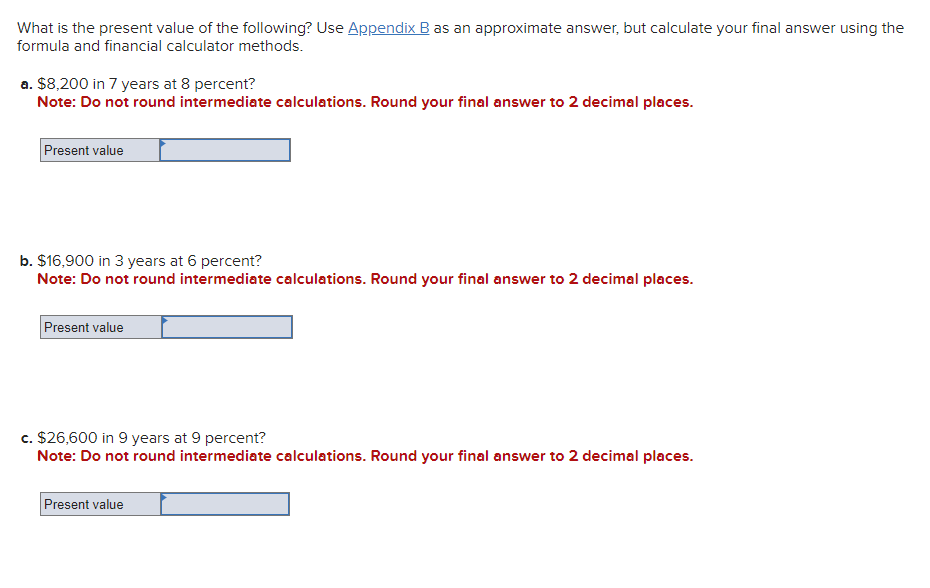
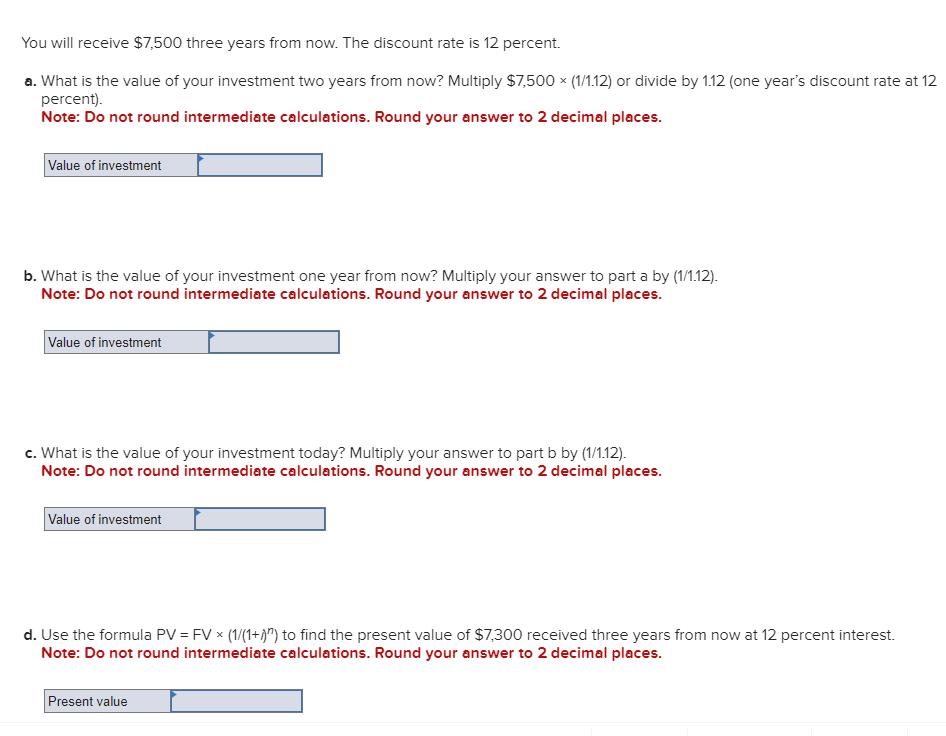
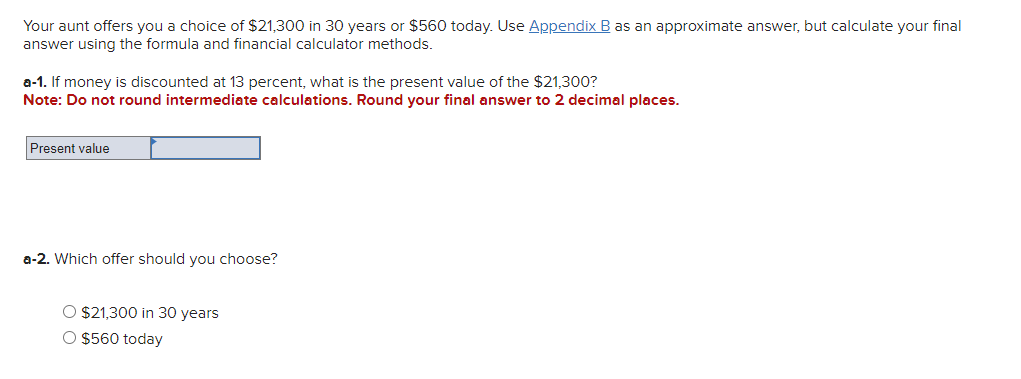
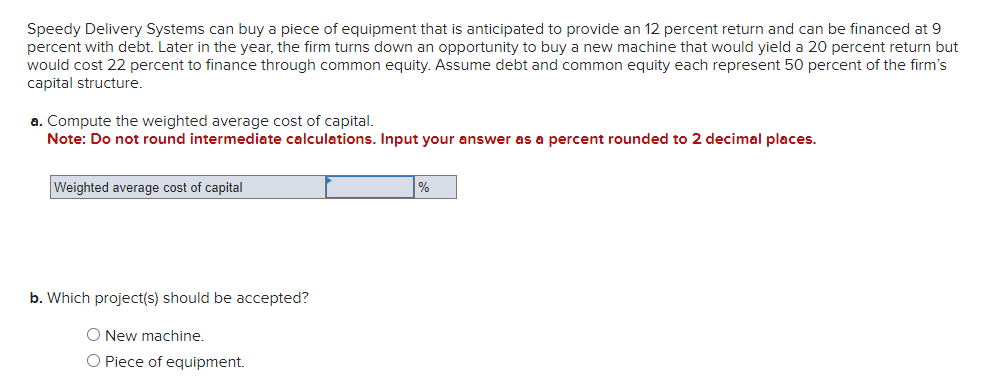
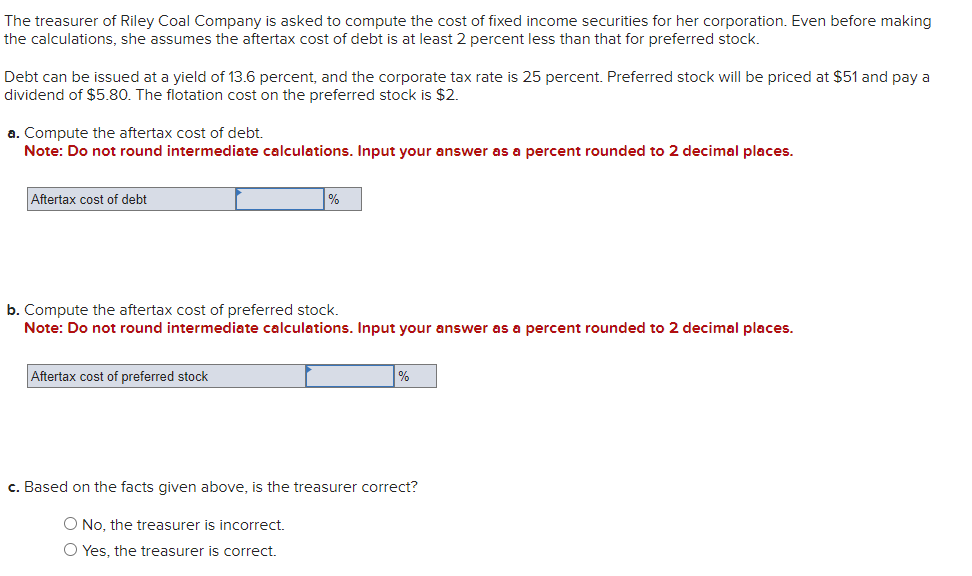
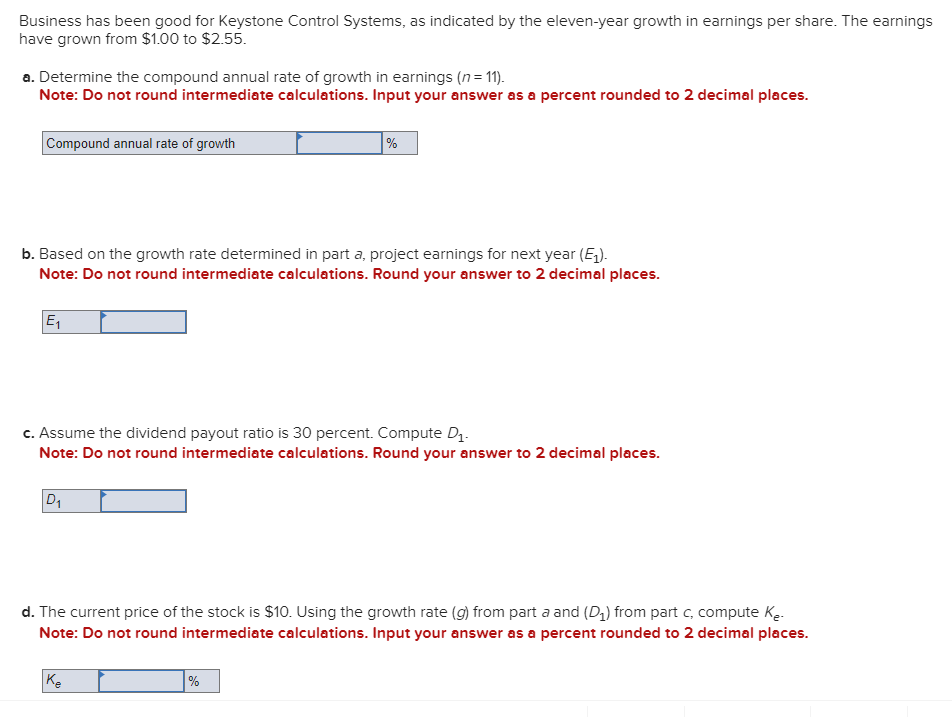
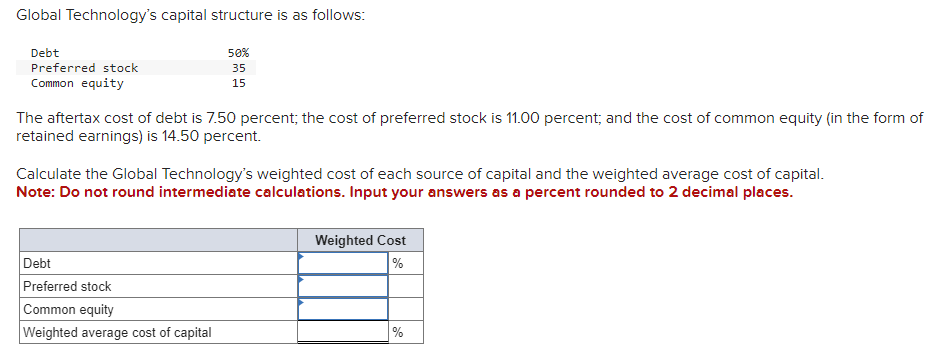
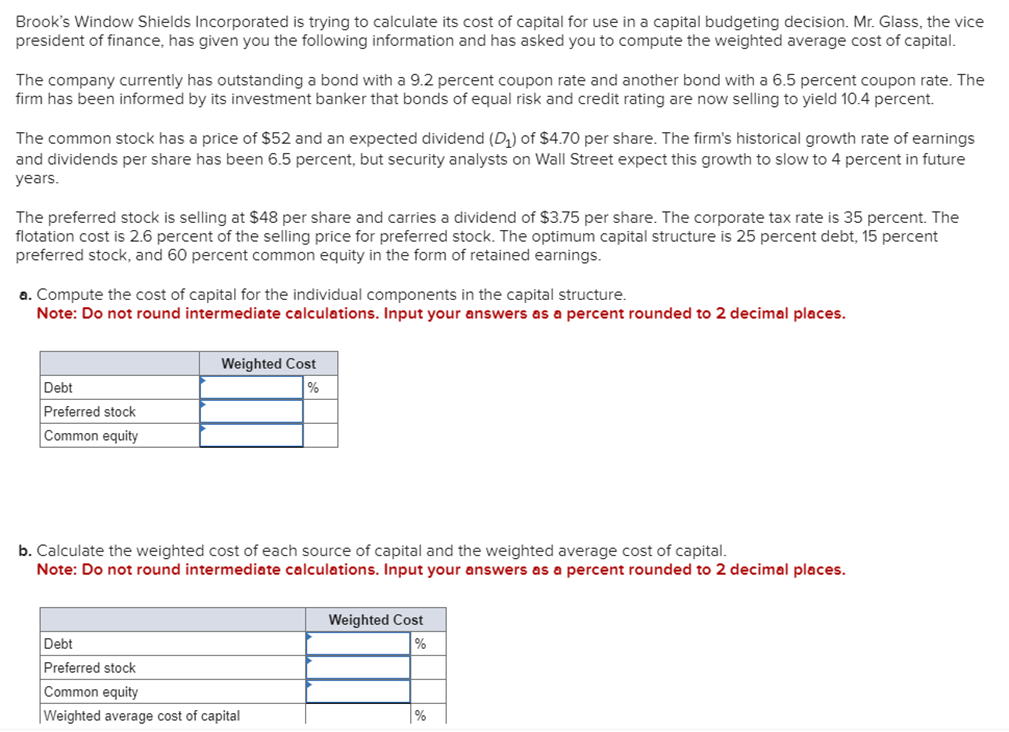 Business has been good for Keystone Control Systems, as indicated by the eleven-year growth in earnings per share. The earnings have grown from $1.00 to $2.55. a. Determine the compound annual rate of growth in earnings (n=11). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b. Based on the growth rate determined in part a, project earnings for next year (E1). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. c. Assume the dividend payout ratio is 30 percent. Compute D1. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. d. The current price of the stock is $10. Using the growth rate (g) from part a and (D1) from part c, compute Ke. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. Evans Technology has the following capital structure. The aftertax cost of debt is 8.00 percent, and the cost of common equity (in the form of retained earnings) is 15.00 percent. a. What is the firm's weighted average cost of capital? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. An outside consultant has suggested that because debt is cheaper than equity, the firm should switch to a capital structure that is 50 percent debt and 50 percent equity. Under this new and more debt-oriented arrangement, the aftertax cost of debt is 9.00 percent, and the cost of common equity (in the form of retained earnings) is 17.00 percent. b. Recalculate the firm's weighted average cost of capital. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. A brilliant young scientist is killed in a plane crash. It is anticipated that he could have earned $250,000 a year for the next 20 years. The attorney for the plaintiff's estate argues that the lost income should be discounted back to the present at 4 percent. The lawyer for the defendant's insurance company argues for a discount rate of 9 percent. What is the difference between the present value of the settlement at 4 percent and 9 percent? Compute each one separately. Use Appendix D for an approximate answer but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. You invest $3,700 for three years at 8 percent. a. What is the value of your investment after one year? Multiply $3,7001.08 b. What is the value of your investment after two years? Multiply your answer to part a by 1.08 . Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. c. What is the value of your investment after three years? Multiply your answer to part b by 1.08 . This gives your final answer. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. d. Combine these steps using the formula FV =PV(1+i)n to find the future value of $3,700 in 3 years at 8 percent interest. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Brook's Window Shields Incorporated is trying to calculate its cost of capital for use in a capital budgeting decision. Mr. Glass, the vice president of finance, has given you the following information and has asked you to compute the weighted average cost of capital. The company currently has outstanding a bond with a 9.2 percent coupon rate and another bond with a 6.5 percent coupon rate. The firm has been informed by its investment banker that bonds of equal risk and credit rating are now selling to yield 10.4 percent. The common stock has a price of $52 and an expected dividend (D1) of $4.70 per share. The firm's historical growth rate of earnings and dividends per share has been 6.5 percent, but security analysts on Wall Street expect this growth to slow to 4 percent in future years. The preferred stock is selling at $48 per share and carries a dividend of $3.75 per share. The corporate tax rate is 35 percent. The flotation cost is 2.6 percent of the selling price for preferred stock. The optimum capital structure is 25 percent debt, 15 percent preferred stock, and 60 percent common equity in the form of retained earnings. a. Compute the cost of capital for the individual components in the capital structure. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b. Calculate the weighted cost of each source of capital and the weighted average cost of capital. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. Global Technology's capital structure is as follows: The aftertax cost of debt is 7.50 percent; the cost of preferred stock is 11.00 percent; and the cost of common equity (in the form of retained earnings) is 14.50 percent. Calculate the Global Technology's weighted cost of each source of capital and the weighted average cost of capital. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. Your aunt offers you a choice of $21,300 in 30 years or $560 today. Use Appendix B as an approximate answer, but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. a-1. If money is discounted at 13 percent, what is the present value of the $21,300 ? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. a-2. Which offer should you choose? $21,300in30years$560today a. What is the present value of $250,000 to be received after 40 years with a 15 percent discount rate? Use Appendix B as an approximate answer, but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. b. Would the present value of the funds in part a be enough to buy a $990 concert ticket? No Yes Telecom Systems can issue debt yielding 12 percent. The company is in a 40 percent bracket. What is its aftertax cost of debt? Note: Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. The treasurer of Riley Coal Company is asked to compute the cost of fixed income securities for her corporation. Even before making the calculations, she assumes the aftertax cost of debt is at least 2 percent less than that for preferred stock. Debt can be issued at a yield of 13.6 percent, and the corporate tax rate is 25 percent. Preferred stock will be priced at $51 and pay a dividend of $5.80. The flotation cost on the preferred stock is $2. a. Compute the aftertax cost of debt. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b. Compute the aftertax cost of preferred stock. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. c. Based on the facts given above, is the treasurer correct? No, the treasurer is incorrect. Yes, the treasurer is correct. Speedy Delivery Systems can buy a piece of equipment that is anticipated to provide an 12 percent return and can be financed at 9 percent with debt. Later in the year, the firm turns down an opportunity to buy a new machine that would yield a 20 percent return but would cost 22 percent to finance through common equity. Assume debt and common equity each represent 50 percent of the firm's capital structure. a. Compute the weighted average cost of capital. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b. Which project(s) should be accepted? New machine. Piece of equipment. What is the present value of the following? Use Appendix B as an approximate answer, but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. a. $8,200 in 7 years at 8 percent? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. b. $16,900 in 3 years at 6 percent? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. c. $26,600 in 9 years at 9 percent? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. You are going to receive $209,000 in 40 years. What is the difference in present value between using a discount rate of 12 percent versus 7 percent? Use Appendix B as an approximate answer, but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. Note: Input your answer as a positive value. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. You will receive $7,500 three years from now. The discount rate is 12 percent. a. What is the value of your investment two years from now? Multiply $7,500(1/1.12) or divide by 1.12 (one year's discount rate at 12 percent). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. b. What is the value of your investment one year from now? Multiply your answer to part a by (1/1.12). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. c. What is the value of your investment today? Multiply your answer to part b by (1/1.12). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. d. Use the formula PV=FV(1/(1+i)n) to find the present value of $7,300 received three years from now at 12 percent interest. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places
Business has been good for Keystone Control Systems, as indicated by the eleven-year growth in earnings per share. The earnings have grown from $1.00 to $2.55. a. Determine the compound annual rate of growth in earnings (n=11). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b. Based on the growth rate determined in part a, project earnings for next year (E1). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. c. Assume the dividend payout ratio is 30 percent. Compute D1. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. d. The current price of the stock is $10. Using the growth rate (g) from part a and (D1) from part c, compute Ke. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. Evans Technology has the following capital structure. The aftertax cost of debt is 8.00 percent, and the cost of common equity (in the form of retained earnings) is 15.00 percent. a. What is the firm's weighted average cost of capital? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. An outside consultant has suggested that because debt is cheaper than equity, the firm should switch to a capital structure that is 50 percent debt and 50 percent equity. Under this new and more debt-oriented arrangement, the aftertax cost of debt is 9.00 percent, and the cost of common equity (in the form of retained earnings) is 17.00 percent. b. Recalculate the firm's weighted average cost of capital. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. A brilliant young scientist is killed in a plane crash. It is anticipated that he could have earned $250,000 a year for the next 20 years. The attorney for the plaintiff's estate argues that the lost income should be discounted back to the present at 4 percent. The lawyer for the defendant's insurance company argues for a discount rate of 9 percent. What is the difference between the present value of the settlement at 4 percent and 9 percent? Compute each one separately. Use Appendix D for an approximate answer but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. You invest $3,700 for three years at 8 percent. a. What is the value of your investment after one year? Multiply $3,7001.08 b. What is the value of your investment after two years? Multiply your answer to part a by 1.08 . Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. c. What is the value of your investment after three years? Multiply your answer to part b by 1.08 . This gives your final answer. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. d. Combine these steps using the formula FV =PV(1+i)n to find the future value of $3,700 in 3 years at 8 percent interest. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Brook's Window Shields Incorporated is trying to calculate its cost of capital for use in a capital budgeting decision. Mr. Glass, the vice president of finance, has given you the following information and has asked you to compute the weighted average cost of capital. The company currently has outstanding a bond with a 9.2 percent coupon rate and another bond with a 6.5 percent coupon rate. The firm has been informed by its investment banker that bonds of equal risk and credit rating are now selling to yield 10.4 percent. The common stock has a price of $52 and an expected dividend (D1) of $4.70 per share. The firm's historical growth rate of earnings and dividends per share has been 6.5 percent, but security analysts on Wall Street expect this growth to slow to 4 percent in future years. The preferred stock is selling at $48 per share and carries a dividend of $3.75 per share. The corporate tax rate is 35 percent. The flotation cost is 2.6 percent of the selling price for preferred stock. The optimum capital structure is 25 percent debt, 15 percent preferred stock, and 60 percent common equity in the form of retained earnings. a. Compute the cost of capital for the individual components in the capital structure. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b. Calculate the weighted cost of each source of capital and the weighted average cost of capital. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. Global Technology's capital structure is as follows: The aftertax cost of debt is 7.50 percent; the cost of preferred stock is 11.00 percent; and the cost of common equity (in the form of retained earnings) is 14.50 percent. Calculate the Global Technology's weighted cost of each source of capital and the weighted average cost of capital. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. Your aunt offers you a choice of $21,300 in 30 years or $560 today. Use Appendix B as an approximate answer, but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. a-1. If money is discounted at 13 percent, what is the present value of the $21,300 ? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. a-2. Which offer should you choose? $21,300in30years$560today a. What is the present value of $250,000 to be received after 40 years with a 15 percent discount rate? Use Appendix B as an approximate answer, but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. b. Would the present value of the funds in part a be enough to buy a $990 concert ticket? No Yes Telecom Systems can issue debt yielding 12 percent. The company is in a 40 percent bracket. What is its aftertax cost of debt? Note: Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. The treasurer of Riley Coal Company is asked to compute the cost of fixed income securities for her corporation. Even before making the calculations, she assumes the aftertax cost of debt is at least 2 percent less than that for preferred stock. Debt can be issued at a yield of 13.6 percent, and the corporate tax rate is 25 percent. Preferred stock will be priced at $51 and pay a dividend of $5.80. The flotation cost on the preferred stock is $2. a. Compute the aftertax cost of debt. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b. Compute the aftertax cost of preferred stock. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. c. Based on the facts given above, is the treasurer correct? No, the treasurer is incorrect. Yes, the treasurer is correct. Speedy Delivery Systems can buy a piece of equipment that is anticipated to provide an 12 percent return and can be financed at 9 percent with debt. Later in the year, the firm turns down an opportunity to buy a new machine that would yield a 20 percent return but would cost 22 percent to finance through common equity. Assume debt and common equity each represent 50 percent of the firm's capital structure. a. Compute the weighted average cost of capital. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Input your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. b. Which project(s) should be accepted? New machine. Piece of equipment. What is the present value of the following? Use Appendix B as an approximate answer, but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. a. $8,200 in 7 years at 8 percent? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. b. $16,900 in 3 years at 6 percent? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. c. $26,600 in 9 years at 9 percent? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. You are going to receive $209,000 in 40 years. What is the difference in present value between using a discount rate of 12 percent versus 7 percent? Use Appendix B as an approximate answer, but calculate your final answer using the formula and financial calculator methods. Note: Input your answer as a positive value. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. You will receive $7,500 three years from now. The discount rate is 12 percent. a. What is the value of your investment two years from now? Multiply $7,500(1/1.12) or divide by 1.12 (one year's discount rate at 12 percent). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. b. What is the value of your investment one year from now? Multiply your answer to part a by (1/1.12). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. c. What is the value of your investment today? Multiply your answer to part b by (1/1.12). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. d. Use the formula PV=FV(1/(1+i)n) to find the present value of $7,300 received three years from now at 12 percent interest. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


