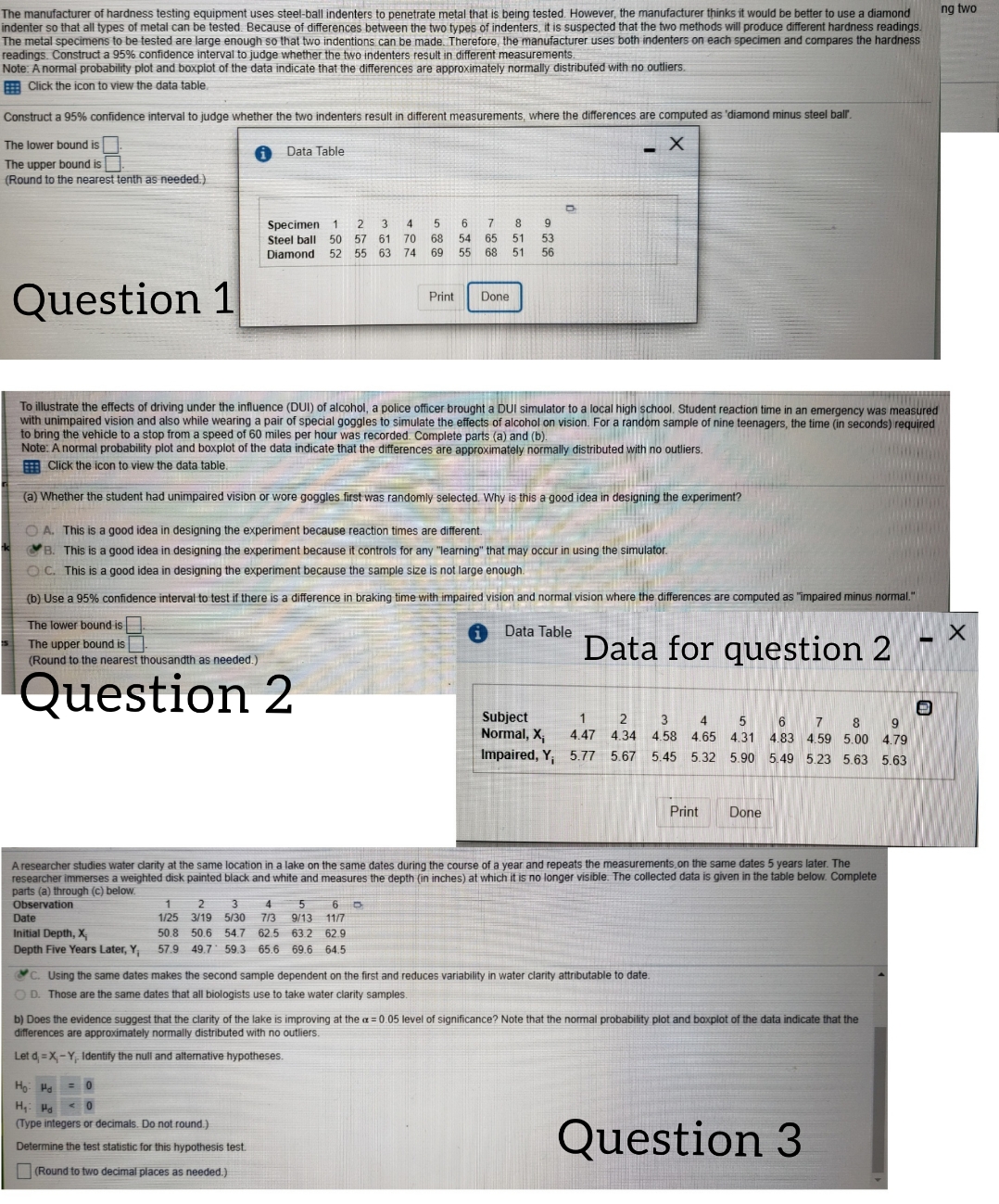
Question 1: The manufacturer of hardness testing equipment uses steel ball... Question 2: To illustrate the effects of driving... Question 3: A researcher studies water clarity...
The manufacturer of hardness testing equipment uses steel-ball indenters to penetrate metal that is being tested. However, the manufacturer thinks it would be better to use a diamond ng two indenter so that all types of metal can be tested. Because of differences between the two types of indenters, it is suspected that the two methods will produce different hardness readings. The metal specimens to be tested are large enough so that two indentions can be made. Therefore, the manufacturer uses both indenters on each specimen and compares the hardness readings. Construct a 95% confidence interval to judge whether the two indenters result in different measurements. Note: A normal probability plot and boxplot of the data indicate that the differences are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Click the icon to view the data table. Construct a 95% confidence interval to judge whether the two indenters result in different measurements, where the differences are computed as 'diamond minus steel ball The lower bound is Data Table X The upper bound is (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.) Specimen 1 2 3 4 Steel ball 50 57 61 70 68 65 Diamond 57 55 63 74 65 Question 1 Print Done To illustrate the effects of driving under the influence (DUI) of alcohol, a police officer brought a DUI simulator to a local high school. Student reaction time in an emergency was measured with unimpaired vision and also while wearing a pair of special goggles to simulate the effects of alcohol on vision. For a random sample of nine teenagers, the time (in seconds) required to bring the vehicle to a stop from a speed of 60 miles per hour was recorded. Complete parts (a) and (b). Note: A normal probability plot and boxplot of the data indicate that the differences are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Click the icon to view the data table. (a) Whether the student had unimpaired vision or wore goggles first was randomly selected. Why is this a good idea in designing the experiment? O A. This is a good idea in designing the experiment because reaction times are different. B. This is a good idea in designing the experiment because it controls for any "learning" that may occur in using the simulator. O C. This is a good idea in designing the experiment because the sample size is not large enough. (b) Use a 95% confidence interval to test if there is a difference in braking time with impaired vision and normal vision where the differences are computed as "impaired minus normal." The lower bound is The upper bound is i Data Table (Round to the nearest thousandth as needed.) Data for question 2 X Question 2 Subject Normal, X; 4.47 4.34 4 58 4.65 4.31 4.83 4.59 5.00 4.79 5 6 7 8 9 Impaired, Y, 5.77 5.67 5.45 5.32 5.90 5.49 5.23 5.63 5.63 Print Done A researcher studies water clarity at the same location in a lake on the same dates during the course of a year and repeats the measurements. on the same dates 5 years later. The researcher immerses a weighted disk painted black and white and measures the depth (in inches) at which it is no longer visible. The collected data is given in the table below. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. Observation 2 3 4 5 6 9 Date 1/25 3/19 5/30 3 9/13 11/7 Initial Depth, X; 50.8 50.6 54.7 62.5 63.2 62 9 Depth Five Years Later, Y, 57.9 49.7 59.3 65.6 69.6 64.5 C. Using the same dates makes the second sample dependent on the first and reduces variability in water clarity attributable to date. OD. Those are the same dates that all b ists use to take water clarity samples b) Does the evidence suggest that the clarity of the lake is improving at the a = 0.05 level of significance? Note that the normal probability plot and boxplot of the data indicate that the differences are approximately normally distributed with no outliers. Let dj = X - Y, Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho Ho = 0 Hy : H8 0 (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Determine the test statistic for this hypothesis test. Question 3 (Round to two decimal places as needed.)