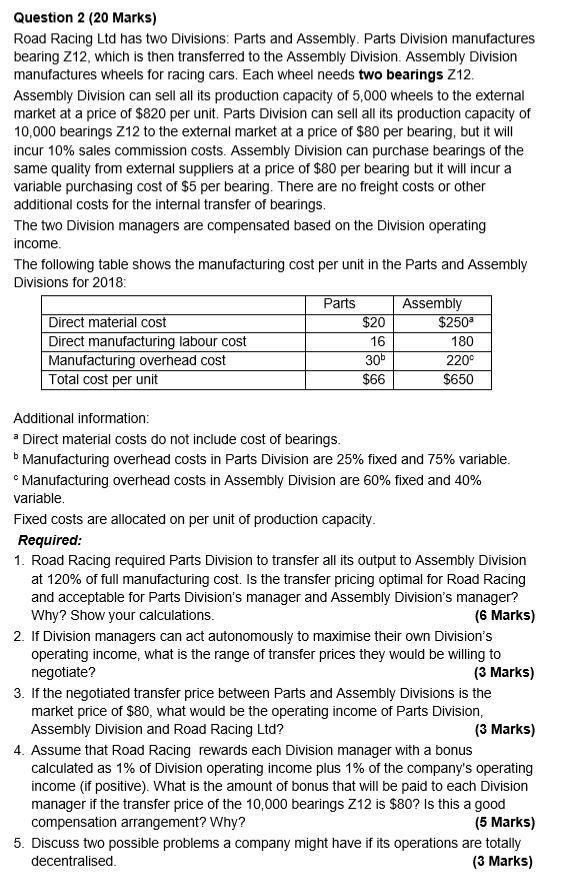
Question 2 (20 Marks) Road Racing Ltd has two Divisions: Parts and Assembly. Parts Division manufactures bearing Z12, which is then transferred to the Assembly Division. Assembly Division manufactures wheels for racing cars. Each wheel needs two bearings Z12. Assembly Division can sell all its production capacity of 5,000 wheels to the external market at a price of $820 per unit. Parts Division can sell all its production capacity of 10,000 bearings Z12 to the external market at a price of $80 per bearing, but it will incur 10% sales commission costs. Assembly Division can purchase bearings of the same quality from external suppliers at a price of $80 per bearing but it will incur a variable purchasing cost of $5 per bearing. There are no freight costs or other additional costs for the internal transfer of bearings The two Division managers are compensated based on the Division operating income. The following table shows the manufacturing cost per unit in the Parts and Assembly Divisions for 2018: Parts Assembly Direct material cost $20 $250" Direct manufacturing labour cost 16 180 Manufacturing overhead cost 306 220 Total cost per unit $66 $650 Additional information: a Direct material costs do not include cost of bearings. Manufacturing overhead costs in Parts Division are 25% fixed and 75% variable Manufacturing overhead costs in Assembly Division are 60% fixed and 40% variable. Fixed costs are allocated on per unit of production capacity. Required: 1. Road Racing required Parts Division to transfer all its output to Assembly Division at 120% of full manufacturing cost. Is the transfer pricing optimal for Road Racing and acceptable for Parts Division's manager and Assembly Division's manager? Why? Show your calculations. (6 Marks) 2. If Division managers can act autonomously to maximise their own Division's operating income, what is the range of transfer prices they would be willing to negotiate? (3 Marks) 3. If the negotiated transfer price between Parts and Assembly Divisions is the market price of $80, what would be the operating income of Parts Division, Assembly Division and Road Racing Ltd? (3 Marks) 4. Assume that Road Racing rewards each Division manager with a bonus calculated as 1% of Division operating income plus 1% of the company's operating income (if positive). What is the amount of bonus that will be paid to each Division manager if the transfer price of the 10,000 bearings Z12 is $80? Is this a good compensation arrangement? Why? (5 Marks) 5. Discuss two possible problems a company might have if its operations are totally decentralised. (3 Marks) Question 2 (20 Marks) Road Racing Ltd has two Divisions: Parts and Assembly. Parts Division manufactures bearing Z12, which is then transferred to the Assembly Division. Assembly Division manufactures wheels for racing cars. Each wheel needs two bearings Z12. Assembly Division can sell all its production capacity of 5,000 wheels to the external market at a price of $820 per unit. Parts Division can sell all its production capacity of 10,000 bearings Z12 to the external market at a price of $80 per bearing, but it will incur 10% sales commission costs. Assembly Division can purchase bearings of the same quality from external suppliers at a price of $80 per bearing but it will incur a variable purchasing cost of $5 per bearing. There are no freight costs or other additional costs for the internal transfer of bearings The two Division managers are compensated based on the Division operating income. The following table shows the manufacturing cost per unit in the Parts and Assembly Divisions for 2018: Parts Assembly Direct material cost $20 $250" Direct manufacturing labour cost 16 180 Manufacturing overhead cost 306 220 Total cost per unit $66 $650 Additional information: a Direct material costs do not include cost of bearings. Manufacturing overhead costs in Parts Division are 25% fixed and 75% variable Manufacturing overhead costs in Assembly Division are 60% fixed and 40% variable. Fixed costs are allocated on per unit of production capacity. Required: 1. Road Racing required Parts Division to transfer all its output to Assembly Division at 120% of full manufacturing cost. Is the transfer pricing optimal for Road Racing and acceptable for Parts Division's manager and Assembly Division's manager? Why? Show your calculations. (6 Marks) 2. If Division managers can act autonomously to maximise their own Division's operating income, what is the range of transfer prices they would be willing to negotiate? (3 Marks) 3. If the negotiated transfer price between Parts and Assembly Divisions is the market price of $80, what would be the operating income of Parts Division, Assembly Division and Road Racing Ltd? (3 Marks) 4. Assume that Road Racing rewards each Division manager with a bonus calculated as 1% of Division operating income plus 1% of the company's operating income (if positive). What is the amount of bonus that will be paid to each Division manager if the transfer price of the 10,000 bearings Z12 is $80? Is this a good compensation arrangement? Why? (5 Marks) 5. Discuss two possible problems a company might have if its operations are totally decentralised







