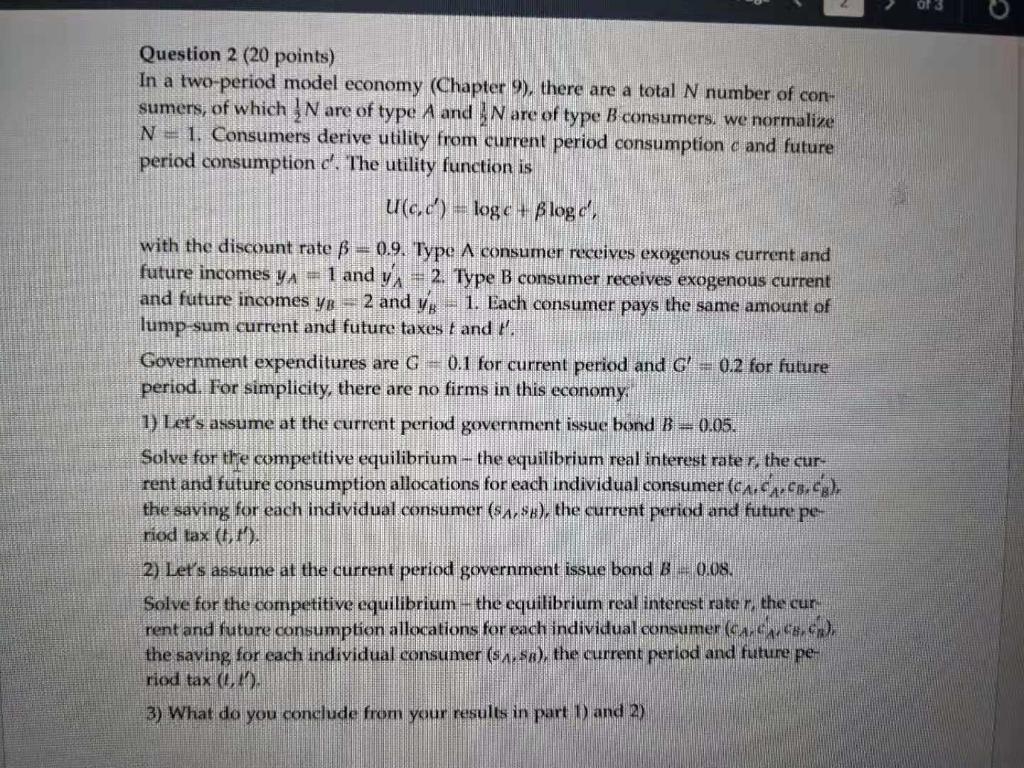
Question 2 (20 points) In a two-period model economy (Chapter 9), there are a total N number of con- sumers, of which N are of type A and I are of type B consumers, we normalize N - 1. Consumers derive utility from current period consumption c and future period consumption d'. The utility function is U(c,d) = loge + Blog d', with the discount rate = 0.9. Type A consumer receives exogenous current and future incomes YA = 1 and yA + 2. Type B consumer receives exogenous current and future incomes yo =2 and yg = 1. Each consumer pays the same amount of lump-sum current and future taxes t and Government expenditures are G = 0.1 for current period and C -- 0.2 for future period. For simplicity, there are no firms in this economy. 1) Let's assume at the current period government issue bond B = 0.05. Solve for the competitive equilibrium - the equilibrium real interest rate r, the cur- rent and future consumption allocations for each individual consumer (c. dr.sce), the saving for each individual consumer ($ 1,$s), the current period and future pe- riod tax (IM) 2) Let's assume at the current period government issue bond B 0.08. Solve for the competitive equilibrium - the equilibrium real interest rater, the cur rent and future consumption allocations for each individual consumer (ca.dc.), the saving for each individual consumer (s 1.5x), the current period and future pe riod tax (0, 3) What do you conclude from your results in part 1 and 2) Question 2 (20 points) In a two-period model economy (Chapter 9), there are a total N number of con- sumers, of which N are of type A and I are of type B consumers, we normalize N - 1. Consumers derive utility from current period consumption c and future period consumption d'. The utility function is U(c,d) = loge + Blog d', with the discount rate = 0.9. Type A consumer receives exogenous current and future incomes YA = 1 and yA + 2. Type B consumer receives exogenous current and future incomes yo =2 and yg = 1. Each consumer pays the same amount of lump-sum current and future taxes t and Government expenditures are G = 0.1 for current period and C -- 0.2 for future period. For simplicity, there are no firms in this economy. 1) Let's assume at the current period government issue bond B = 0.05. Solve for the competitive equilibrium - the equilibrium real interest rate r, the cur- rent and future consumption allocations for each individual consumer (c. dr.sce), the saving for each individual consumer ($ 1,$s), the current period and future pe- riod tax (IM) 2) Let's assume at the current period government issue bond B 0.08. Solve for the competitive equilibrium - the equilibrium real interest rater, the cur rent and future consumption allocations for each individual consumer (ca.dc.), the saving for each individual consumer (s 1.5x), the current period and future pe riod tax (0, 3) What do you conclude from your results in part 1 and 2)







