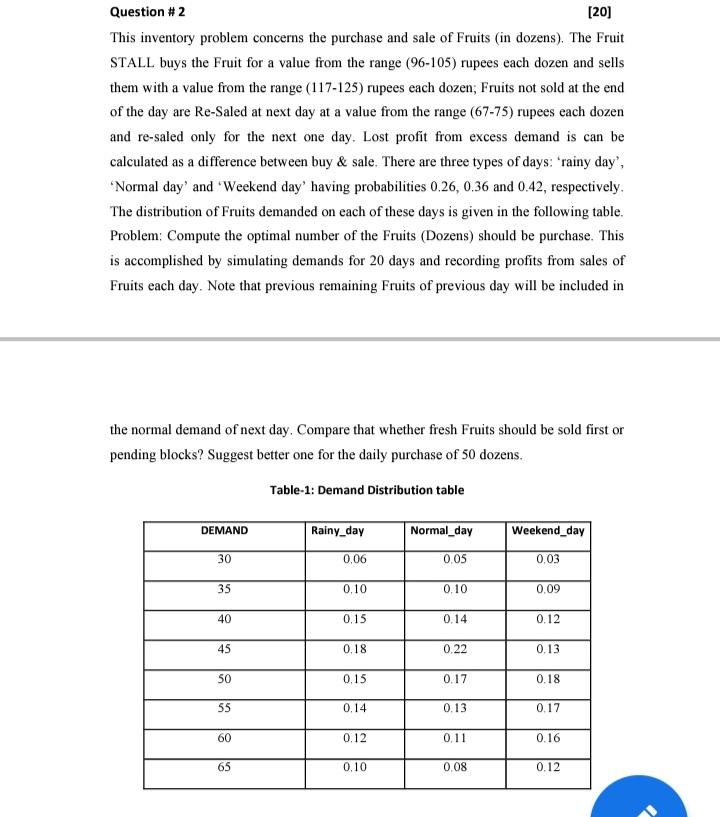
Question #2 [20] This inventory problem concerns the purchase and sale of Fruits (in dozens). The Fruit STALL buys the Fruit for a value from the range (96-105) rupees each dozen and sells them with a value from the range (117-125) rupees each dozen; Fruits not sold at the end of the day are Re-Saled at next day at a value from the range (67-75) rupees each dozen and re-saled only for the next one day, Lost profit from excess demand is can be calculated as a difference between buy & sale. There are three types of days: "rainy day, "Normal day' and 'Weekend day' having probabilities 0.26, 0.36 and 0.42, respectively, The distribution of Fruits demanded on each of these days is given in the following table. Problem: Compute the optimal number of the Fruits (Dozens) should be purchase. This is accomplished by simulating demands for 20 days and recording profits from sales of Fruits each day. Note that previous remaining Fruits of previous day will be included in the normal demand of next day. Compare that whether fresh Fruits should be sold first or pending blocks? Suggest better one for the daily purchase of 50 dozens. Table-1: Demand Distribution table DEMAND Rainy_day Normal_day Weekend_day 30 0.06 0.05 0.03 35 0.10 0.10 0.09 40 0.15 0.14 0.12 45 0.18 0.22 0.13 50 0.15 0.17 0.18 55 0.14 0.13 0.17 60 0.12 0.11 0.16 65 0.10 0.08 0.12 Question #2 [20] This inventory problem concerns the purchase and sale of Fruits (in dozens). The Fruit STALL buys the Fruit for a value from the range (96-105) rupees each dozen and sells them with a value from the range (117-125) rupees each dozen; Fruits not sold at the end of the day are Re-Saled at next day at a value from the range (67-75) rupees each dozen and re-saled only for the next one day, Lost profit from excess demand is can be calculated as a difference between buy & sale. There are three types of days: "rainy day, "Normal day' and 'Weekend day' having probabilities 0.26, 0.36 and 0.42, respectively, The distribution of Fruits demanded on each of these days is given in the following table. Problem: Compute the optimal number of the Fruits (Dozens) should be purchase. This is accomplished by simulating demands for 20 days and recording profits from sales of Fruits each day. Note that previous remaining Fruits of previous day will be included in the normal demand of next day. Compare that whether fresh Fruits should be sold first or pending blocks? Suggest better one for the daily purchase of 50 dozens. Table-1: Demand Distribution table DEMAND Rainy_day Normal_day Weekend_day 30 0.06 0.05 0.03 35 0.10 0.10 0.09 40 0.15 0.14 0.12 45 0.18 0.22 0.13 50 0.15 0.17 0.18 55 0.14 0.13 0.17 60 0.12 0.11 0.16 65 0.10 0.08 0.12







