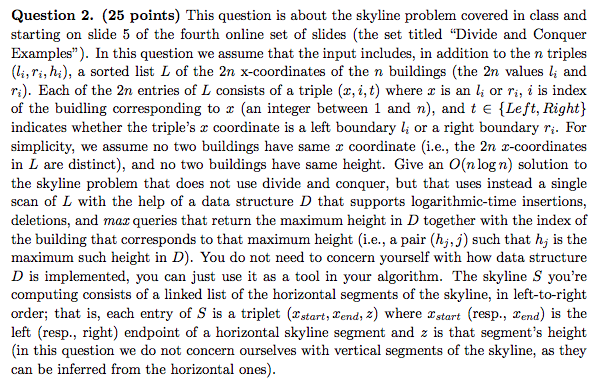
Question 2. (25 points) This question is about the skyline problem covered in class and starting on slide 5 of the fourth online set of slides (the set titled "Divide and Conquer Examples"). In this question we assume that the input includes, in addition to the n triples (liri, hi), a sorted list L of the 2n x-coordinates of the n buildings (the 2n values li and ri). Each of the 2n entries of L consists of a triple (2, 1,t) where is an lior ri, i is index of the buidling corresponding to 2 (an integer between 1 and n), and te {Left, Right} indicates whether the triple's 2 coordinate is a left boundary li or a right boundary r;. For simplicity, we assume no two buildings have same coordinate (i.e., the 2n -coordinates in L are distinct), and no two buildings have same height. Give an O(n log n) solution to the skyline problem that does not use divide and conquer, but that uses instead a single scan of L with the help of a data structure D that supports logarithmic-time insertions, deletions, and max queries that return the maximum height in D together with the index of the building that corresponds to that maximum height (i.e., a pair (hj,]) such that h; is the maximum such height in D). You do not need to concern yourself with how data structure D is implemented, you can just use it as a tool in your algorithm. The skyline S you're computing consists of a linked list of the horizontal segments of the skyline, in left-to-right order; that is, each entry of S is a triplet (I start, Bend, 2) where I start (resp., Bend) is the left (resp., right) endpoint of a horizontal skyline segment and z is that segment's height (in this question we do not concern ourselves with vertical segments of the skyline, as they can be inferred from the horizontal ones). Question 2. (25 points) This question is about the skyline problem covered in class and starting on slide 5 of the fourth online set of slides (the set titled "Divide and Conquer Examples"). In this question we assume that the input includes, in addition to the n triples (liri, hi), a sorted list L of the 2n x-coordinates of the n buildings (the 2n values li and ri). Each of the 2n entries of L consists of a triple (2, 1,t) where is an lior ri, i is index of the buidling corresponding to 2 (an integer between 1 and n), and te {Left, Right} indicates whether the triple's 2 coordinate is a left boundary li or a right boundary r;. For simplicity, we assume no two buildings have same coordinate (i.e., the 2n -coordinates in L are distinct), and no two buildings have same height. Give an O(n log n) solution to the skyline problem that does not use divide and conquer, but that uses instead a single scan of L with the help of a data structure D that supports logarithmic-time insertions, deletions, and max queries that return the maximum height in D together with the index of the building that corresponds to that maximum height (i.e., a pair (hj,]) such that h; is the maximum such height in D). You do not need to concern yourself with how data structure D is implemented, you can just use it as a tool in your algorithm. The skyline S you're computing consists of a linked list of the horizontal segments of the skyline, in left-to-right order; that is, each entry of S is a triplet (I start, Bend, 2) where I start (resp., Bend) is the left (resp., right) endpoint of a horizontal skyline segment and z is that segment's height (in this question we do not concern ourselves with vertical segments of the skyline, as they can be inferred from the horizontal ones)







