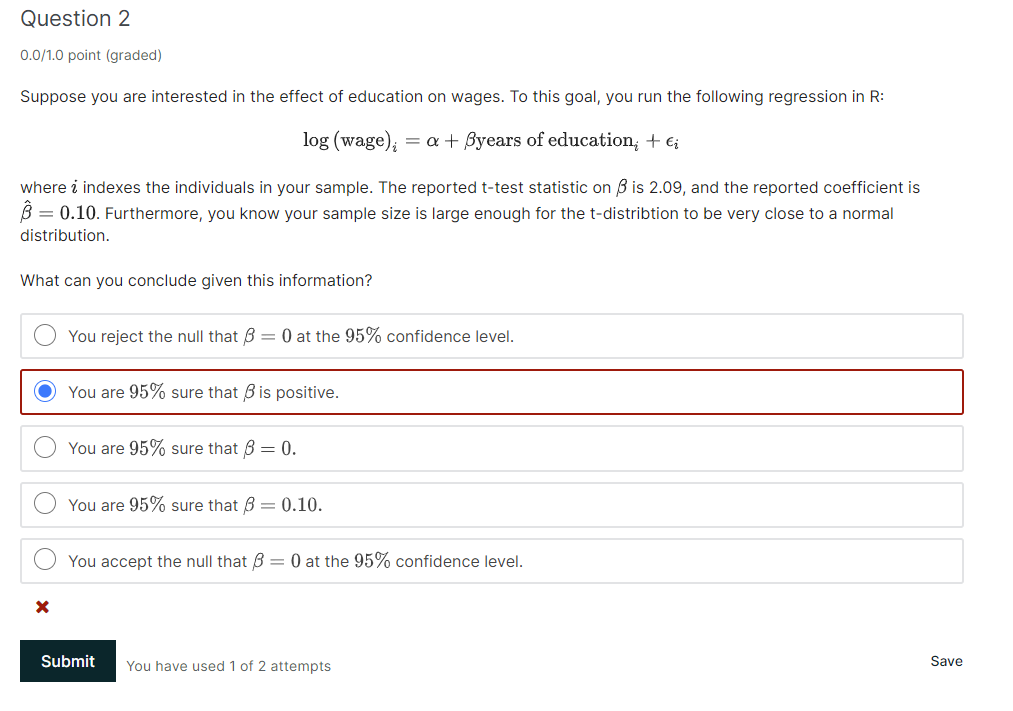
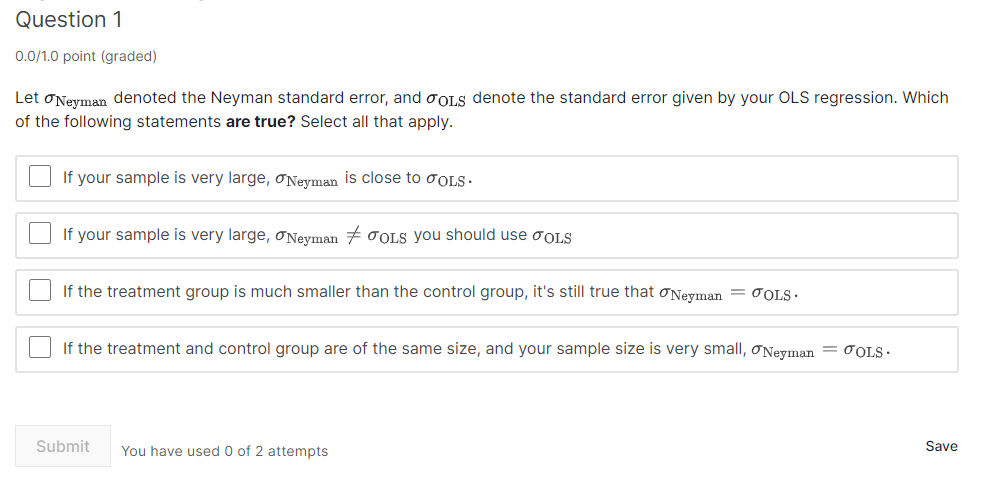
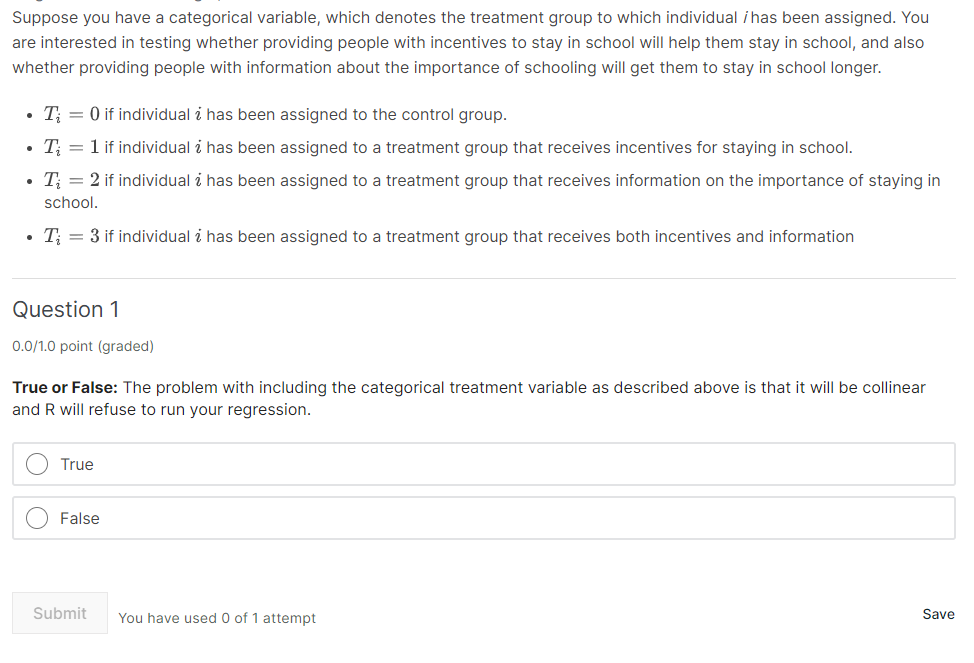
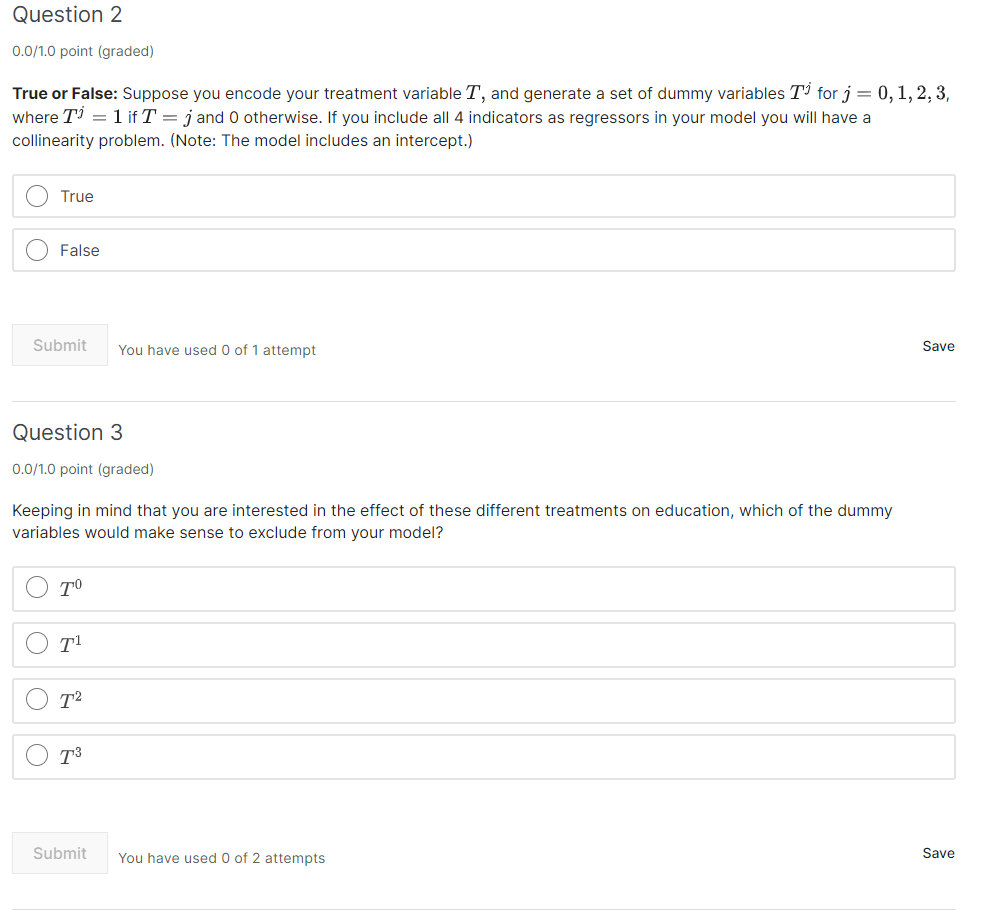
Question 2 D.Df1.D point (graded) Suppose you are interested in the effect of education on wages. To this goal, you run the following regression in R: 10g (wage) 1.. = a + years of educatiom + Et' wheres' indexes the individuals in your sample. The reported t-test statistic on ,8 is 2.09, and the reported coefficient is E = 9.10. Furthermore, you know your sample size is large enough for the t-distribtion to be very close to a normal distribution. What can you conclude given this information? 0 You reject the null that ,8 = D at the 95% confidence level. 0 You are 95% sure that ,6 = 0. Q You are 95% sure that ,8 = 0.10. Q You accept the null that l3 = D at the 95% confidence level. You have used 'I of 2 attempts Save Question 1 DDHD point (graded) Let \"New denoted the Neyman standard error, and 001,3 denote the standard error given by your OLS regression. Which of the following statements are true? Select all that apply. E] If your sample is very large, \"Newman is close to JOLs. E] If your sample is very large, JNEymm 79 001,3 you should use JOLS E] If the treatment group is much smaller than the control group, it's still true that swarm\" = EOLS. E] If the treatment and control group are of the same size, and your sample size is very small, 01.1mm = EOLS. Submit You have used 0 of 2 attempts Save Suppose you have a categorical variable, which denotes the treatment group to which individual .r'has been assigned. You are interested in testing whether providing people with incentives to stay in school will help them stay in schoolI and also whether providing people with information about the importance of schooling will get them to stay in school longer. - Ti; = [I if individual 1' has been assigned to the control group. . T; = 1 if individual 1' has been assigned to a treatment group that receives incentives for staying in school. . T; = 2 if individual 1' has been assigned to a treatment group that receives information on the importance of staying in school - T; = 3 if individual 1' has been assigned to a treatment group that receives both incentives and information Question 1 DDHD point {graded} True or False: The problem with including the categorical treatment variable as described above is that it will be collinear and R will refuse to run your regression. Smeit You have used 0 off attempt 33"9 Question 2 DDHD point (graded) True or False: Suppose you encode your treatment variable T, and generate a set of dummy variables Tj for j = U,1,2,3, where T-1 = 1 if T = j and 0 otherwise. If you include all 4 indicators as regressors in your model you will have a collinearity problem. (Note: The model includes an intercept.) 5meit You have used 0 of1 attempt Save Question 3 DDHD point (graded) Keeping in mind that you are interested in the effect of these different treatments on education, which of the dummy variables would make sense to exclude from your model? Submit You have used 0 of 2 attempts Save