Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 2 ( Total: 3 4 marks ) Nitric acid ( H N O 3 ) is used extensively for the production of inorganic and
Question Total: marks
Nitric acid is used extensively for the production of inorganic and organic nitrates,
various kinds of metal treatments and photoengraving. is produced by oxidizing ammonia
to nitric oxide NO in a catalytic converter Equation followed by further NO oxidation and
hydration in a second reactor Equation
Equation :
Equation :
An undesired reaction Equation that lowers yield is the oxidation of ammonia to
nitrogen and water vapor in the converter.
Equation :
Saturated ammonia vapor, produced by vaporizing pure liquid ammonia at kPa absolute is
mixed with a stoichiometric quantity of air ie consisting the quantity of oxygen theoretically
required to convert all of the ammonia to and the combined stream enters the converter.
The air enters at and atm with a relative humidity of
In the converter, the ammonia reacts completely, with forming NO and the balance forming
The product gas exiting the converter is subjected to further oxidation and hydration in the
second reactor, in which all NO is completely oxidized and combined with all the water some of
which is present in the product gas leaving the converter, the rest of which is added as liquid
water to form a aqueous nitric acid solution. The product gas from the process may be
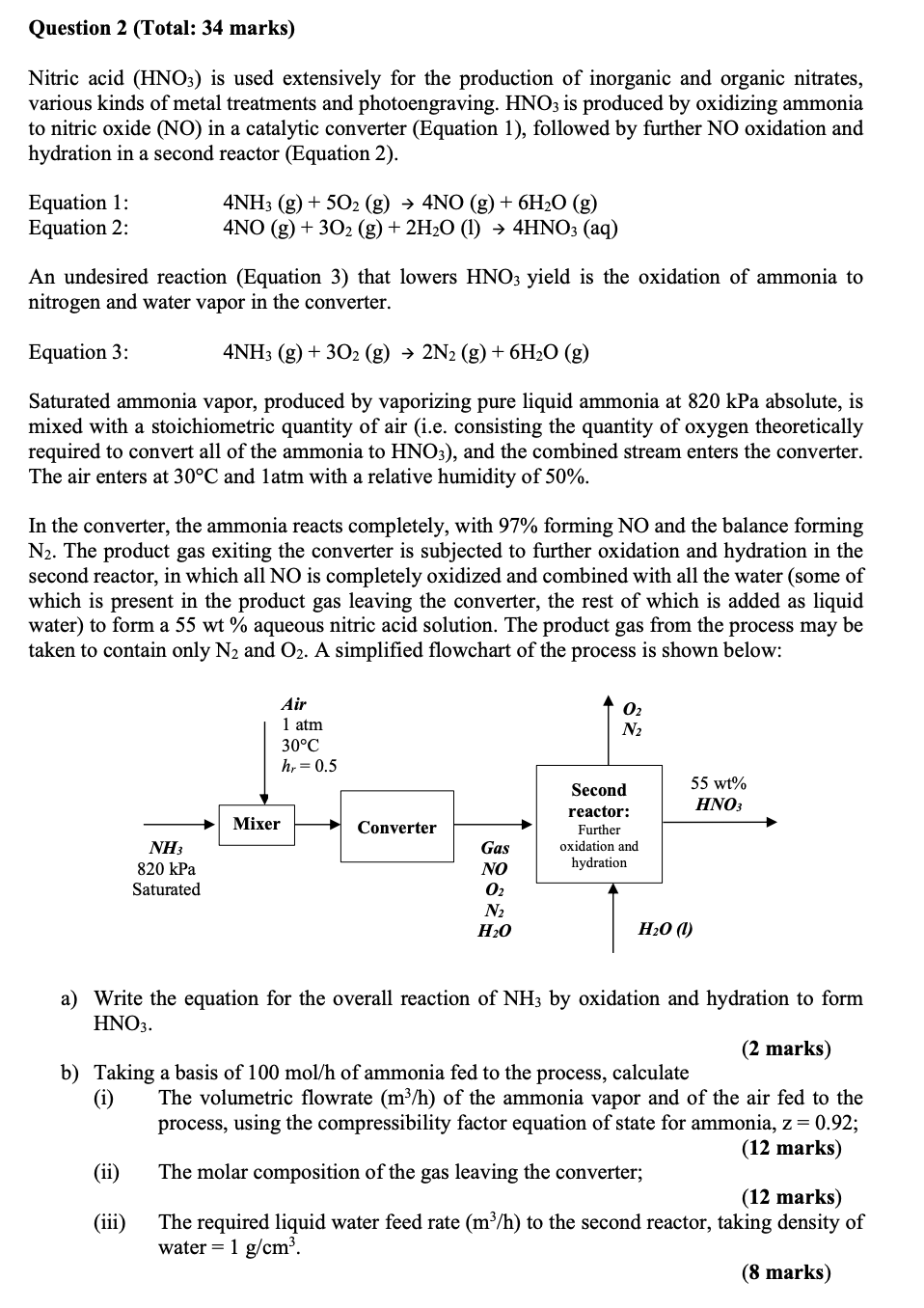
taken to contain only and A simplified flowchart of the process is shown below:
a Write the equation for the overall reaction of by oxidation and hydration to form
marks
b Taking a basis of of ammonia fed to the process, calculate
i The volumetric flowrate of the ammonia vapor and of the air fed to the
process, using the compressibility factor equation of state for ammonia, ;
marks
ii The molar composition of the gas leaving the converter;
marks
iii The required liquid water feed rate to the second reactor, taking density of
water
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


