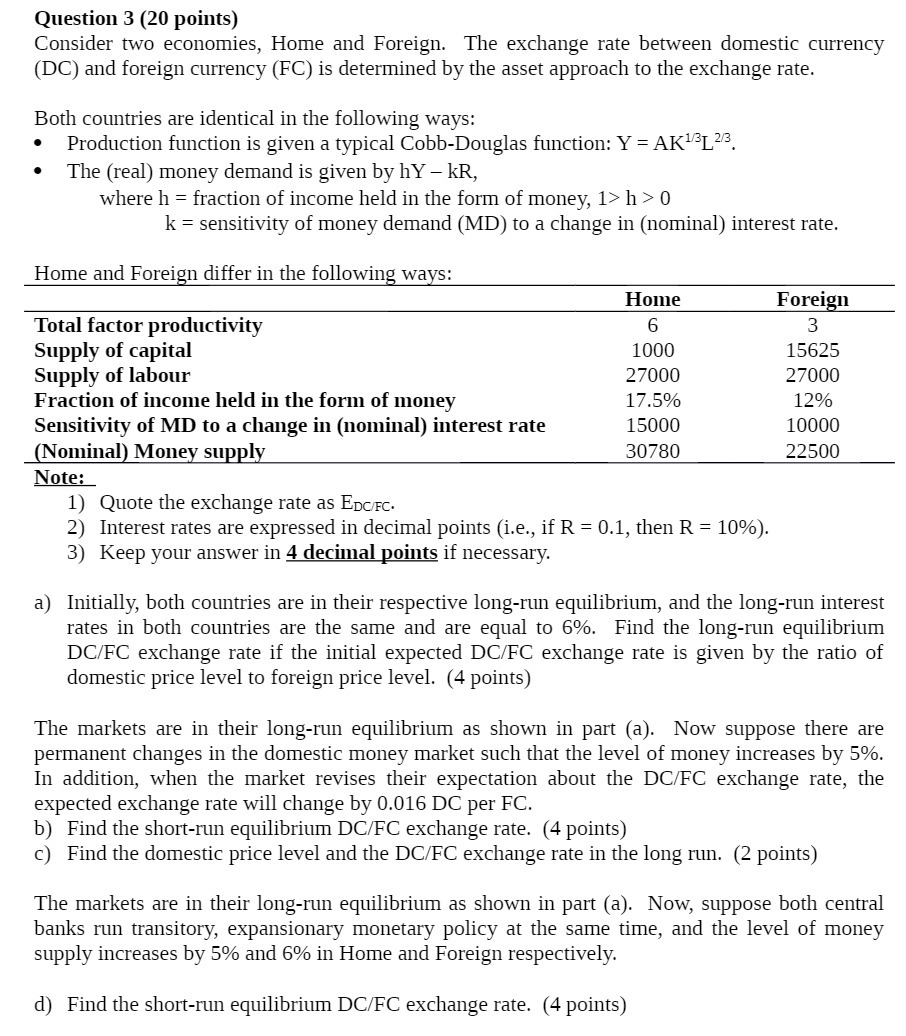
Question 3 (20 points) Consider two economies, Home and Foreign. The exchange rate between domestic currency (DC) and foreign currency (F C) is determined by the asset approach to the exchange rate. Both countries are identical in the following ways: ' Production function is given a typical Cobb-Douglas function: Y = AKL'BLZ'B. - The (real) money demand is given by hY kR, where h = fraction of income held in the form of money, 13> h > 0 k = sensitivity of money demand (MD) to a change in (nominal) interest rate. Home and Foreign differ in the following ways: Home Foreig Total factor productivity 6 3 Supply of capital 1000 15625 Supply of labour 27000 27000 Fraction of income held in the form of money 17.5% 12% Sensitivity of MD to a change in (nominal) interest rate 15000 10000 Nominal Mon su 30780 22500 Note: 1) Quote the exchange rate as Em. 2) Interest rates are expressed in decimal points (i.e., if R = 0.1, then R = 10%). 3) Keep your answer in 4 decimal points if necessary. a) Initially, both countries are in their respective long-run equilibrium, and the long-run interest rates in both countries are the same and are equal to 6%. Find the long-run equilibrium DCJFC exchange rate if the initial expected DCIFC exchange rate is given by the ratio of domestic price level to foreign price level. (4 points) The markets are in their long-run equilibrium as shown in part (a). Now suppose there are permanent changes in the domestic money market such that the level of money increases by 5%. In addition, when the market revises their expectation about The DCJ'FC exchange rate, the expected exchange rate will change by 0.016 DC per FC. b) Find the short-run equilibrium DCI'FC exchange rate. (4 points) c) Find the domestic price level and the DCfF C exchange rate in the long run. (2 points) The markets are in their long-run equilibrium as shown in part (a). Now, suppose both central banks run transitory, expansionary monetary policy at the same time, and the level of money supply increases by 5% and 6% in Home and Foreign respectively. d) Find the short-run equilibrium DCI'FC exchange rate. (4 points)