Question
QUESTION 4 (20 MARKS) Case study. As Spartan, Inc., is considering the development of a subsidiary in Singapore that would manufacture and sell tennis rackets
QUESTION 4 (20 MARKS)
Case study.
As Spartan, Inc., is considering the development of a subsidiary in Singapore that would manufacture and sell tennis rackets locally. Spartans financial managers have asked the manufacturing, marketing, and financial departments to provide them with relevant input so they can apply a capital budgeting analysis to this project. In addition, some Spartan executives have met with government officials in Singapore to discuss the proposed subsidiary. The project would end in four years. All relevant information follows.
Initial investment. The project would require an initial investment of 20 million Singapore dollars (S$), which includes funds to support working capital. Given the existing spot rate of $.50 per Singapore dollar, the U.S. dollar amount of the parents initial investment is S$20 million $.50 is $10 million.
Price and consumer demand. The estimated price and demand schedules during each of the next four years are shown here: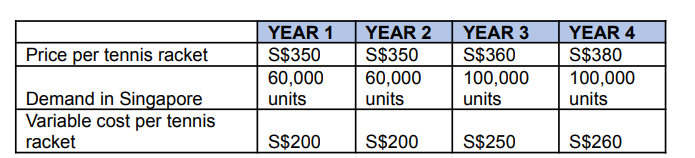
The expense of leasing extra office space is S$1 million per year. Other annual overhead expenses are expected to be S$1 million per year.
Tax laws. The Singapore government will allow Spartans subsidiary to depreciate the cost of the plant and equipment at a maximum rate of S$2 million per year, which is the rate the subsidiary will use. The Singapore government will impose a 20 percent tax rate on income. In addition, it will impose a 10 percent withholding tax on any funds remitted by the subsidiary to the parent. The U.S. government will allow a tax credit on taxes paid in Singapore; therefore, earnings remitted to the U.S. parent will not be taxed by the U.S. government.
Remitted funds. The Spartan subsidiary plans to send all net cash flows received back to the parent firm at the end of each year. The Singapore government promises no restrictions on the cash flows to be sent back to the parent firm but does impose a 10 percent withholding tax on any funds sent to the parent, as mentioned previously.
Exchange rates. The spot exchange rate of the Singapore dollar is $.50. Spartan uses the spot rate as its forecast for all future periods.
Salvage value. The Singapore government will pay the parent S$12 million to assume ownership of the subsidiary at the end of four years. Assume that there is no capital gains tax on the sale of the subsidiary. Required rate of return. Spartan, Inc., requires a 15 percent return on this project.
You were required to:
(a) Based on the case study above, calculate the total revenue for year 1 until year 4. (4 marks)
(b) Compute the total expenses for year 1 until year 4. (4 marks)
(c) Find the S$ remittance after withholding taxes year 1 until year 4. (6 marks)
(d) Calculate the cumulative Net Present Value(NPV) year 1 until year 4. (6 marks)
\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline & YEAR 1 & YEAR 2 & YEAR 3 & YEAR 4 \\ \hline Price per tennis racket & S$350 & S$350 & S$360 & S$380 \\ \hline DemandinSingaporeunits & 60,000units & 100,000units & 100,000units \\ \hline Variablecostpertennisracket & S$200 & S$200 & S$250 & S$260 \\ \hline \end{tabular}Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


