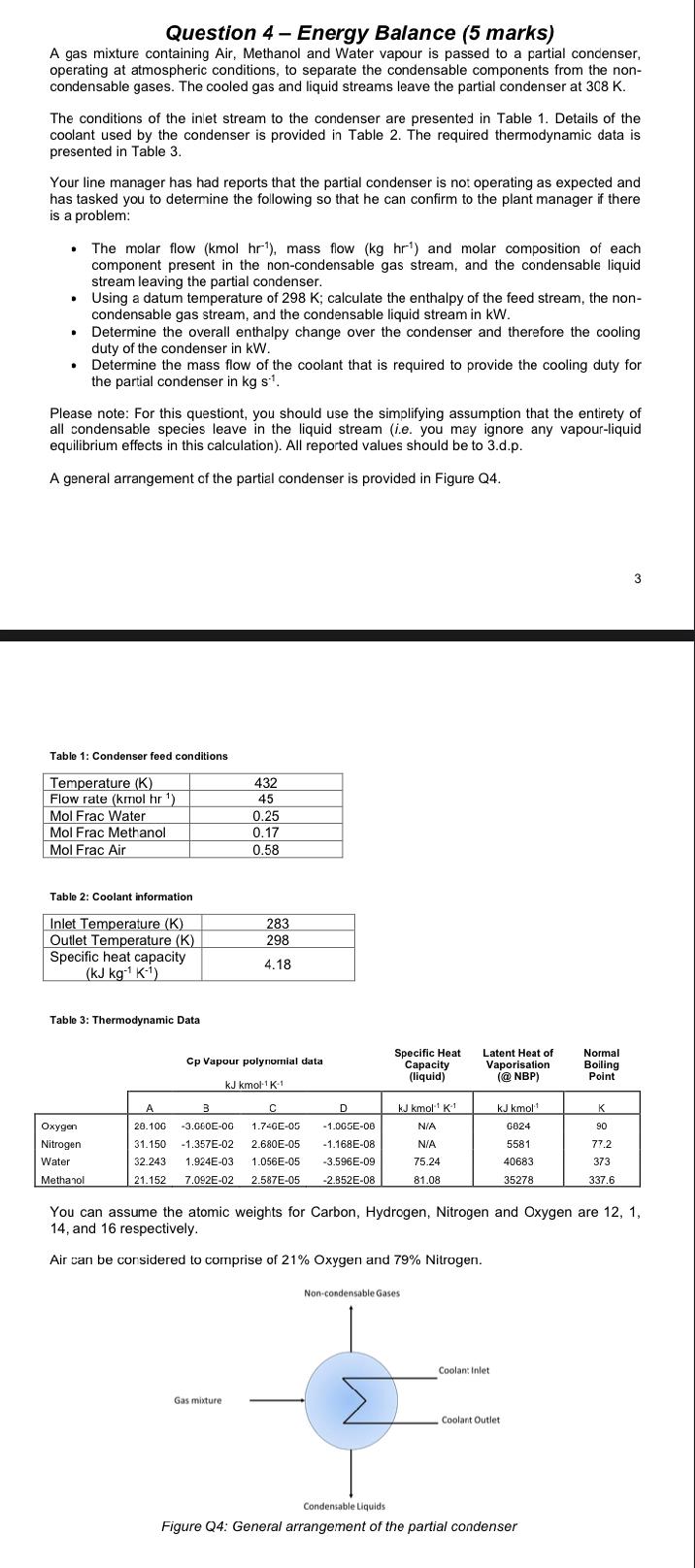
Question 4 - Energy Balance (5 marks) A gas mixture containing Air, Methanol and Water vapour is passed to a partial condenser, operating at atmospheric conditions, to separate the condensable components from the non- condensable gases. The cooled gas and liquid streams leave the partial condenser at 308 K. The conditions of the inlet stream to the condenser are presented in Table 1. Details of the coolant used by the condenser is provided in Table 2. The required thermodynamic data is presented in Table 3. Your line manager has had reports that the partial condenser is no: operating as expected and has tasked you to determine the following so that he can confirm to the plant manager if there is a problem: The molar flow (kmol hr), mass flow (kg hrt) and molar composition of each component present in the non-condensable gas stream, and the condensable liquid stream leaving the partial condenser. Using a datum temperature of 298 K; calculate the enthalpy of the feed stream, the non- condensable gas stream, and the condensable liquid stream in kW. Determine the overall enthalpy change over the condenser and therefore the cooling duty of the condenser in kW. Determine the mass flow of the coolant that is required to provide the cooling duty for the partial condenser in kg s. Please note: For this questiont, you should use the simplifying assumption that the entirety of all condensable species leave in the liquid stream (i.e. you may ignore any vapour-liquid equilibrium effects in this calculation). All reported values should be to 3.d.p. A general arrangement of the partial condenser is provided in Figure Q4. 3 Table 1: Condenser feed conditions Temperature (K) Flow rate (kmol hr) Mol Frac Water Mol Frac Methanol Mol Frac Air 432 45 0.25 0.17 0.58 Table 2: Coolant information 283 298 Inlet Temperature (K) Outlet Temperature (K) Specific heat capacity (kJ kg K-1) 4.18 Table 3: Thermodynamic Data Cp Vapour polynomial data Specific Heat Capacity (liquid) Latent Heat of Vaporisation (@NBP) Normal Bolling Point kJ kmol-1K1 D K 90 Oxygen 20.100 31.150 kJ kmol K1 N/A N/A 3 -3.000E-OG -1.357E-02 1.924E-03 7.092E-02 Nitrogen Water 1.740E-05 2.680E-05 1.056E-05 2.587E-05 -1.00GE-00 - 1.168E-08 -3.596E-09 -2.852E-08 kJ kmolt 6824 5581 40683 35278 77.2 373 32.243 75.24 Methanol 21.152 81.08 337.6 You can assume the atomic weights for Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Oxygen are 12, 1, 14, and 16 respectively. Air can be considered to comprise of 21% Oxygen and 79% Nitrogen. Non-condensable Gases Coolant Inlet Gas mixture Coolant Outlet Condensable Liquids Figure Q4: General arrangement of the partial condenser







