Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Question 4 Samuel King Limited, an all equity firm, has expected earnings before interest and taxes of GHC6million a year. Samuel King's tax rate
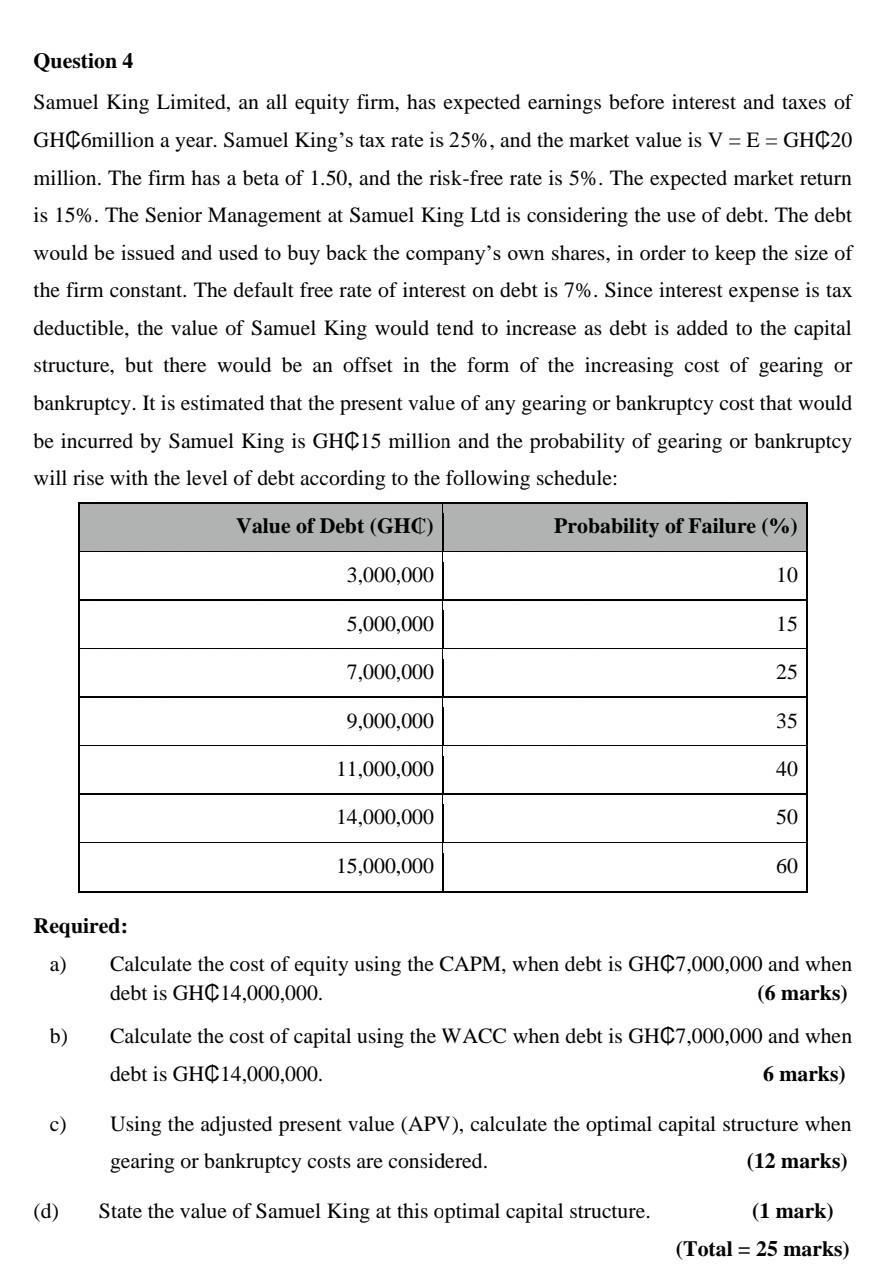
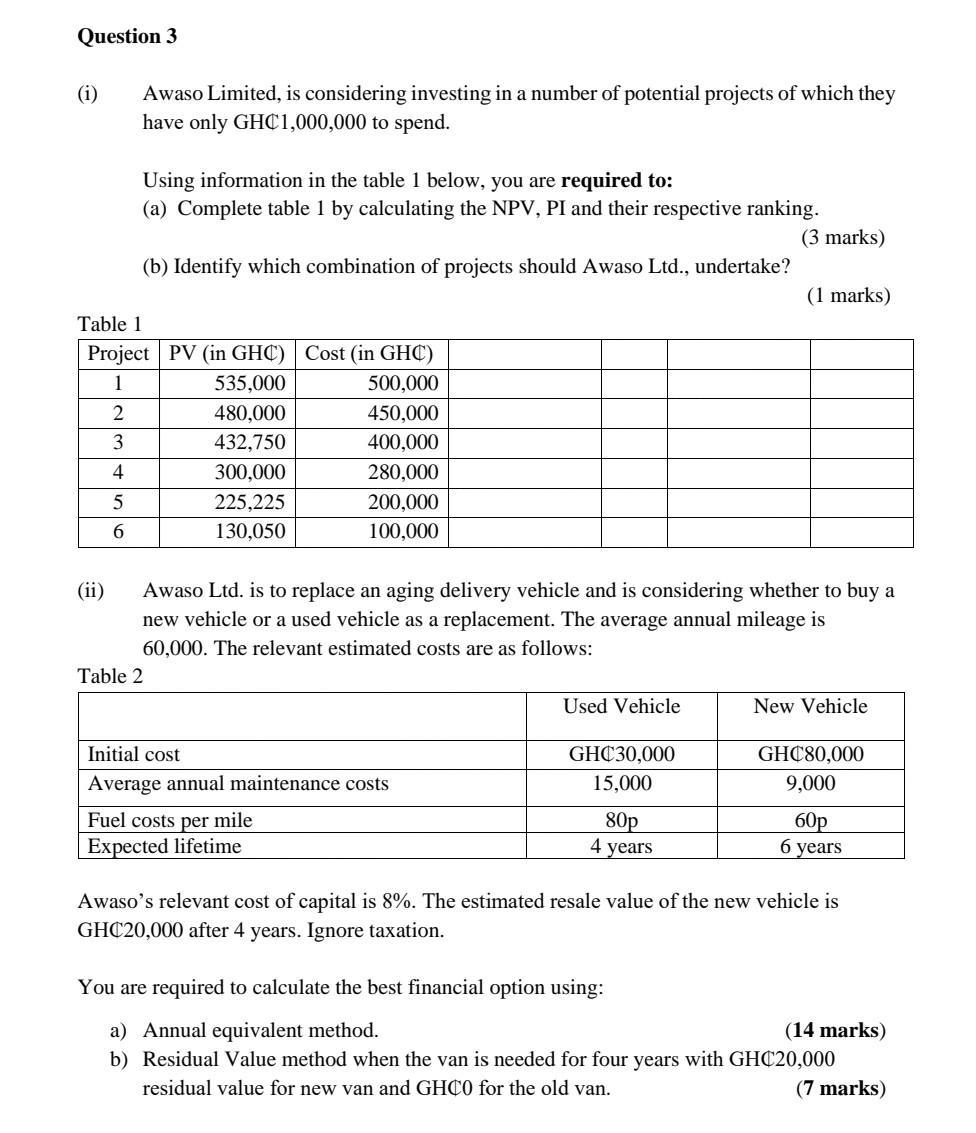
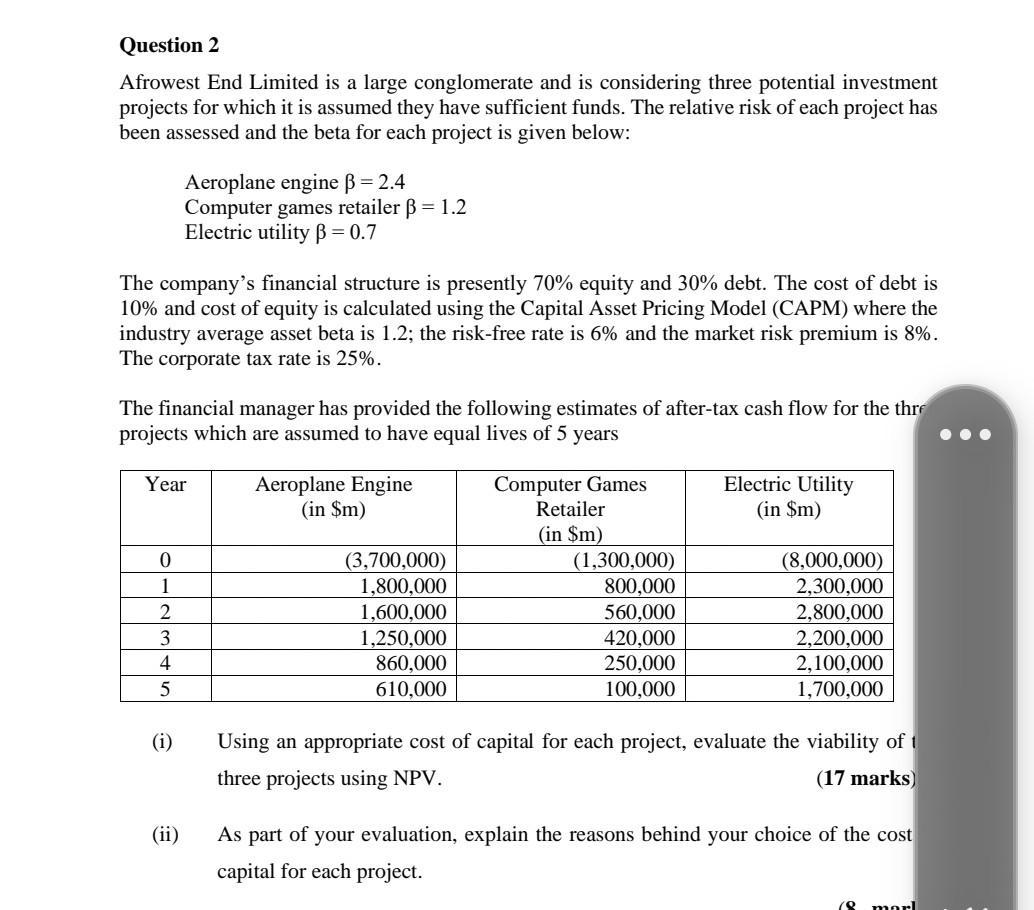
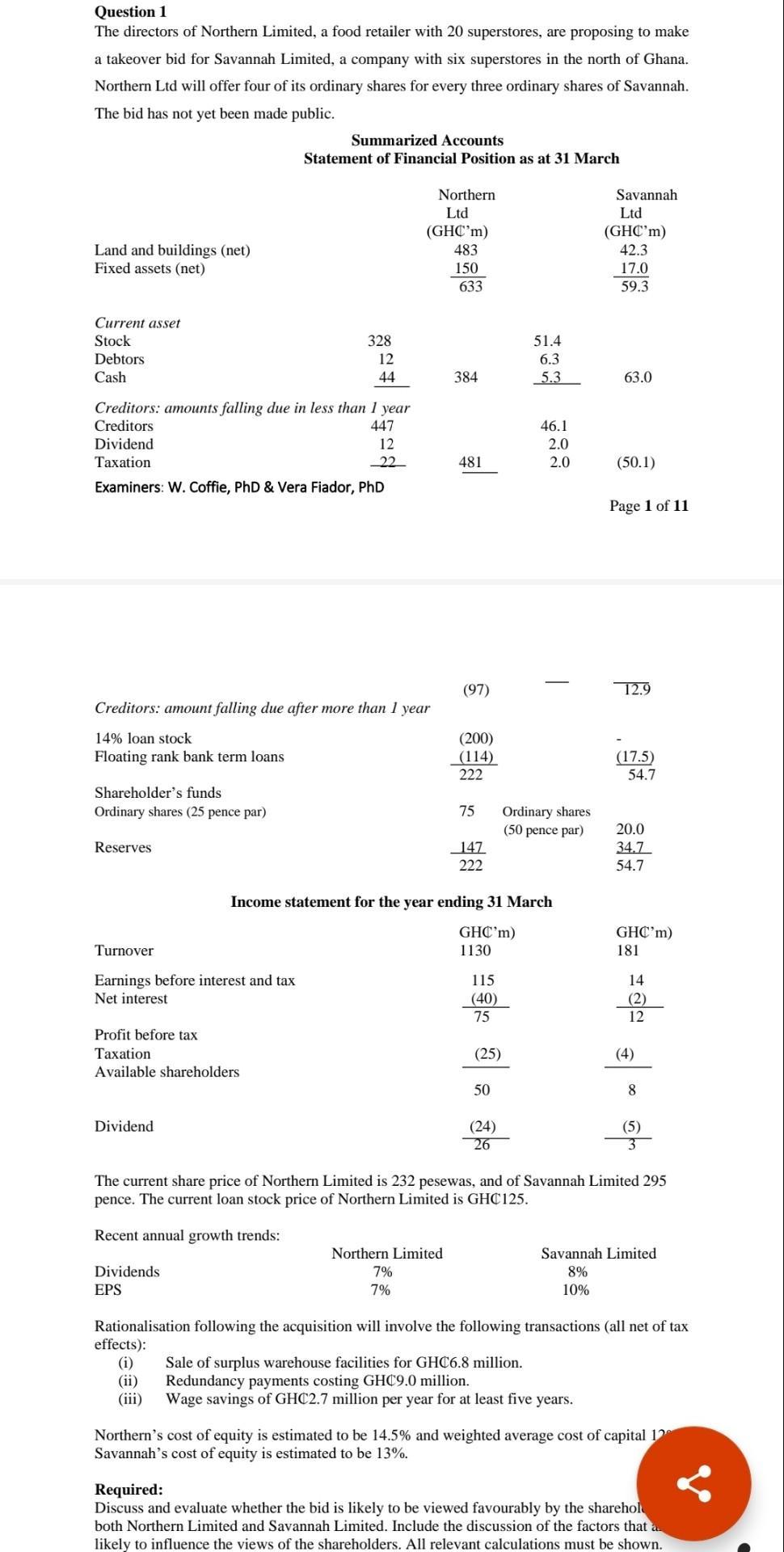


Question 4 Samuel King Limited, an all equity firm, has expected earnings before interest and taxes of GHC6million a year. Samuel King's tax rate is 25%, and the market value is V = E= GHC20 million. The firm has a beta of 1.50, and the risk-free rate is 5%. The expected market return is 15%. The Senior Management at Samuel King Ltd is considering the use of debt. The debt would be issued and used to buy back the company's own shares, in order to keep the size of the firm constant. The default free rate of interest on debt is 7%. Since interest expense is tax deductible, the value of Samuel King would tend to increase as debt is added to the capital structure, but there would be an offset in the form of the increasing cost of gearing or bankruptcy. It is estimated that the present value of any gearing or bankruptcy cost that would be incurred by Samuel King is GHC15 million and the probability of gearing or bankruptcy will rise with the level of debt according to the following schedule: Value of Debt (GHC) Required: a) b) c) (d) 3,000,000 5,000,000 7,000,000 9,000,000 11,000,000 14,000,000 15,000,000 Probability of Failure (%) 10 15 25 (Total 35 40 50 60 Calculate the cost of equity using the CAPM, when debt is GHC7,000,000 and when debt is GHC14,000,000. (6 marks) Calculate the cost of capital using the WACC when debt is GHC7,000,000 and when debt is GHC14,000,000. 6 marks) Using the adjusted present value (APV), calculate the optimal capital structure when gearing or bankruptcy costs are considered. (12 marks) State the value of Samuel King at this optimal capital structure. (1 mark) 25 marks) Question 3 (i) Awaso Limited, is considering investing in a number of potential projects of which they have only GHC1,000,000 to spend. Using information in the table 1 below, you are required to: (a) Complete table 1 by calculating the NPV, PI and their respective ranking. (3 marks) 2 3 4 5 6 (b) Identify which combination of projects should Awaso Ltd., undertake? Table 1 Project PV (in GHC) Cost (in GHC) 1 535,000 500,000 480,000 432,750 300,000 225,225 130,050 Table 2 450,000 400,000 280,000 200,000 100,000 Awaso Ltd. is to replace an aging delivery vehicle and is considering whether to buy a new vehicle or a used vehicle as a replacement. The average annual mileage is 60,000. The relevant estimated costs are as follows: Initial cost Average annual maintenance costs Fuel costs per mile Expected lifetime Used Vehicle GHC30,000 15,000 (1 marks) 80p 4 years New Vehicle GHC80,000 9,000 60p 6 years Awaso's relevant cost of capital is 8%. The estimated resale value of the new vehicle is GHC20,000 after 4 years. Ignore taxation. You are required to calculate the best financial option using: a) Annual equivalent method. (14 marks) b) Residual Value method when the van is needed for four years with GHC20,000 residual value for new van and GHCO for the old van. (7 marks) Question 2 Afrowest End Limited is a large conglomerate and is considering three potential investment projects for which it is assumed they have sufficient funds. The relative risk of each project has been assessed and the beta for each project is given below: Aeroplane engine = 2.4 Computer games retailer = 1.2 Electric utility B = 0.7 The company's financial structure is presently 70% equity and 30% debt. The cost of debt is 10% and cost of equity is calculated using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) where the industry average asset beta is 1.2; the risk-free rate is 6% and the market risk premium is 8%. The corporate tax rate is 25%. The financial manager has provided the following estimates of after-tax cash flow for the thre projects which are assumed to have equal lives of 5 years Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 Aeroplane Engine (in $m) (3,700,000) 1,800,000 1,600,000 1,250,000 860,000 610,000 Computer Games Retailer (in $m) (1,300,000) 800,000 560,000 420,000 250,000 100,000 Electric Utility (in $m) (8,000,000) 2,300,000 2,800,000 2,200,000 2,100,000 1,700,000 Using an appropriate cost of capital for each project, evaluate the viability of t three projects using NPV. (17 marks) As part of your evaluation, explain the reasons behind your choice of the cost capital for each project. (8 marl Question 1 The directors of Northern Limited, a food retailer with 20 superstores, are proposing to make a takeover bid for Savannah Limited, a company with six superstores in the north of Ghana. Northern Ltd will offer four of its ordinary shares for every three ordinary shares of Savannah. The bid has not yet been made public. Land and buildings (net) Fixed assets (net) Current asset Stock Debtors Cash Creditors: amounts falling due in less than 1 year Creditors 447 Dividend 12 Taxation 22 Examiners: W. Coffie, PhD & Vera Fiador, PhD Shareholder's funds Ordinary shares (25 pence par) Reserves Creditors: amount falling due after more than 1 year 14% loan stock Floating rank bank term loans Turnover Earnings before interest and tax Net interest Summarized Accounts Statement of Financial Position as at 31 March Profit before tax Taxation Available shareholders Dividend 328 12 44 Dividends EPS Northern Ltd (GHC'm) 483 150 633 384 Northern Limited 7% 7% 481 (97) (200) (114) 222 75 147 222 Income statement for the year ending 31 March GHC'm) 1130 115 (40) 75 (25) 50 51.4 6.3 5.3 (24) 26 46.1 2.0 2.0 Ordinary shares (50 pence par) Savannah Ltd (GHC'm) 42.3 17.0 59.3 63.0 Sale of surplus warehouse facilities for GHC6.8 million. Redundancy payments costing GHC9.0 million. Wage savings of GHC2.7 million per year for at least five years. (50.1) Page 1 of 11 12.9 (17.5) 54.7 20.0 34.7 54.7 GHC'm) 181 14 (2) 12 (4) The current share price of Northern Limited is 232 pesewas, and of Savannah Limited 295 pence. The current loan stock price of Northern Limited is GHC125. Recent annual growth trends: 8 (5) Savannah Limited 8% 10% Rationalisation following the acquisition will involve the following transactions (all net of tax effects): (i) (ii) (iii) Northern's cost of equity is estimated to be 14.5% and weighted average cost of capital 12 Savannah's cost of equity is estimated to be 13%. Required: Discuss and evaluate whether the bid is likely to be viewed favourably by the sharehol both Northern Limited and Savannah Limited. Include the discussion of the factors that a likely to influence the views of the shareholders. All relevant calculations must be shown. Questions 2 (a) Jireh Housing Limited is a UK based property developer and is considering a project in Ghana which would require an outlay of 1.6 million at the outset. The money cash flows receivable from sales will depend on the specific inflation rate for Jireh property. This is anticipated to be 4% per annum. Cash outflows consist of four elements: labour, materials, overheads, and machinery maintenance. Labour costs are expected to increase by 5% per annum, materials by 3%, overheads by 4%, and machinery maintenance by 1%. Jireh's requires a real rate of return of 16% on projects of this risk class, and anticipates the general rate of inflation to be 2% per annum over the 3-year life of the project. Annual cash flows in present (Time 0) prices are as follows: m Inflation 3.4 0.8 Sales Labour Materials Overheads Machinery maintenance 0.5 0.05 0.01 Calculate the NPV of the project using either method (i.e. nominal and real) of adjusting for inflation. (20 marks) Year 1 2 3 4 4% 5% 3% 4% (b) Jireh Limited also manufactures prefab components for the housing industry. They have just been offered a new four year contract to supply a component, subject to them meeting certain quality requirements set by GREDA Ghana. The production manager is concerned that the current machine, which has been fully depreciated, will not be able to meet the stringent quality controls that will be required because the technology is obsolete, and the machine is unreliable. The company currently spends 50,000 per year to maintain and operate this machine which has no secondhand market value. On the basis of the production manager's recommendation, management has decided to replace the current machine. It is estimated that the replacement machine will cost 1 million with a four-year useful life. The company's depreciation policy is to use a 20% reducing balance method over the life of the asset. As part of the purchase agreement for the new machine, the suppliers are offering a special maintenance contract costing 10,000 for each of the four years. The following forecast financial information has been prepared: 1% 1. Revenues and Costs - The estimated annual revenues and costs from the project for the next four years are: Revenues (in ) 800,000 850,000 880,000 920,000 Costs (in ) 350,000 385,000 410,000 435,000 2. Taxation: (i) Capital allowances - The new machine will attract a 20% declining balance writing- down allowance each year. (ii) The company pays corporate tax at a rate of 20% of taxable profit and this is paid in the year the profit is generated. 3. It is estimated that the machine will be sold for 350,000 at the end of year 4 4. The company uses an after tax cost of capital of 18% for investments of this risk class. Required: Taking into account the annual capital allowances for the machine, the annual tax liability and the annual cash flows, evaluate the viability of the four-year contract to supply the components. (30 marks) Question 1 (a) Farmers Alliance Limited is considering investing in new equipment with the initial cost of project/investment to be $100,000. This project is expected to generate EBIT of $15,000 per year forever (perpetuity). This project or investment can be financed either with $100,000 in equity (assume from internally generated fund) or with $40,000 of debt and $60,000 equity. The shareholders required return on an all equity financed project in this risk class is 10%. The firm's marginal tax rate is 40%. The cost of any debt is 5% before taxes. Note that in the world of Modigliani & Miller, all cash flows are perpetual and debt does not mature. Required: (i) Required: (i) (ii) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) If the project is financed entirely by equity, how much would be its net worth? (5 marks) What is the adjusted net worth of the project? (5 marks) Use the weighted average cost of capital method to value the project. What is the value of equity? What is the value of debt? (10 marks) Use the flow to equity method to calculate the value of the project's net worth to equity holders. (5 marks) Compare and contrast the strengths and weaknesses of the adjusted present value, weighted average cost of capital, and flow to equity approaches to investment appraisal. Which method, in your opinion, is the best? Explain. (200 words max) (9 marks) (b) When a firm raises funds through external debt or equity, it must incur issue costs (in contradiction to the Modigliani & Miller theorem). Introducing gearing or leverage increases (1) firm value due to tax benefits (M&M, 1963), (2) cost of equity as a result of shareholders exposure to financial distress risk (M&M, 1958) and (3) cost of debt due to bankruptcy risk or firm's probability of failure. Explain the effect of issuance cost on firm value. (2 marks) Evaluate the effect of gearing on cost of capital and firm value taking into consideration the three issues above. (9 marks) Discuss when and how to use the WACC as a discount rate for valuation. (5 marks) Question 4 Samuel King Limited, an all equity firm, has expected earnings before interest and taxes of GHC6million a year. Samuel King's tax rate is 25%, and the market value is V = E= GHC20 million. The firm has a beta of 1.50, and the risk-free rate is 5%. The expected market return is 15%. The Senior Management at Samuel King Ltd is considering the use of debt. The debt would be issued and used to buy back the company's own shares, in order to keep the size of the firm constant. The default free rate of interest on debt is 7%. Since interest expense is tax deductible, the value of Samuel King would tend to increase as debt is added to the capital structure, but there would be an offset in the form of the increasing cost of gearing or bankruptcy. It is estimated that the present value of any gearing or bankruptcy cost that would be incurred by Samuel King is GHC15 million and the probability of gearing or bankruptcy will rise with the level of debt according to the following schedule: Value of Debt (GHC) Required: a) b) c) (d) 3,000,000 5,000,000 7,000,000 9,000,000 11,000,000 14,000,000 15,000,000 Probability of Failure (%) 10 15 25 (Total 35 40 50 60 Calculate the cost of equity using the CAPM, when debt is GHC7,000,000 and when debt is GHC14,000,000. (6 marks) Calculate the cost of capital using the WACC when debt is GHC7,000,000 and when debt is GHC14,000,000. 6 marks) Using the adjusted present value (APV), calculate the optimal capital structure when gearing or bankruptcy costs are considered. (12 marks) State the value of Samuel King at this optimal capital structure. (1 mark) 25 marks) Question 3 (i) Awaso Limited, is considering investing in a number of potential projects of which they have only GHC1,000,000 to spend. Using information in the table 1 below, you are required to: (a) Complete table 1 by calculating the NPV, PI and their respective ranking. (3 marks) 2 3 4 5 6 (b) Identify which combination of projects should Awaso Ltd., undertake? Table 1 Project PV (in GHC) Cost (in GHC) 1 535,000 500,000 480,000 432,750 300,000 225,225 130,050 Table 2 450,000 400,000 280,000 200,000 100,000 Awaso Ltd. is to replace an aging delivery vehicle and is considering whether to buy a new vehicle or a used vehicle as a replacement. The average annual mileage is 60,000. The relevant estimated costs are as follows: Initial cost Average annual maintenance costs Fuel costs per mile Expected lifetime Used Vehicle GHC30,000 15,000 (1 marks) 80p 4 years New Vehicle GHC80,000 9,000 60p 6 years Awaso's relevant cost of capital is 8%. The estimated resale value of the new vehicle is GHC20,000 after 4 years. Ignore taxation. You are required to calculate the best financial option using: a) Annual equivalent method. (14 marks) b) Residual Value method when the van is needed for four years with GHC20,000 residual value for new van and GHCO for the old van. (7 marks) Question 2 Afrowest End Limited is a large conglomerate and is considering three potential investment projects for which it is assumed they have sufficient funds. The relative risk of each project has been assessed and the beta for each project is given below: Aeroplane engine = 2.4 Computer games retailer = 1.2 Electric utility B = 0.7 The company's financial structure is presently 70% equity and 30% debt. The cost of debt is 10% and cost of equity is calculated using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) where the industry average asset beta is 1.2; the risk-free rate is 6% and the market risk premium is 8%. The corporate tax rate is 25%. The financial manager has provided the following estimates of after-tax cash flow for the thre projects which are assumed to have equal lives of 5 years Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 Aeroplane Engine (in $m) (3,700,000) 1,800,000 1,600,000 1,250,000 860,000 610,000 Computer Games Retailer (in $m) (1,300,000) 800,000 560,000 420,000 250,000 100,000 Electric Utility (in $m) (8,000,000) 2,300,000 2,800,000 2,200,000 2,100,000 1,700,000 Using an appropriate cost of capital for each project, evaluate the viability of t three projects using NPV. (17 marks) As part of your evaluation, explain the reasons behind your choice of the cost capital for each project. (8 marl Question 1 The directors of Northern Limited, a food retailer with 20 superstores, are proposing to make a takeover bid for Savannah Limited, a company with six superstores in the north of Ghana. Northern Ltd will offer four of its ordinary shares for every three ordinary shares of Savannah. The bid has not yet been made public. Land and buildings (net) Fixed assets (net) Current asset Stock Debtors Cash Creditors: amounts falling due in less than 1 year Creditors 447 Dividend 12 Taxation 22 Examiners: W. Coffie, PhD & Vera Fiador, PhD Shareholder's funds Ordinary shares (25 pence par) Reserves Creditors: amount falling due after more than 1 year 14% loan stock Floating rank bank term loans Turnover Earnings before interest and tax Net interest Summarized Accounts Statement of Financial Position as at 31 March Profit before tax Taxation Available shareholders Dividend 328 12 44 Dividends EPS Northern Ltd (GHC'm) 483 150 633 384 Northern Limited 7% 7% 481 (97) (200) (114) 222 75 147 222 Income statement for the year ending 31 March GHC'm) 1130 115 (40) 75 (25) 50 51.4 6.3 5.3 (24) 26 46.1 2.0 2.0 Ordinary shares (50 pence par) Savannah Ltd (GHC'm) 42.3 17.0 59.3 63.0 Sale of surplus warehouse facilities for GHC6.8 million. Redundancy payments costing GHC9.0 million. Wage savings of GHC2.7 million per year for at least five years. (50.1) Page 1 of 11 12.9 (17.5) 54.7 20.0 34.7 54.7 GHC'm) 181 14 (2) 12 (4) The current share price of Northern Limited is 232 pesewas, and of Savannah Limited 295 pence. The current loan stock price of Northern Limited is GHC125. Recent annual growth trends: 8 (5) Savannah Limited 8% 10% Rationalisation following the acquisition will involve the following transactions (all net of tax effects): (i) (ii) (iii) Northern's cost of equity is estimated to be 14.5% and weighted average cost of capital 12 Savannah's cost of equity is estimated to be 13%. Required: Discuss and evaluate whether the bid is likely to be viewed favourably by the sharehol both Northern Limited and Savannah Limited. Include the discussion of the factors that a likely to influence the views of the shareholders. All relevant calculations must be shown. Questions 2 (a) Jireh Housing Limited is a UK based property developer and is considering a project in Ghana which would require an outlay of 1.6 million at the outset. The money cash flows receivable from sales will depend on the specific inflation rate for Jireh property. This is anticipated to be 4% per annum. Cash outflows consist of four elements: labour, materials, overheads, and machinery maintenance. Labour costs are expected to increase by 5% per annum, materials by 3%, overheads by 4%, and machinery maintenance by 1%. Jireh's requires a real rate of return of 16% on projects of this risk class, and anticipates the general rate of inflation to be 2% per annum over the 3-year life of the project. Annual cash flows in present (Time 0) prices are as follows: m Inflation 3.4 0.8 Sales Labour Materials Overheads Machinery maintenance 0.5 0.05 0.01 Calculate the NPV of the project using either method (i.e. nominal and real) of adjusting for inflation. (20 marks) Year 1 2 3 4 4% 5% 3% 4% (b) Jireh Limited also manufactures prefab components for the housing industry. They have just been offered a new four year contract to supply a component, subject to them meeting certain quality requirements set by GREDA Ghana. The production manager is concerned that the current machine, which has been fully depreciated, will not be able to meet the stringent quality controls that will be required because the technology is obsolete, and the machine is unreliable. The company currently spends 50,000 per year to maintain and operate this machine which has no secondhand market value. On the basis of the production manager's recommendation, management has decided to replace the current machine. It is estimated that the replacement machine will cost 1 million with a four-year useful life. The company's depreciation policy is to use a 20% reducing balance method over the life of the asset. As part of the purchase agreement for the new machine, the suppliers are offering a special maintenance contract costing 10,000 for each of the four years. The following forecast financial information has been prepared: 1% 1. Revenues and Costs - The estimated annual revenues and costs from the project for the next four years are: Revenues (in ) 800,000 850,000 880,000 920,000 Costs (in ) 350,000 385,000 410,000 435,000 2. Taxation: (i) Capital allowances - The new machine will attract a 20% declining balance writing- down allowance each year. (ii) The company pays corporate tax at a rate of 20% of taxable profit and this is paid in the year the profit is generated. 3. It is estimated that the machine will be sold for 350,000 at the end of year 4 4. The company uses an after tax cost of capital of 18% for investments of this risk class. Required: Taking into account the annual capital allowances for the machine, the annual tax liability and the annual cash flows, evaluate the viability of the four-year contract to supply the components. (30 marks) Question 1 (a) Farmers Alliance Limited is considering investing in new equipment with the initial cost of project/investment to be $100,000. This project is expected to generate EBIT of $15,000 per year forever (perpetuity). This project or investment can be financed either with $100,000 in equity (assume from internally generated fund) or with $40,000 of debt and $60,000 equity. The shareholders required return on an all equity financed project in this risk class is 10%. The firm's marginal tax rate is 40%. The cost of any debt is 5% before taxes. Note that in the world of Modigliani & Miller, all cash flows are perpetual and debt does not mature. Required: (i) Required: (i) (ii) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) If the project is financed entirely by equity, how much would be its net worth? (5 marks) What is the adjusted net worth of the project? (5 marks) Use the weighted average cost of capital method to value the project. What is the value of equity? What is the value of debt? (10 marks) Use the flow to equity method to calculate the value of the project's net worth to equity holders. (5 marks) Compare and contrast the strengths and weaknesses of the adjusted present value, weighted average cost of capital, and flow to equity approaches to investment appraisal. Which method, in your opinion, is the best? Explain. (200 words max) (9 marks) (b) When a firm raises funds through external debt or equity, it must incur issue costs (in contradiction to the Modigliani & Miller theorem). Introducing gearing or leverage increases (1) firm value due to tax benefits (M&M, 1963), (2) cost of equity as a result of shareholders exposure to financial distress risk (M&M, 1958) and (3) cost of debt due to bankruptcy risk or firm's probability of failure. Explain the effect of issuance cost on firm value. (2 marks) Evaluate the effect of gearing on cost of capital and firm value taking into consideration the three issues above. (9 marks) Discuss when and how to use the WACC as a discount rate for valuation. (5 marks)
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.44 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a Risk free rate 5 005 Beta 15 Expected Market rate 15 015 Cost of Equity RiskFree Rate of Return Be...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


