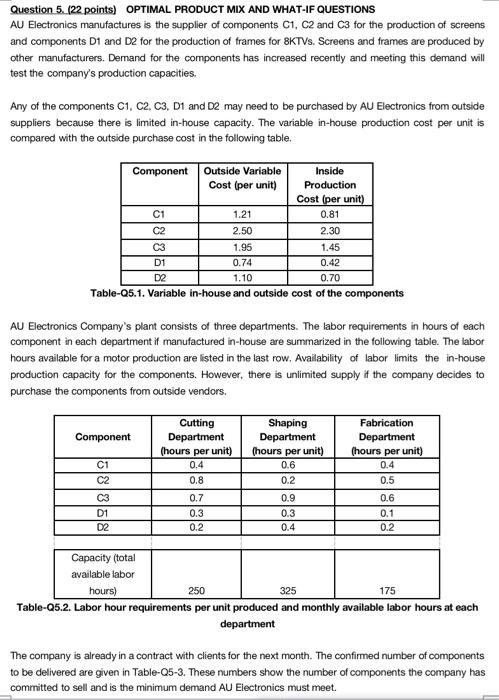
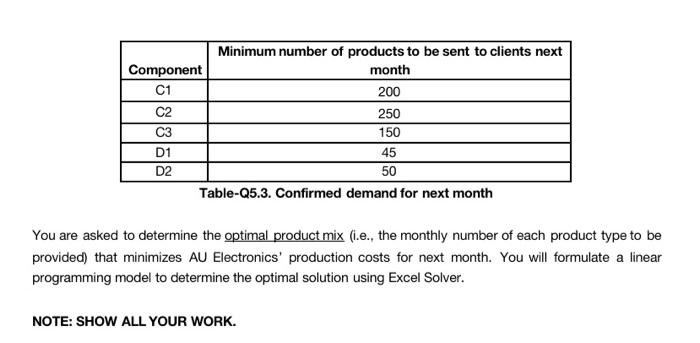
Question 5. (22 points) OPTIMAL PRODUCT MIX AND WHAT-IF QUESTIONS AU Electronics manufactures is the supplier of components C1, C2 and C3 for the production of screens and components D1 and D2 for the production of frames for SKTVS. Screens and frames are produced by other manufacturers. Demand for the components has increased recently and meeting this demand will test the company's production capacities. Any of the components C1, C2, C3, D1 and D2 may need to be purchased by AU Electronics from outside suppliers because there is limited in-house capacity. The variable in-house production cost per unit is compared with the outside purchase cost in the following table. Component Outside Variable Inside Cost (per unit) Production Cost (per unit) C1 1.21 0.81 C2 2.50 2.30 C3 1.95 1.45 D1 0.74 0.42 D2 0.70 Table-25.1. Variable in-house and outside cost of the components 1.10 AU Electronics Company's plant consists of three departments. The labor requirements in hours of each component in each department if manufactured in-house are summarized in the following table. The labor hours available for a motor production are listed in the last row. Availability of labor limits the in-house production capacity for the components. However, there is unlimited supply if the company decides to purchase the components from outside vendors. Component Fabrication Department (hours per unit) 0.4 Cutting Department (hours per unit) 0.4 0.8 0.7 0.3 0.2 Shaping Department (hours per unit) 0.6 0.2 0.9 C1 C2 C3 D1 D2 0.5 0.3 0.4 0.6 0.1 0.2 Capacity (total available labor hours) 250 325 175 Table-05.2. Labor hour requirements per unit produced and monthly available labor hours at each department The company is already in a contract with clients for the next month. The confirmed number of components to be delivered are given in Table-05-3. These numbers show the number of components the company has committed to sell and is the minimum demand AU Electronics must meet. Minimum number of products to be sent to clients next Component month C1 200 250 C3 150 D1 45 D2 50 Table-25.3. Confirmed demand for next month You are asked to determine the optimal product mix (i.e., the monthly number of each product type to be provided) that minimizes AU Electronics' production costs for next month. You will formulate a linear programming model to determine the optimal solution using Excel Solver. NOTE: SHOW ALL YOUR WORK. f) (1 point) Compute the labor utilization at each department. g) (2 points) Suppose the company hires new employees and the available labor hours for the fabrication department goes up to 220 hours per month. What effect does this have on the optimal product mix and the optimal cost? What is the change in the optimal cost value? Can you explain clearly why the cost changes (or does not change) when more employees are available at the fabrication department? h) (3 points) Answer this question independent of part g: Suppose the company did not have the capacity limits as stated in Table 25.3. What would be the optimal product mix for the company? Use Excel Solver to find the new solution. What is the new optimal product mix and the new optimal cost? Is the new optimal cost lower or higher than the one in part (e)? Why do you think this is? Explain clearly. Is having contracts with clients and committing to deliveries to clients beneficial in this problem? Explain clearly why or why not. Question 5. (22 points) OPTIMAL PRODUCT MIX AND WHAT-IF QUESTIONS AU Electronics manufactures is the supplier of components C1, C2 and C3 for the production of screens and components D1 and D2 for the production of frames for SKTVS. Screens and frames are produced by other manufacturers. Demand for the components has increased recently and meeting this demand will test the company's production capacities. Any of the components C1, C2, C3, D1 and D2 may need to be purchased by AU Electronics from outside suppliers because there is limited in-house capacity. The variable in-house production cost per unit is compared with the outside purchase cost in the following table. Component Outside Variable Inside Cost (per unit) Production Cost (per unit) C1 1.21 0.81 C2 2.50 2.30 C3 1.95 1.45 D1 0.74 0.42 D2 0.70 Table-25.1. Variable in-house and outside cost of the components 1.10 AU Electronics Company's plant consists of three departments. The labor requirements in hours of each component in each department if manufactured in-house are summarized in the following table. The labor hours available for a motor production are listed in the last row. Availability of labor limits the in-house production capacity for the components. However, there is unlimited supply if the company decides to purchase the components from outside vendors. Component Fabrication Department (hours per unit) 0.4 Cutting Department (hours per unit) 0.4 0.8 0.7 0.3 0.2 Shaping Department (hours per unit) 0.6 0.2 0.9 C1 C2 C3 D1 D2 0.5 0.3 0.4 0.6 0.1 0.2 Capacity (total available labor hours) 250 325 175 Table-05.2. Labor hour requirements per unit produced and monthly available labor hours at each department The company is already in a contract with clients for the next month. The confirmed number of components to be delivered are given in Table-05-3. These numbers show the number of components the company has committed to sell and is the minimum demand AU Electronics must meet. Minimum number of products to be sent to clients next Component month C1 200 250 C3 150 D1 45 D2 50 Table-25.3. Confirmed demand for next month You are asked to determine the optimal product mix (i.e., the monthly number of each product type to be provided) that minimizes AU Electronics' production costs for next month. You will formulate a linear programming model to determine the optimal solution using Excel Solver. NOTE: SHOW ALL YOUR WORK. f) (1 point) Compute the labor utilization at each department. g) (2 points) Suppose the company hires new employees and the available labor hours for the fabrication department goes up to 220 hours per month. What effect does this have on the optimal product mix and the optimal cost? What is the change in the optimal cost value? Can you explain clearly why the cost changes (or does not change) when more employees are available at the fabrication department? h) (3 points) Answer this question independent of part g: Suppose the company did not have the capacity limits as stated in Table 25.3. What would be the optimal product mix for the company? Use Excel Solver to find the new solution. What is the new optimal product mix and the new optimal cost? Is the new optimal cost lower or higher than the one in part (e)? Why do you think this is? Explain clearly. Is having contracts with clients and committing to deliveries to clients beneficial in this problem? Explain clearly why or why not